【Cancer Cell】2024年1-4月刊论文导读
期刊介绍:
Cancer Cell创刊于2002年,由CELL PRESS出版商出版,收稿方向涵盖医学-肿瘤学全领域,在行业领域中学术影响力很大,属于TOP期刊,国际一流期刊。审议手稿的主要标准是研究是否在回答与自然发生的癌症有关的重要问题方面取得重大进展。影响因子指数50.3。2024年1-4月一共发表62篇,包括Commentary 2篇,preview 14篇,Review 4篇,Article 31篇,Letter 3篇,Report 4篇,Correction 4篇。
Jan 08, 2024 Volume 42, Issue 1, p1-168
在2024年1月,Cancer Cell共发表14篇文章,其中包括Commentary 1篇,Letter 1篇,Preview 3篇,Review 1篇,Article 7篇,Report 1篇。
1.Immune determinants of CAR-T cell expansion in solid tumor patients receiving GD2 CAR-T cell therapy.
接受GD2 CAR-T细胞疗法的实体瘤患者的CAR-T细胞扩增的免疫决定因素

美国马里兰州贝塞斯达国立卫生研究院国立癌症研究所癌症研究中心儿科肿瘤科
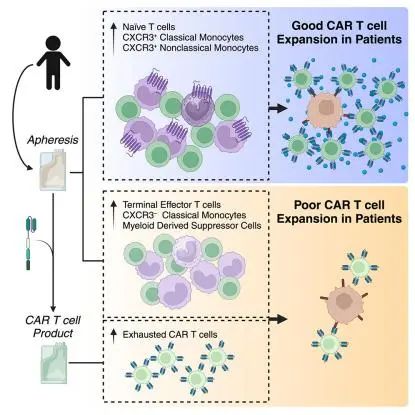
Chimeric antigen receptor T cells (CAR-Ts) have remarkable efficacy in liquid tumors, but limited responses in solid tumors. We conducted a Phase I trial (NCT02107963) of GD2 CAR-Ts (GD2-CAR.OX40.28.z.iC9), demonstrating feasibility and safety of administration in children and young adults with osteosarcoma and neuroblastoma. Since CAR-T efficacy requires adequate CAR-T expansion, patients were grouped into good or poor expanders across dose levels. Patient samples were evaluated by multi-dimensional proteomic, transcriptomic, and epigenetic analyses. T cell assessments identified naive T cells in pre-treatment apheresis associated with good expansion, and exhausted T cells in CAR-T products with poor expansion. Myeloid cell assessment identified CXCR3+ monocytes in pre-treatment apheresis associated with good expansion. Longitudinal analysis of post-treatment samples identified increased CXCR3- classical monocytes in all groups as CAR-T numbers waned. Together, our data uncover mediators of CAR-T biology and correlates of expansion that could be utilized to advance immunotherapies for solid tumor patients.
嵌合抗原受体T细胞(chimericantigenreceptorTcells,CAR-Ts)在血液肿瘤中的疗效比较显著,但在实体瘤中的效果有限。该研究对GD2CAR-Ts(GD2-CAR.OX40.28.z.iC9)疗法开展了Ⅰ期临床试验(NCT02107963),证明了GD2CAR-Ts治疗儿童和年轻人的骨肉瘤和神经母细胞瘤的可行性和安全性。由于CAR-T治疗的有效性和CAR-Ts的充分扩增相关,因此研究通过多维度蛋白质组、转录组和表观遗传学分析,根据患者CAR-Ts的扩增情况将各剂量组的患者又分为扩增良好组和扩增不良组,并观察各组治疗前患者血液单采细胞成分与CAR-Ts扩增的关系。结果发现,CAR-T治疗前患者血液单采的幼稚T细胞的水平与CAR-Ts扩增良好相关,以及患者CAR-Ts中衰竭T细胞的水平与CAR-Ts扩增不良相关。而且,针对髓系细胞的分析发现,CAR-Ts治疗前患者血液单采中的CXCR3+单核细胞水平与CAR-Ts良好的扩增能力有关。另外,对患者治疗后的纵向分析发现,随着CAR-Ts数量的减少,所有组别中的CXCR3-经典单核细胞都有所增加。总之,这些数据揭示了CAR-T扩增的相关因素,其研究结果可用于推动实体瘤免疫治疗的进展。
2.B3GALT6 promotes dormant breast cancer cell survival and recurrence by enabling heparan sulfate-mediated FGF signaling.
B3GALT6通过激活硫酸乙酰肝素介导的FGF信号传导促进休眠乳腺癌细胞的存活和复发

美国宾夕法尼亚大学佩雷尔曼医学院肿瘤生物学教研室
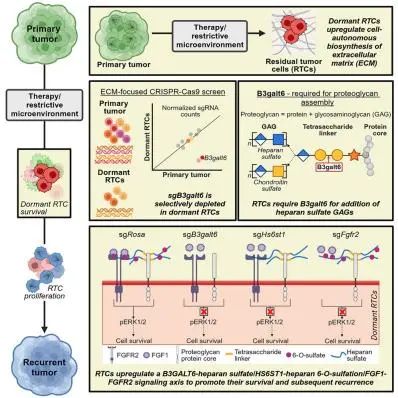
Breast cancer mortality results from incurable recurrences thought to be seeded by dormant, therapy-refractory residual tumor cells (RTCs). Understanding the mechanisms enabling RTC survival is therefore essential for improving patient outcomes. Here, we derive a dormancy-associated RTC signature that mirrors the transcriptional response to neoadjuvant therapy in patients and is enriched for extracellular matrix-related pathways. In vivo CRISPR-Cas9 screening of dormancy-associated candidate genes identifies the galactosyltransferase B3GALT6 as a functional regulator of RTC fitness. B3GALT6 is required for glycosaminoglycan (GAG) linkage to proteins to generate proteoglycans, and its germline loss of function in patients causes skeletal dysplasias. We find that B3GALT6-mediated biosynthesis of heparan sulfate GAGs predicts poor patient outcomes and promotes tumor recurrence by enhancing dormant RTC survival in multiple contexts, and does so via a B3GALT6-heparan sulfate/HS6ST1-heparan 6-O-sulfation/FGF1-FGFR2 signaling axis. These findings implicate B3GALT6 in cancer and nominate FGFR2 inhibition as a promising approach to eradicate dormant RTCs and prevent recurrence.
乳腺癌的复发是其致死的主要原因,而乳腺癌复发通常被认为是由休眠的、难以治疗的残余肿瘤细胞( RTCs )造成的。因此,了解RTC存活的机制对于改善患者的预后至关重要。在此,我们发现了一个休眠相关的RTC信号,它反映了患者对新辅助治疗的转录反应,且功能富集于细胞外基质相关的通路中。进一步通过体内CRISPR - Cas9技术筛选休眠相关的候选基因,确定了半乳糖基转移酶B3GALT6是RTC健康状况的功能调节因子。B3GALT6是糖胺聚糖( GAG )与蛋白质连接生成蛋白聚糖所必需的酶,据报道,患者生殖细胞的B3GALT6功能缺失会导致骨骼发育不良。该研究发现B3GALT6介导的硫酸乙酰肝素糖胺聚糖的生物合成,可以预测乳腺癌患者的不良结局,还可以通过促进休眠RTC的存活促进肿瘤复发,这是通过B3GALT6-heparan sulfate/HS6ST1-heparan 6-O-sulfation/FGF1-FGFR2 信号轴来实现的。上述发现暗示了B3GALT6在癌症中的作用,并提出抑制FGFR2是一种消除休眠RTCs和防止乳腺癌复发的很有前景的方法。
3.Single-cell and spatial profiling identify three response trajectories to pembrolizumab and radiation therapy in triple negative breast cancer.
单细胞和空间分析确定了三阴性乳腺癌对帕博利珠单抗(Pembrolizumab)和放疗的三种响应轨迹。
美国洛杉矶雪松-西奈医学中心放射肿瘤科
Strategies are needed to better identify patients that will benefit from immunotherapy alone or who may require additional therapies like chemotherapy or radiotherapy to overcome resistance. Here we employ single-cell transcriptomics and spatial proteomics to profile triple negative breast cancer biopsies taken at baseline, after one cycle of pembrolizumab, and after a second cycle of pembrolizumab given with radiotherapy. Non-responders lack immune infiltrate before and after therapy and exhibit minimal therapyinduced immune changes. Responding tumors form two groups that are distinguishable by a classifier prior to therapy, with one showing high major histocompatibility complex expression, evidence of tertiary lymphoid structures, and displaying anti-tumor immunity before treatment. The other responder group resembles non-responders at baseline and mounts a maximal immune response, characterized by cytotoxic T cell and antigen presenting myeloid cell interactions, only after combination therapy, which is mirrored in a murine model of triple negative breast cancer.
目前仍需要采取更好的策略来识别癌症患者个体最适合的治疗方法,包括单用免疫治疗、免疫治疗联合化疗以及免疫治疗联合放疗等。因此,该研究利用单细胞转录组学和空间蛋白组学分别对三阴性乳腺癌在基线、帕博利珠单抗治疗一个周期后和帕博利珠单抗联合放疗的第二个周期后的活检组织进行了分析。结果发现了三阴性乳腺癌针对免疫治疗和放疗的三种应答轨迹,无应答者在治疗前和治疗后均缺乏免疫浸润,表现出最弱的治疗诱导的免疫变化。反应性肿瘤在根据治疗前的基线差异分为两组,其中一组在治疗前的基线时就表现出主要组织相容性复合物的高表达、有三级淋巴结构和抗肿瘤免疫。另一应答组的肿瘤在基线时和单用免疫治疗后类似于无应答组,只有在联合治疗后,才会出现以细胞毒性T细胞和抗原提呈髓系细胞相互作用为特征的最强免疫应答,这在三阴性乳腺癌小鼠模型中得到了印证。
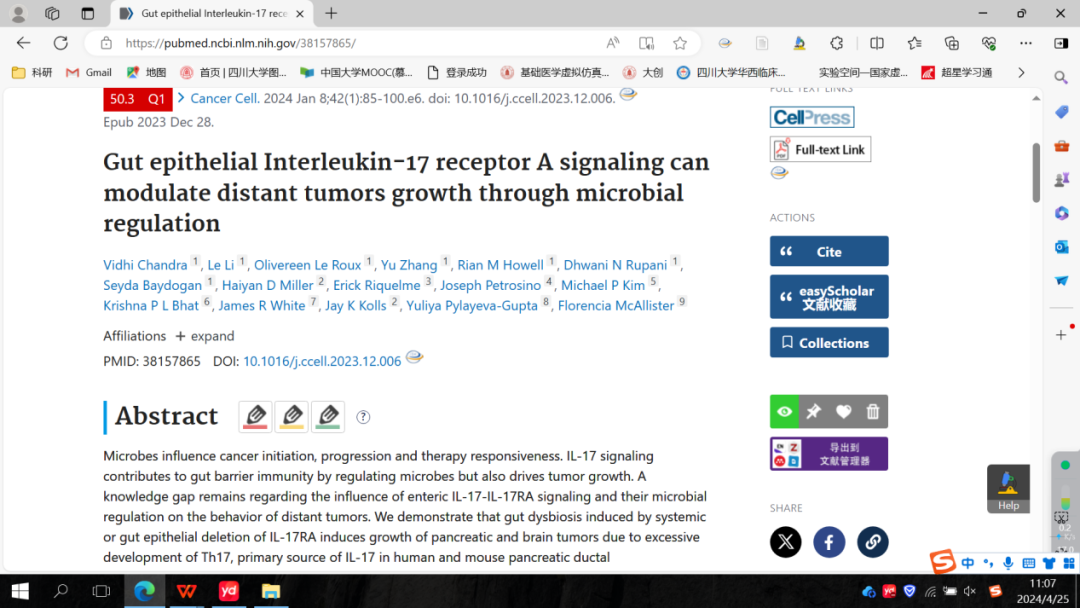
4.Gut epithelial Interleukin-17 receptor A signaling can modulate distant tumors growth through microbial regulation.
肠道上皮IL - 17受体A信号可以通过肠道微生物调控来调节远处肿瘤的生长
美国德克萨斯大学MD安德森癌症中心临床癌症预防系
Microbes influence cancer initiation, progression and therapy responsiveness. IL-17 signaling contributes to gut barrier immunity by regulating microbes but also drives tumor growth. A knowledge gap remains regarding the influence of enteric IL-17-IL-17RA signaling and their microbial regulation on the behavior of distant tumors. We demonstrate that gut dysbiosis induced by systemic or gut epithelial deletion of IL-17RA induces growth of pancreatic and brain tumors due to excessive development of Th17, primary source of IL-17 in human and mouse pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, as well as B cells that circulate to distant tumors. Microbial dependent IL-17 signaling increases DUOX2 signaling in tumor cells. Inefficacy of pharmacological inhibition of IL-17RA is overcome with targeted microbial ablation that blocks the compensatory loop. These findings demonstrate the complexities of IL-17-IL-17RA signaling in different compartments and the relevance for accounting for its homeostatic host defense function during cancer therapy.
微生物会影响癌症的发生、发展和治疗反应。IL - 17信号可以通过调节微生物促进肠道屏障免疫,但同时也驱动肿瘤生长。关于肠道IL - 17 -IL - 17RA信号对微生物调控及其对远处肿瘤行为的影响,目前仍知之甚少。该研究表明,系统性或肠上皮IL-17RA缺失诱导的肠道菌群失调会导致Th17的过度发育从而引起胰腺和脑肿瘤的生长,因为Th17和循环到远处肿瘤的B细胞是人和小鼠胰腺导管腺癌中IL - 17的主要来源,这些微生物依赖的IL - 17信号会增强肿瘤细胞中的DUOX2信号。通过针对微生物的消减治疗可以阻断代偿环路,克服IL - 17RA药理学抑制的无效性。上述发现证明了IL - 17 - IL - 17RA信号在不同环境中的复杂性,以及解释了在肿瘤治疗中微生物稳态与宿主防御功能的相关性。
5.EGFR-activated myofibroblasts promote metastasis of pancreatic cancer.
EGFR激活的肌成纤维细胞促进胰腺癌转移。
英国剑桥大学癌症研究所

Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) has a dismal prognosis. Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) are recognized potential therapeutic targets, but poor understanding of these heterogeneous cell populations has limited the development of effective treatment strategies. We previously identified transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) as a main driver of myofibroblastic CAFs (myCAFs). Here, we show that epidermal growth factor receptor/Erb-B2 receptor (EGFR/ERBB2) signaling is induced by TGF-β in myCAFs through an autocrine process mediated by amphiregulin. Inhibition of this EGFR/ERBB2-signaling network in PDAC organoid-derived cultures and mouse models differentially impacts distinct CAF subtypes, providing insights into mechanisms underpinning their heterogeneity. Remarkably, EGFR-activated myCAFs promote PDAC metastasis in mice, unmasking functional significance in myCAF heterogeneity. Finally, analyses of other cancer datasets suggest that these processes might operate in other malignancies. These data provide functional relevance to myCAF heterogeneity and identify a candidate target for preventing tumor invasion in PDAC.
胰腺导管腺癌( pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma,PDAC )预后极差,癌症相关的成纤维细胞( CAFs )是其公认的潜在治疗靶点,但由于我们对这些异质性细胞群体的认识不足,有效治疗策略的发展受到限制。过去我们发现转化生长因子β ( TGF-β )是癌症相关的肌成纤维细胞 ( myCAFs )的主要驱动因子。在本研究中,我们发现在myCAFs中,表皮生长因子受体/ Erb - B2受体( EGFR / ERBB2 )信号通过双调蛋白介导的自分泌过程是由TGF - β所诱导。并且,在PDAC类器官培养物和小鼠模型中抑制EGFR / ERBB2信号网络,会对不同的CAF亚型产生不同的影响,从而帮助我们深入了解其异质性的机制。值得注意的是,我们发现EGFR激活的myCAFs能促进小鼠PDAC的转移,这揭示了myCAF异质性的功能意义。最后,对其他癌症数据集的分析表明,这些过程也可能发生在其他恶性肿瘤中。这些数据提供了与myCAF异质性相关的功能,并确定了预防PDAC侵袭的候选靶点。
6.Immune evasion of dormant disseminated tumor cells is due to their scarcity and can be overcome by T cell immunotherapies.
T细胞免疫疗法可以消除由于潜伏期扩散性肿瘤细胞数量少引起的免疫逃逸

美国弗雷德·哈钦森癌症中心公共卫生科学部
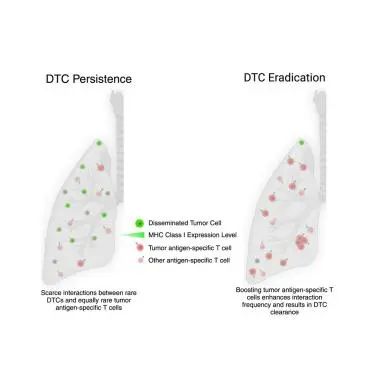
The period between ‘‘successful’’ treatment of localized breast cancer and the onset of distant metastasis can last many years, representing an unexploited window to eradicate disseminated disease and prevent metastases. We find that the source of recurrence—disseminated tumor cells (DTCs) —evade endogenous immunity directed against tumor neoantigens. Although DTCs downregulate major histocompatibility complex I, this does not preclude recognition by conventional T cells. Instead, the scarcity of interactions between two relatively rare populations—DTCs and endogenous antigen-specific T cells—underlies DTC persistence. This scarcity is overcome by any one of three immunotherapies that increase the number of tumor-specific T cells: T cell-based vaccination, or adoptive transfer of T cell receptor or chimeric antigen receptor T cells. Each approach achieves robust DTC elimination, motivating discovery of MHC-restricted and -unrestricted DTC antigens that can be targeted with T cell-based immunotherapies to eliminate the reservoir of metastasis-initiating cells in patients.
从"成功"治疗局限性乳腺癌到发生远处转移可以间隔很多年,这段时间也是防止疾病播散和预防癌症转移的一个未开发的窗口期。我们发现扩散的肿瘤细胞( DTCs )是乳腺癌复发的根源,它们可以逃避针对肿瘤新抗原的内源性免疫。尽管DTCs可以下调MHC-I,但这并不妨碍传统T细胞对DTCs的识别。DTCs免疫逃逸的关键在于DTCs和内源性抗原特异性T细胞数量上的缺乏,导致它们之间的相互作用缺乏,这是DTCs持续存在的主要原因。针对这种不足可以通过免疫治疗,可以通过增加肿瘤特异性T细胞的数量来克服,包括基于T细胞的疫苗接种、过继转移T细胞受体(TCR-t)或嵌合抗原受体T细胞(CAR -t)。上述每一种方法都能实现强效的DTCs清除,激发免疫系统发现MHC限制性和非限制性的DTC抗原,以消除患者体内转移起始细胞的储存。
7.Integrated multi-omics profiling to dissect the spatiotemporal evolution of metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma.
整合多组学图谱解析转移性肝细胞癌的时空演化
复旦大学中山医院肝癌研究所肝脏外科
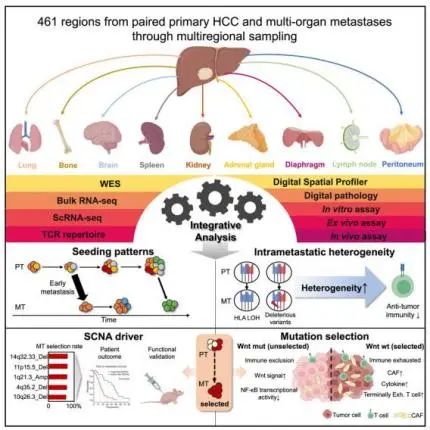
Comprehensive molecular analyses of metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) are lacking. Here, we generate multi-omic profiling of 257 primary and 176 metastatic regions from 182 HCC patients. Primary tumors rich in hypoxia signatures facilitated polyclonal dissemination. Genomic divergence between primary and metastatic HCC is high, and early dissemination is prevalent. The remarkable neoantigen intratumor heterogeneity observed in metastases is associated with decreased T cell reactivity, resulting from disruptions to neoantigen presentation. We identify somatic copy number alterations as highly selected events driving metastasis. Subclones without Wnt mutations show a stronger selective advantage for metastasis than those with Wnt mutations and are characterized by a microenvironment rich in activated fibroblasts favoring a prometastatic phenotype. Finally, metastases without Wnt mutations exhibit higher enrichment of immunosuppressive B cells that mediate terminal exhaustion of CD8+ T cells via HLA-E:CD94-NKG2A checkpoint axis. Collectively, our results provide a multi-dimensional dissection of the complex evolutionary process of metastasis.
目前,转移性肝细胞癌(HCC)缺乏全面的分子分析。因此,该研究从182名HCC患者中选择了257个原发灶和176个转移灶区域进行多组学分析。结果发现,富含乏氧特征的原发性肿瘤有利于肿瘤多克隆播散。原发性和转移性HCC之间的基因组差异较大,并且HCC的早期播散普遍存在。另外,研究发现在转移灶中观察到的新抗原瘤内异质性与T细胞反应性降低有关,这是由新抗原呈递被中断引起的。研究还将体细胞拷贝数变异认定为驱动肿瘤转移的高度选择事件,发现没有Wnt突变的亚克隆比有Wnt突变的亚克隆有更强的转移选择性优势,其肿瘤微环境富含活化的成纤维细胞,有利于肿瘤转移。而且,没有Wnt突变的转移灶表现出更多免疫抑制性B细胞的富集,并通过HLA-E:CD94-NKG2A检查点轴介导CD8+T细胞的终末耗竭。总的来说,该研究的结果从多维度剖析了肿瘤转移的复杂演变过程。

Feb 12, 2024, Volume 42, Issue 2, p169-324
在2024年2月,Cancer Cell共发表16篇文章,其中包括Letter 1篇,Preview 3篇,Review 1篇,Article 8篇,Correction 3篇。
1.A global phase 3 study of serplulimab plus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for advanced squamous non-small-cell lung cancer.
一项关于斯鲁利单抗联合化疗用于晚期鳞状非小细胞肺癌一线治疗的全球3期临床试验。
上海市肺科医院肿瘤科
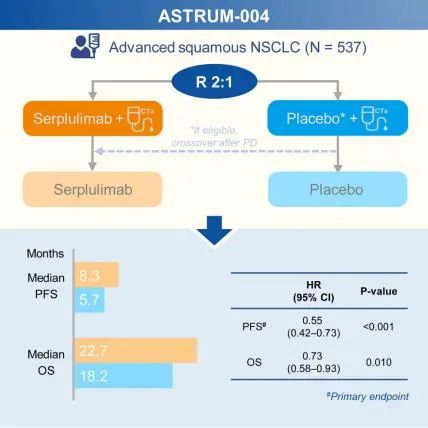
Combining immunotherapy with chemotherapy can provide improved survival in advanced squamous nonsmall-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients without targetable gene alterations. 537 previously untreated patients with stage IIIB/IIIC or IV squamous NSCLC without targetable gene alterations were enrolled and randomized (2:1) to receive serplulimab 4.5 mg/kg or placebo, both in combination with nab-paclitaxel and carboplatin, intravenously in 3-week cycles. The primary endpoint of progression-free survival (PFS) was met at the first interim analysis. At the second interim analysis, PFS benefit was maintained in serplulimab-chemotherapy group (hazard ratio [HR] 0.53, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.42–0.67). At the final analysis, serplulimab-chemotherapy significantly improved median OS compared to placebo-chemotherapy (HR 0.73, 95% CI 0.58–0.93; p = 0.010). Grade≥3 serplulimab or placebo-related adverse events occurred in 126 (35.2%) and 58 (32.4%) patients, respectively. Our results demonstrate that adding serplulimab to chemotherapy significantly improves survival in advanced squamous NSCLC patients, with manageable safety.
将免疫治疗与化疗相结合,可以提高没有靶基因改变的晚期鳞状非小细胞肺癌( NSCLC )患者的生存率。因此,该研究纳入了537例未经治疗的无靶基因改变的ⅢB /ⅢC期或Ⅳ期鳞状NSCLC患者,并随机分到两组( 2:1 )分别接受斯鲁利单抗4.5 mg / kg和安慰剂,两组都联合白蛋白结合型紫杉醇和卡铂进行化疗,静脉注射以3周为一个周期。无进展生存期( PFS )在第一次中期分析到达了主要终点。在第二次中期分析中,斯鲁利单抗联合化疗组患者PFS延长(风险比( HR )为0.53 , 95 %可信区间( CI )为0.42 ~ 0.67)。在最后的分析中,斯鲁利单抗联合化疗组与安慰剂联合化疗组相比中位OS显著提高( HR 0.73 , 95 % CI 0.58 ~ 0.93 ; p = 0.010)。另外,126例患者( 35.2 % )发生≥3级的斯普利单抗相关不良事件,以及58例患者( 32.4 %)发生≥3级的安慰剂相关不良事件。总的来说,该研究结果表明,在化疗中加入斯鲁利单抗可显著提高晚期鳞状NSCLC患者的生存率,且安全性良好。
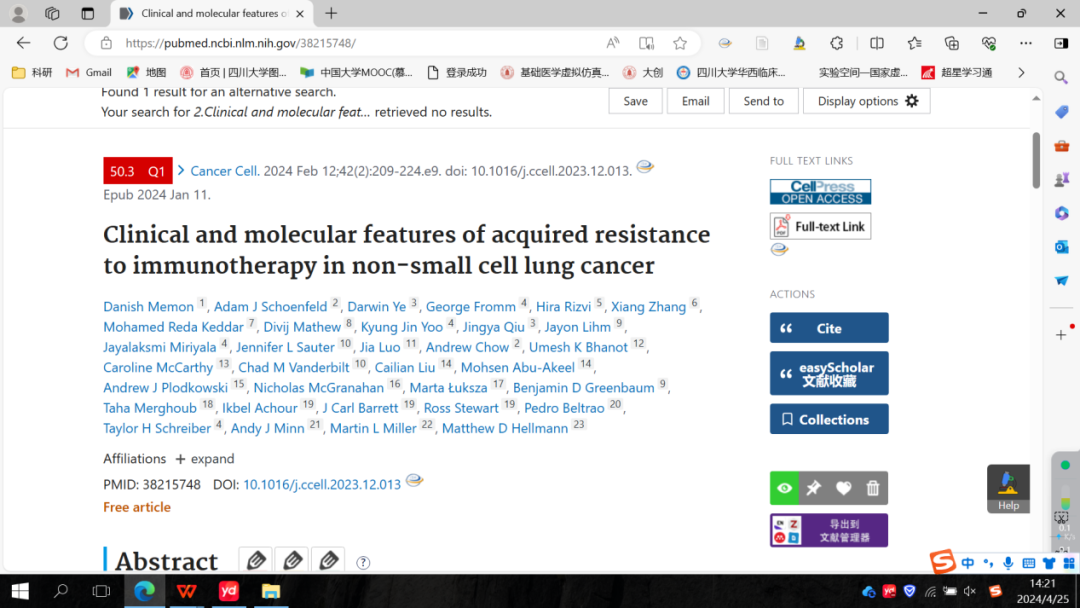
2.Clinical and molecular features of acquired resistance to immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer.
非小细胞肺癌免疫治疗获得性耐药的临床和分子特征。
欧洲分子生物学实验室(EMBL),欧洲生物信息学研究所
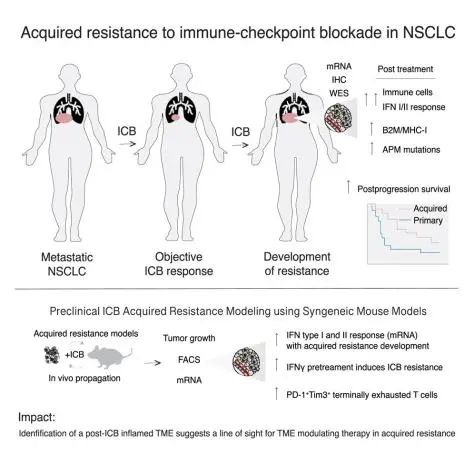
Although immunotherapy with PD-(L)1 blockade is routine for lung cancer, little is known about acquired resistance. Among 1,201 patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated with PD-(L)1 blockade, acquired resistance is common, occurring in >60% of initial responders. Acquired resistance shows differential expression of inflammation and interferon (IFN) signaling. Relapsed tumors can be separated by upregulated or stable expression of IFNγ response genes. Upregulation of IFNγ response genes is associated with putative routes of resistance characterized by signatures of persistent IFN signaling, immune dysfunction, and mutations in antigen presentation genes which can be recapitulated in multiple murine models of acquired resistance to PD-(L)1 blockade after in vitro IFNγ treatment. Acquired resistance to PD-(L)1 blockade in NSCLC is associated with an ongoing, but altered IFN response. The persistently inflamed, rather than excluded or deserted, tumor microenvironment of acquired resistance may inform therapeutic strategies to effectively reprogram and reverse acquired resistance.
尽管PD - ( L ) 1阻断的免疫治疗是肺癌的常规治疗方法,但我们对其引起获得性耐药的相关机制还不清楚。因此,该研究统计了1201例接受PD - ( L ) 1阻断治疗的非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC )患者,发现在超过60 %的有初始反应的患者中出现获得性耐药。获得性耐药的患者表现为炎症和干扰素( IFN )信号的差异表达。复发的肿瘤可以通过IFNγ反应基因的上调或稳定表达来区分。IFNγ反应基因的上调与潜在的耐药途径有关,这种耐药性呈现出有持续的IFN信号、免疫功能失调和抗原呈递基因的突变特征,并且,有PD - ( L ) 1阻断剂获得性耐药的小鼠模型在多种体外IFNγ治疗后可以重现上述耐药性特征。NSCLC患者对PD - ( L ) 1阻断剂的获得性耐药与持续但变化的IFN反应有关。总的来说,获得性耐药肿瘤微环境有持续炎症的这一特点,可能为逆转肿瘤获得性耐药提供有效的治疗策略。
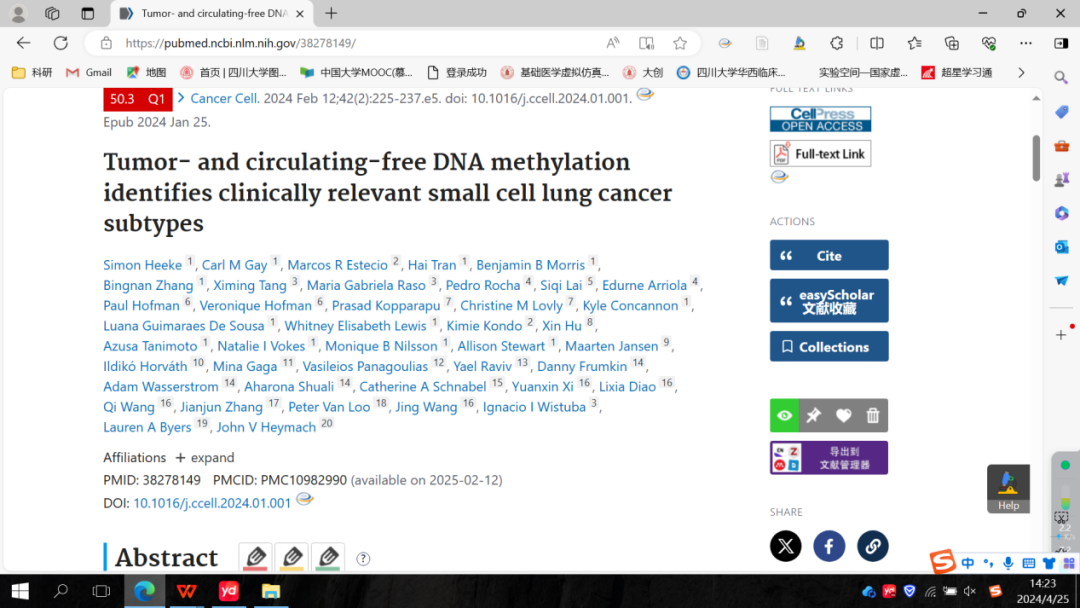
3.Tumor- and circulating-free DNA methylation identifies clinically relevant small cell lung cancer subtypes.
肿瘤和循环游离的DNA甲基化识别临床相关的小细胞肺癌亚型
美国德克萨斯大学MD安德森癌症中心胸/头颈肿瘤科
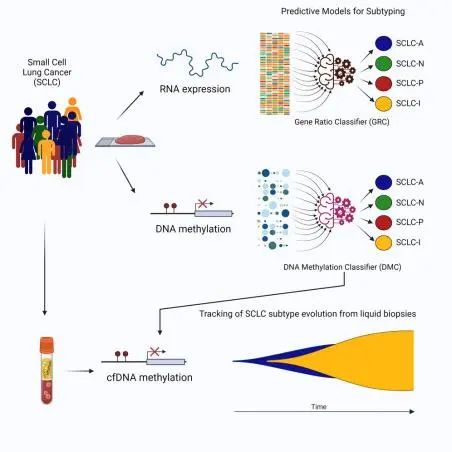
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive malignancy composed of distinct transcriptional subtypes, but implementing subtyping in the clinic has remained challenging, particularly due to limited tissue availability. Given the known epigenetic regulation of critical SCLC transcriptional programs, we hypothesized that subtype-specific patterns of DNA methylation could be detected in tumor or blood from SCLC patients. Using genomic-wide reduced-representation bisulfite sequencing (RRBS) in two cohorts totaling 179 SCLC patients and using machine learning approaches, we report a highly accurate DNA methylation-based classifier (SCLC-DMC) that can distinguish SCLC subtypes. We further adjust the classifier for circulating-free DNA (cfDNA) to subtype SCLC from plasma. Using the cfDNA classifier (cfDMC), we demonstrate that SCLC phenotypes can evolve during disease progression, highlighting the need for longitudinal tracking of SCLC during clinical treatment. These data establish that tumor and cfDNA methylation can be used to identify SCLC subtypes and might guide precision SCLC therapy.
小细胞肺癌( small cell lung cancer,SCLC )是一种侵袭性恶性肿瘤,有不同转录亚型,但在临床上由于组织获得很有限,因此很难对其进行分型。鉴于SCLC关键转录程序已知的表观遗传调控,我们假设肿瘤亚型特异性的DNA甲基化模式可以在SCLC患者的肿瘤或血液中检测到。通过对两个队列共179例SCLC患者进行全基因组简化基因组重亚硫酸盐测序(RRBS),并使用机器学习方法,我们报道了一个可以区分SCLC亚型的高精度DNA甲基化分类器( SCLC-DMC )。我们进一步将分类器调整为基于循环游离DNA ( cfDNA )的分类器以通过血浆对SCLC分型。利用cfDNA分类器( cf DMC ),我们证明了SCLC表型可以在疾病进展过程中演变,强调了在临床治疗过程中对SCLC进行纵向跟踪的必要性。总之,上述数据表明,肿瘤和cfDNA的甲基化可以用于鉴别SCLC亚型,并能指导SCLC的精准治疗。
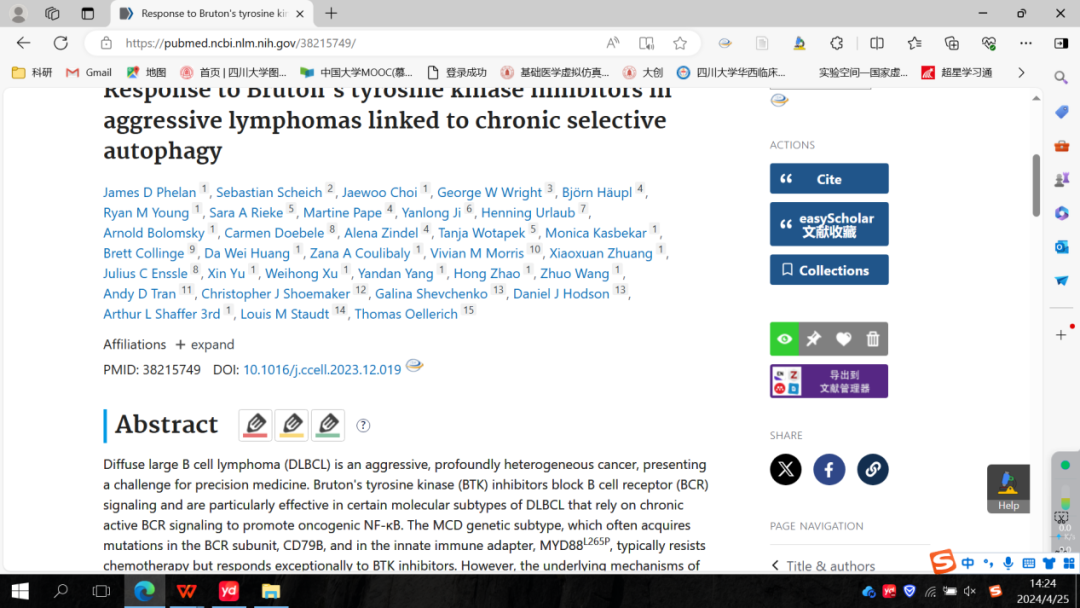
4.Response to Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors in aggressive lymphomas linked to chronic selective autophagy.
与慢性选择性自噬相关的侵袭性淋巴瘤对布鲁顿酪氨酸激酶(BTK)抑制剂的反应
美国国立卫生研究院国家癌症研究所淋巴恶性肿瘤科
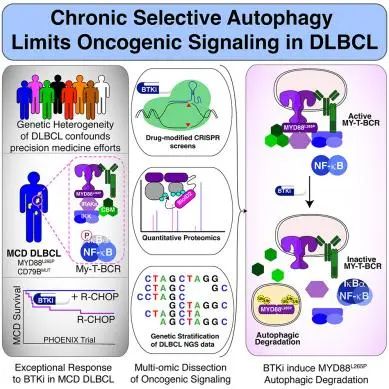
Diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is an aggressive, profoundly heterogeneous cancer, presenting a challenge for precision medicine. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors block B cell receptor (BCR) signaling and are particularly effective in certain molecular subtypes of DLBCL that rely on chronic active BCR signaling to promote oncogenic NF-kB. The MCD genetic subtype, which often acquires mutations in the BCR subunit, CD79B, and in the innate immune adapter, MYD88L265P, typically resists chemotherapy but responds exceptionally to BTK inhibitors. However, the underlying mechanisms of response to BTK inhibitors are poorly understood. Herein, we find a non-canonical form of chronic selective autophagy in MCD DLBCL that targets ubiquitinated MYD88L265P for degradation in a TBK1-dependent manner. MCD tumors acquire genetic and epigenetic alterations that attenuate this autophagic tumor suppressive pathway. In contrast, BTK inhibitors promote autophagic degradation of MYD88L265P, thus explaining their exceptional clinical benefit in MCD DLBCL.
弥漫大B细胞淋巴瘤(diffuse large B cell lymphoma,DLBCL)是一种侵袭性强、高度异质性的肿瘤,这对精准医疗来说是巨大的挑战。目前的研究发现,通过布鲁顿酪氨酸激酶(BTK)抑制剂阻断B细胞受体(BCR)信号,对某些分子亚型的DLBCL很有效,这些DLBCL依赖慢性活性BCR信号促进致癌性NF-kB信号通路。MCD基因亚型是DLBCL在BCR亚基、CD79B和先天性免疫适配器蛋白MYD88L265P中获得突变的亚型,通常对化疗耐药,但对BTK抑制剂有反应。然而,目前MCD对BTK抑制剂有反应的潜在机制还不明确。在本研究中,研究者在MCD DLBCL中发现了一种非经典形式的慢性选择性自噬,它以TBK1依赖的方式靶向降解泛素化的MYD88L265P。MCD肿瘤获得的遗传和表观遗传学改变,减弱了这种自噬肿瘤抑制通路。相反,BTK抑制剂能促进MYD88L265P的自噬降解,从而解释了它在治疗MCD DLBCL中的特殊临床作用。
5.Interferon-stimulated neutrophils as a predictor of immunotherapy response. 干扰素刺激的中性粒细胞可以作为免疫治疗反应的预测因子。
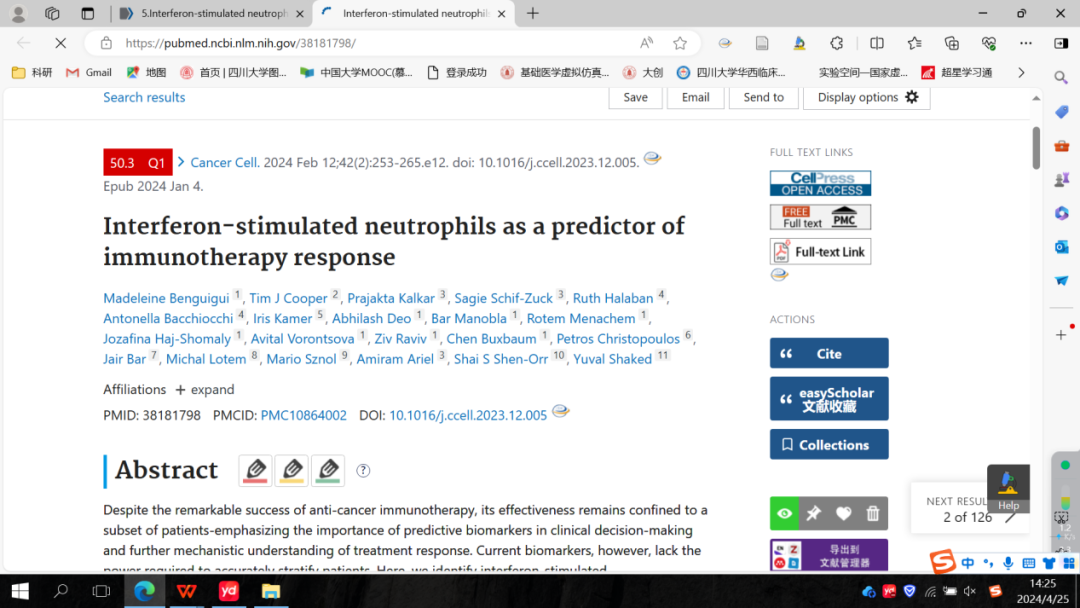
以色列理工学院拉帕波特医学院细胞生物学和癌症科学
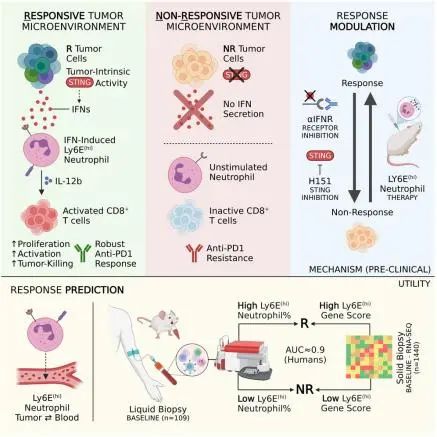
Despite the remarkable success of anti-cancer immunotherapy, its effectiveness remains confined to a subset of patients—emphasizing the importance of predictive biomarkers in clinical decision-making and further mechanistic understanding of treatment response. Current biomarkers, however, lack the power required to accurately stratify patients. Here, we identify interferon-stimulated, Ly6Ehi neutrophils as a blood-borne biomarker of anti-PD1 response in mice at baseline. Ly6Ehi neutrophils are induced by tumor-intrinsic activation of the STING (stimulator of interferon genes) signaling pathway and possess the ability to directly sensitize otherwise non-responsive tumors to anti-PD1 therapy, in part through IL12b-dependent activation of cytotoxic T cells. By translating our pre-clinical findings to a cohort of patients with non-small cell lung cancer and melanoma (n = 109), and to public data (n = 1440), we demonstrate the ability of Ly6Ehi neutrophils to predict immunotherapy response in humans with high accuracy (average AUC≈0.9). Overall, our study identifies a functionally active biomarker for use in both mice and humans.
尽管抗癌免疫治疗取得了显著成功,但其有效性仍然局限于一部分患者,这突显了预测性生物标志物在临床决策中的重要性,及其对于进一步理解治疗反应机制的必要性。然而,当前的生物标志物无法准确地将患者分层。在这项研究中,研究者发现干扰素刺激的 Ly6Ehi中性粒细胞可以作为小鼠对抗 PD1 抗体治疗反应的血液生物标志物。这些中性粒细胞是由肿瘤内部 STING(干扰素基因激活器)信号通路的激活诱导的,并且具有直接使原本对抗PD1抗体治疗不敏感的肿瘤敏感化的能力,另外,部分中性粒细胞还通过 IL12b 依赖的方式激活细胞毒性 T 细胞。此外,研究还将这些临床前的发现应用到了非小细胞肺癌和黑色素瘤患者队列(n = 109)以及公共数据(n = 1440)中,证明了 Ly6Ehi中性粒细胞有高精度预测免疫治疗反应的能力(平均 AUC≈0.9)。总的来说,该研究确定了一种生物标志物,可用于预测小鼠和人类免疫治疗反应。
6.Inosine induces stemness features in CAR-T cells and enhances potency. 肌苷能诱导 CAR-T 细胞的干细胞特性并增强其功能。
斯坦福大学医学院癌症研究所癌细胞治疗中心
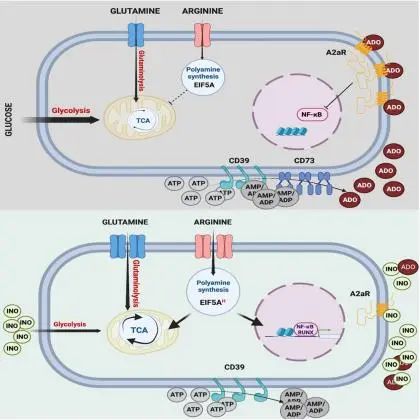
Adenosine (Ado) mediates immune suppression in the tumor microenvironment and exhausted CD8+ CAR-T cells express CD39 and CD73, which mediate proximal steps in Ado generation. Here, we sought to enhance CAR-T cell potency by knocking out CD39, CD73, or adenosine receptor 2a (A2aR) but observed only modest effects. In contrast, overexpression of Ado deaminase (ADA-OE), which metabolizes Ado to inosine (INO), induced stemness and enhanced CAR-T functionality. Similarly, CAR-T cell exposure to INO augmented function and induced features of stemness. INO induced profound metabolic reprogramming, diminishing glycolysis, increasing mitochondrial and glycolytic capacity, glutaminolysis and polyamine synthesis, and reprogrammed the epigenome toward greater stemness. Clinical scale manufacturing using INO generated enhanced potency CAR-T cell products meeting criteria for clinical dosing. These results identify INO as a potent modulator of CAR-T cell metabolism and epigenetic stemness programming and deliver an enhanced potency platform for cell manufacturing.
腺苷(Ado)在肿瘤微环境中有免疫抑制的作用,但CD8+ CAR-T细胞表达的CD39和CD73会参与腺苷的生成。因此,该研究希望通过敲除CD39、CD73或腺苷受体2a(A2aR)来增强CAR-T细胞的功能,但治疗效果只得到了轻微的改善。相反,该研究发现,增加腺苷脱氨酶(ADA-OE)的表达会将腺苷代谢成肌苷(INO),从而使CAR-T细胞表现出干细胞的特征并增强其功能。同样地,暴露于肌苷中的CAR-T细胞也表现出增强的功能和干细胞性特征。从机制上解释,肌苷能诱导CAR-T细胞的深度代谢重组,减少了糖酵解作用,增加了线粒体和糖酵解的能力,促进了谷氨酰胺代谢和多胺合成,并且使细胞表观遗传组更倾向于干细胞状态。用肌苷生产出效力增强的CAR-T细胞,能使产品达到临床剂量的标准。这些结果表明肌苷是一种强效的CAR-T细胞代谢和干性的调节剂,并提供了一个增强CAR-T细胞功能的平台。
7.Integrative analysis of neuroblastoma by single-cell RNA sequencing identifies the NECTIN2-TIGIT axis as a target for immunotherapy. 基于单细胞RNA测序的神经母细胞瘤整合分析鉴定出NECTIN2-TIGIT轴可以作为免疫治疗的靶点。
荷兰玛希玛公主儿科肿瘤中心
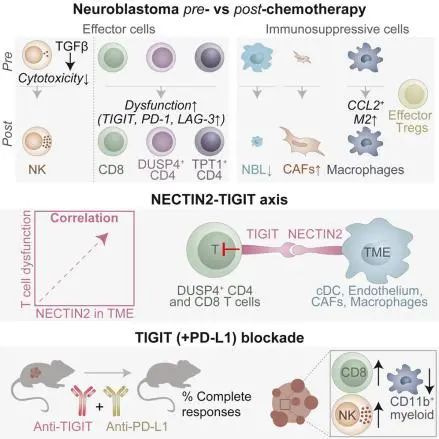
Pediatric patients with high-risk neuroblastoma have poor survival rates and urgently need more effective treatment options with less side effects. Since novel and improved immunotherapies may fill this need, we dissect the immunoregulatory interactions in neuroblastoma by single-cell RNA-sequencing of 24 tumors (10 pre- and 14 post-chemotherapy, including 5 pairs) to identify strategies for optimizing immunotherapy efficacy. Neuroblastomas are infiltrated by natural killer (NK), T and B cells, and immunosuppressive myeloid populations. NK cells show reduced cytotoxicity and T cells have a dysfunctional profile. Interaction analysis reveals a vast immunoregulatory network and identifies NECTIN2-TIGIT as a crucial immune checkpoint. Combined blockade of TIGIT and PD-L1 significantly reduces neuroblastoma growth, with complete responses (CR) in vivo. Moreover, addition of TIGIT+PD-L1 blockade to standard relapse treatment in a chemotherapy-resistant Th-ALKF1174L/MYCN 129/SvJ syngeneic model induces CR. In conclusion, our integrative analysis provides promising targets and a rationale for immunotherapeutic combination strategies.
儿童高危神经母细胞瘤患者生存率低,因此急需更有效、副作用较小的治疗方法。鉴于新型和改进的免疫疗法可能满足这一需求,该研究通过对24个肿瘤(包括10个化疗前和14个化疗后,其中5对样本是配对的)进行单细胞RNA测序,以揭示神经母细胞瘤中的免疫调节相互作用,并确定优化免疫治疗效果的策略。结果显示,神经母细胞瘤中存在自然杀伤细胞(NK细胞)、T细胞、B细胞和免疫抑制性的髓样细胞群的浸润。其中,NK细胞的细胞毒性降低,T细胞呈现功能失调。相互作用分析揭示了广泛的免疫调节网络,并确定了NECTIN2-TIGIT是一个关键的免疫检查点。联合阻断TIGIT和PD-L1能显著抑制神经母细胞瘤的生长,在体内实现完全缓解(CR)。此外,在化疗耐药的Th-ALKF1174L/MYCN 129/SvJ 同种移植模型中,将TIGIT+PD-L1阻断加入标准复发治疗方案,也能实现CR。综上,该研究的整合分析为寻找肿瘤治疗靶点和制定免疫治疗联合策略提供了线索。
8.A comprehensive clinically informed map of dependencies in cancer cells and framework for target prioritization. 一个基于详细的临床信息绘制的癌细胞依赖关系图和目标优先级框架
英国惠康桑格研究所
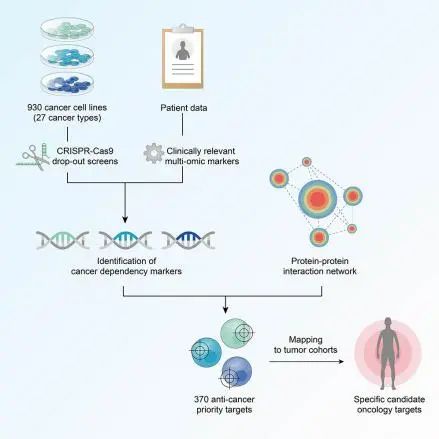
Genetic screens in cancer cell lines inform gene function and drug discovery. More comprehensive screen datasets with multi-omics data are needed to enhance opportunities to functionally map genetic vulnerabilities. Here, we construct a second-generation map of cancer dependencies by annotating 930 cancer cell lines with multi-omic data and analyze relationships between molecular markers and cancer dependencies derived from CRISPR-Cas9 screens. We identify dependency-associated gene expression markers beyond driver genes, and observe many gene addiction relationships driven by gain of function rather than synthetic lethal effects. By combining clinically informed dependency-marker associations with protein-protein interaction networks, we identify 370 anti-cancer priority targets for 27 cancer types, many of which have network-based evidence of a functional link with a marker in a cancer type. Mapping these targets to sequenced tumor cohorts identifies tractable targets in different cancer types. This target prioritization map enhances understanding of gene dependencies and identifies candidate anti-cancer targets for drug development.
在癌症研究中,对癌细胞系进行基因筛查,可以了解基因功能并发现潜在治疗药物。为了更好地了解基因易感性,并为药物研发提供更多机会,我们需要更全面的筛查数据集,其中包含多组学数据。因此,该研究利用多组学数据对930个癌细胞系进行了注释,分析了来自CRISPR-Cas9筛查的分子标记与癌症依赖之间的联系,并构建了第二代癌症依赖关系图。在这个过程中,研究发现了一些驱动基因以外的表达癌症依赖关联分子标记物的基因,并且观察到许多基因与癌症的关系是由基因自身功能增强驱动的,而不是和其他基因发生合成致死效应引起的。通过结合临床信息支持的癌症依赖标记和蛋白质相互作用网络,该研究鉴定了27种癌症类型的370个抗癌优先靶点。这些靶点在网络中显示出与某些癌症的标记物有功能联系。将这些靶点映射到测序的肿瘤队列中,能发现不同癌症类型中可处理的靶点。总的来说,这个靶点优先级图加强了我们对基因依赖性的理解,并为药物研发提供了候选抗癌靶点。

Issue 3, March 11, 2024, p325-496
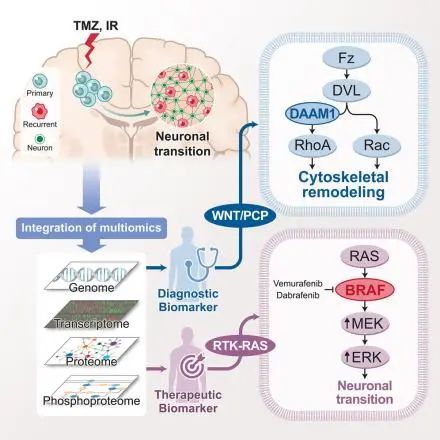
在2024年3月,Cancer Cell共发表15篇文章,其中包括Letter 1篇,Preview 4篇,Review 1篇,Article 6篇,report 3篇。 1.Integrated proteogenomic characterization of glioblastoma evolution 脑胶质母细胞瘤演变过程中的整合蛋白质组和基因组特征。 韩国高阳国立癌症中心癌症科学与政策研究生院癌症生物医学科学系 The evolutionary trajectory of glioblastoma (GBM) is a multifaceted biological process that extends beyond genetic alterations alone. Here, we perform an integrative proteogenomic analysis of 123 longitudinal glioblastoma pairs and identify a highly proliferative cellular state at diagnosis and replacement by activation of neuronal transition and synaptogenic pathways in recurrent tumors. Proteomic and phosphoproteomic analyses reveal that the molecular transition to neuronal state at recurrence is marked by post-translational activation of the wingless-related integration site (WNT)/ planar cell polarity (PCP) signaling pathway and BRAF protein kinase. Consistently, multi-omic analysis of patient-derived xenograft (PDX) models mirror similar patterns of evolutionary trajectory. Inhibition of B-raf proto-oncogene (BRAF) kinase impairs both neuronal transition and migration capability of recurrent tumor cells, phenotypic hallmarks of post-therapy progression. Combinatorial treatment of temozolomide (TMZ) with BRAF inhibitor, vemurafenib, significantly extends the survival of PDX models. This study provides comprehensive insights into the biological mechanisms of glioblastoma evolution and treatment resistance, highlighting promising therapeutic strategies for clinical intervention. 脑胶质母细胞瘤(GBM)的演变轨迹是一个复杂的生物学过程,不仅仅受基因变化的影响。在这项研究中,研究者对123对纵向脑胶质母细胞瘤进行了整合蛋白质组和基因组分析,发现在最初诊断时肿瘤处于高度增殖的细胞状态,而复发肿瘤则表现出激活神经转变和突触生成途径的特征。蛋白质组和磷酸化蛋白质组分析揭示了复发肿瘤细胞向神经细胞转变过程存在的分子转变,这一过程伴随着WNT/平面细胞极性(PCP)信号通路和BRAF蛋白激酶的翻译后活化。同时,针对患者来源的PDX模型的多组学分析呈现出相似的演变轨迹,与前面的分析结果一致。通过抑制BRAF激酶治疗,不仅影响了复发肿瘤细胞向神经状态的转变,还削弱了其迁移能力。另外,将替莫唑胺(TMZ)与BRAF抑制剂维姆拉非尼(vemurafenib)联合治疗能够显著延长PDX模型的存活时间。总的来说,这项研究为理解脑胶质母细胞瘤演变和治疗耐药的生物学机制提供了全面的见解,为临床干预提供了更有前景的治疗策略。 2.Interrogation of endothelial and mural cells in brain metastasis reveals key immune-regulatory mechanisms 对脑转移瘤内皮细胞和基质细胞的分析揭示了关键的免疫调节机制。 瑞士洛桑大学肿瘤系

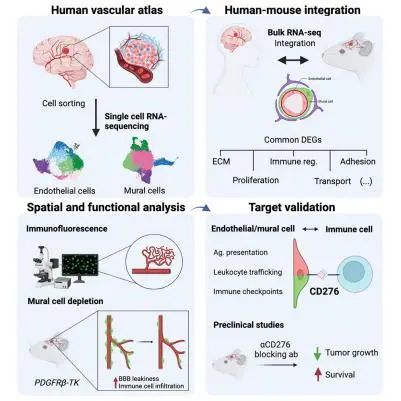
Brain metastasis (BrM) is a common malignancy, predominantly originating from lung, melanoma, and breast cancers. The vasculature is a key component of the BrM tumor microenvironment with critical roles in regulating metastatic seeding and progression. However, the heterogeneity of the major BrM vascular components, namely endothelial and mural cells, is still poorly understood. We perform single-cell and bulk RNA-sequencing of sorted vascular cell types and detect multiple subtypes enriched specifically in BrM compared to non-tumor brain, including previously unrecognized immune regulatory subtypes. We integrate the human data with mouse models, creating a platform to interrogate vascular targets for the treatment of BrM. We find that the CD276 immune checkpoint molecule is significantly upregulated in the BrM vasculature, and anti-CD276 blocking antibodies prolonged survival in preclinical trials. This study provides important insights into the complex interactions between the vasculature, immune cells, and cancer cells, with translational relevance for designing therapeutic interventions.
脑转移(BrM)肿瘤是一种常见的恶性肿瘤,主要来自肺癌、黑色素瘤和乳腺癌。血管系统是BrM肿瘤微环境的关键组成部分,在调控肿瘤转移种植和进展的过程中扮演着重要角色。然而,我们对BrM的血管组分,即内皮细胞和壁细胞的异质性仍然知之甚少。因此,该研究对分选的血管细胞类型进行了单细胞和批量RNA测序,发现与非肿瘤脑相比,BrM中存在特异的多个细胞亚型的富集,包括先前未被认识的免疫调节细胞亚型。另外,该研究将人类数据与小鼠模型相结合,建立了一个平台,用于研究治疗BrM的血管靶点。结果发现CD276免疫检查点分子在BrM血管中显著上调,并且在临床前试验中使用抗CD276阻断抗体能延长BrM的生存期。总的来说,这项研究为血管、免疫细胞和癌细胞之间的复杂相互作用提供了重要的见解,具有转化意义,可用于设计治疗干预的措施。
3.Cancer-associated fibroblast phenotypes are associated with patient outcome in non-small cell lung cancer 癌症相关的成纤维细胞表型与非小细胞肺癌患者的预后相关
瑞士苏黎世大学定量生物医学系
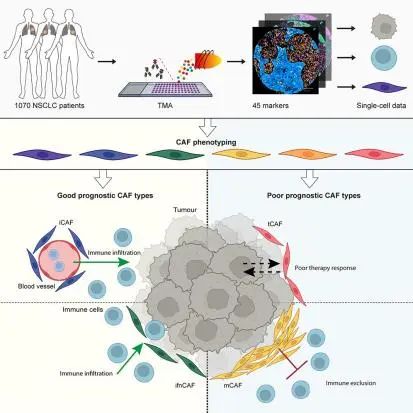
Despite advances in treatment, lung cancer survival rates remain low. A better understanding of the cellular heterogeneity and interplay of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) within the tumor microenvironment will support the development of personalized therapies. We report a spatially resolved single-cell imaging mass cytometry (IMC) analysis of CAFs in a non-small cell lung cancer cohort of 1,070 patients. We identify four prognostic patient groups based on 11 CAF phenotypes with distinct spatial distributions and show that CAFs are independent prognostic factors for patient survival. The presence of tumor-like CAFs is strongly correlated with poor prognosis. In contrast, inflammatory CAFs and interferon-response CAFs are associated with inflamed tumor microenvironments and higher patient survival. High density of matrix CAFs is correlated with low immune infiltration and is negatively correlated with patient survival. In summary, our data identify phenotypic and spatial features of CAFs that are associated with patient outcome in NSCLC.
尽管肺癌在治疗方面已经取得了很多进展,但肺癌的生存率仍然较低。对肿瘤微环境中癌症相关的成纤维细胞(CAFs)的细胞异质性和互作进行更深入的了解,将有助于开发个性化治疗方案。因此,该研究对1,070名非小细胞肺癌患者的CAFs进行了空间单细胞成像质谱细胞学(IMC)分析。结果,研究基于11种在肿瘤中具有不同空间分布的CAFs鉴定出了四个不同的患者预后群体,并表明CAFs是患者生存的独立预后因素。比如,肿瘤样CAFs与不良预后强相关,相反,炎症性CAFs和干扰素响应性CAFs与炎症性肿瘤微环境和更高的患者生存率相关。高密度的基质型CAFs与低免疫浸润相关,并且与患者生存率呈负相关。总的来说,该研究的数据发现了在非小细胞肺癌中与患者预后相关的CAFs表型和空间特征。
4.Adeno-to-squamous transition drives resistance to KRAS inhibition in LKB1 mutant lung cancer 腺癌向鳞癌的转变驱动LKB1突变型肺癌对KRAS抑制剂产生耐药性。
中国科学院分子细胞科学卓越中心,上海生物化学与细胞生物学研究所
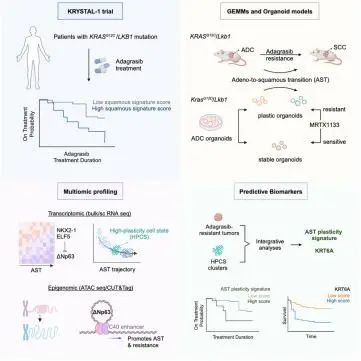
KRASG12C inhibitors (adagrasib and sotorasib) have shown clinical promise in targeting KRASG12C-mutated lung cancers; however, most patients eventually develop resistance. In lung patients with adenocarcinoma with KRASG12C and STK11/LKB1 co-mutations, we find an enrichment of the squamous cell carcinoma gene signature in pre-treatment biopsies correlates with a poor response to adagrasib. Studies of Lkb1-deficient KRASG12C and KrasG12D lung cancer mouse models and organoids treated with KRAS inhibitors reveal tumors invoke a lineage plasticity program, adeno-to-squamous transition (AST), that enables resistance to KRAS inhibition. Transcriptomic and epigenomic analyses reveal △Np63 drives AST and modulates response to KRAS inhibition. We identify an intermediate high-plastic cell state marked by expression of an AST plasticity signature and Krt6a. Notably, expression of the AST plasticity signature and KRT6A at baseline correlates with poor adagrasib responses. These data indicate the role of AST in KRAS inhibitor resistance and provide predictive biomarkers for KRAS-targeted therapies in lung cancer.
KRASG12C抑制剂(如adagrasib和sotorasib)在治疗KRASG12C突变的肺癌中显示出较好的临床潜力,但大多数患者最终会出现耐药性。在针对KRASG12C和STK11/LKB1共突变的肺腺癌患者的研究中,研究者发现术前腺癌活检样本鳞癌基因表达特征的富集与患者对adagrasib的不良反应相关。研究对Lkb1缺失的KRASG12C和KrasG12D肺癌小鼠模型和类器官采用KRAS抑制剂治疗,发现治疗后的肿瘤会启动一种细胞谱系可塑性程序,即腺癌向鳞癌的转变(AST),从而使肿瘤对KRAS抑制剂产生耐药性。转录组和表观基因组分析显示,△Np63促进了AST并调节了对KRAS抑制剂的反应。研究还发现了一种中间高可塑性细胞状态,其特征是表达AST可塑性标志物和Krt6a。值得注意的是,基线时AST可塑性标志物和KRT6A的表达与adagrasib的不良反应相关。这些数据表明AST在肺癌对KRAS抑制剂产生耐药性中具有重要作用,并为肺癌的KRAS靶向治疗的效果提供了可预测的生物标志物。
5.Immune heterogeneity in small-cell lung cancer and vulnerability to immune checkpoint blockade 小细胞肺癌中的免疫异质性及其对免疫检查点阻断治疗的易感性
美国基因泰克公司
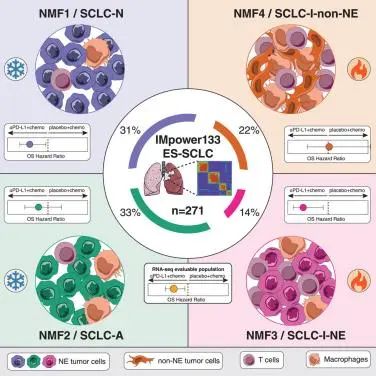
Atezolizumab (anti-PD-L1), combined with carboplatin and etoposide (CE), is now a standard of care for extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC). A clearer understanding of therapeutically relevant SCLC subsets could identify rational combination strategies and improve outcomes. We conduct transcriptomic analyses and non-negative matrix factorization on 271 pre-treatment patient tumor samples from IMpower133 and identify four subsets with general concordance to previously reported SCLC subtypes (SCLC-A, -N, -P, and -I). Deeper investigation into the immune heterogeneity uncovers two subsets with differing neuroendocrine (NE) versus non-neuroendocrine (non-NE) phenotypes, demonstrating immune cell infiltration hallmarks. The NE tumors with low tumor-associated macrophage (TAM) but high T-effector signals demonstrate longer overall survival with PD-L1 blockade and CE versus CE alone than non-NE tumors with high TAM and high T-effector signal. Our study offers a clinically relevant approach to discriminate SCLC patients likely benefitting most from immunotherapies and highlights the complex mechanisms underlying immunotherapy responses.
阿替利珠单抗(抗PD-L1)联合卡铂和依托泊苷(CE)现已成为广泛期小细胞肺癌(ES-SCLC)的标准治疗方案。深入了解治疗相关的SCLC亚型有助于制定合理的联合治疗策略,并改善治疗效果。因此,该研究对来自IMpower133的271例患者的术前肿瘤样本进行了转录组分析和非负矩阵因子分解,确定了四个SCLC亚型子集,与先前报道的SCLC亚型(SCLC-A、-N、-P和-I)大体一致。对免疫异质性的深入研究发现,其中两个亚型,一个表现出神经内分泌(NE)表型,另一个表现出非神经内分泌(non-NE)表型,并显示出免疫细胞浸润的特征。NE肿瘤具有低肿瘤相关巨噬细胞(TAM)但高T效应物信号的特点,在接受PD-L1阻断和CE治疗时的总体生存期较长,非-NE肿瘤有高TAM和高T效应物信号的特点,在接受CE治疗时的总体生存期较短。总的来说,该研究提供了一种临床相关的方法,用于区分哪些SCLC患者最可能从免疫治疗中获益,并凸显了免疫治疗反应的复杂机制。
6.Multi-omic profiling of follicular lymphoma reveals changes in tissue architecture and enhanced stromal remodeling in high-risk patients 滤泡性淋巴瘤的多组学分析揭示了高危患者组织结构的变化和增强的基质重塑特征
美国国立卫生研究院淋巴细胞生物学组和高级组织成像中心,免疫系统生物学实验室
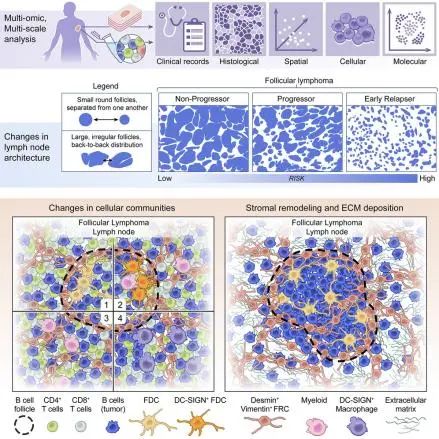
Follicular lymphoma (FL) is a generally incurable malignancy that evolves from developmentally blocked germinal center (GC) B cells. To promote survival and immune escape, tumor B cells undergo significant genetic changes and extensively remodel the lymphoid microenvironment. Dynamic interactions between tumor B cells and the tumor microenvironment (TME) are hypothesized to contribute to the broad spectrum of clinical behaviors observed among FL patients. Despite the urgent need, existing clinical tools do not reliably predict disease behavior. Using a multi-modal strategy, we examined cell-intrinsic and -extrinsic factors governing progression and therapeutic outcomes in FL patients enrolled onto a prospective clinical trial. By leveraging the strengths of each platform, we identify several tumor-specific features and microenvironmental patterns enriched in individuals who experience early relapse, the most high-risk FL patients. These features include stromal desmoplasia and changes to the follicular growth pattern present 20 months before first progression and first relapse.
滤泡性淋巴瘤(FL)是一种通常难以治愈的恶性肿瘤,其起源于发育受阻的生发中心(GC)B细胞。为了促进肿瘤存活和免疫逃逸,肿瘤B细胞经历了显著的遗传变化,并广泛重塑淋巴微环境。据推测,肿瘤B细胞与肿瘤微环境(TME)之间的动态相互作用可能有助于解释FL患者所呈现的广泛临床行为谱。但现有的临床工具却不能可靠地预测疾病行为,因此急需可靠的临床工具。通过多模态策略,该研究通过前瞻性临床试验,检查了影响FL患者病程和治疗结果的细胞内和细胞外因素。结合每个平台的优势,研究确定了一些在早期复发的个体中富集的肿瘤特异性特征和微环境模式,这些个体往往是FL患者中风险最高的患者。这些特征包括纤维结缔组织增生和滤泡生长模式的改变,并且在首次进展和首次复发前20个月就能被发现。

Issue 4, April 08, 2024, p497-722
在2024年4月,Cancer Cell共发表17篇文章,其中包括Commentary 1篇,Preview 4篇,Review 1篇,Article 10篇,Correction 1篇。
1.Pharmacogenomic profiling of intra-tumor heterogeneity using a large organoid biobank of liver cancer 利用大型肝癌类器官样本库对肿瘤内异质性进行药物基因组分析
北京大学第一医院肿瘤转化研究中心
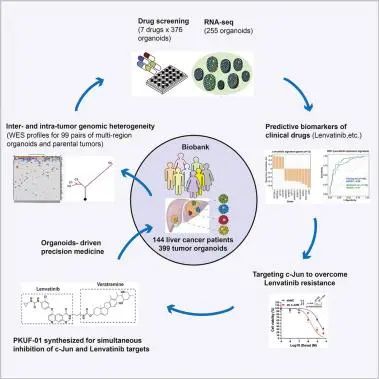
Inter- and intra-tumor heterogeneity is a major hurdle in primary liver cancer (PLC) precision therapy. Here, we establish a PLC biobank, consisting of 399 tumor organoids derived from 144 patients, which recapitulates histopathology and genomic landscape of parental tumors, and is reliable for drug sensitivity screening, as evidenced by both in vivo models and patient response. Integrative analysis dissects PLC heterogeneity, regarding genomic/transcriptomic characteristics and sensitivity to seven clinically relevant drugs, as well as clinical associations. Pharmacogenomic analysis identifies and validates multi-gene expression signatures predicting drug response for better patient stratification. Furthermore, we reveal c-Jun as a major mediator of lenvatinib resistance through JNK and β-catenin signaling. A compound (PKUF-01) comprising moieties of lenvatinib and veratramine (c-Jun inhibitor) is synthesized and screened, exhibiting a marked synergistic effect. Together, our study characterizes the landscape of PLC heterogeneity, develops predictive biomarker panels, and identifies a lenvatinib-resistant mechanism for combination therapy.
肝癌的肿瘤内和肿瘤间的异质性是原发性肝癌(PLC)精准治疗面临的主要障碍。在这项研究中,研究者建立了一个PLC生物样本库,包括来自144名患者的399个肿瘤类器官样本。这些样本忠实地保留了原始肿瘤的组织病理学和基因组景观,并通过体内模型和患者反应验证了其在药物敏感性筛选方面的可靠性。通过综合分析,该研究解析了PLC的异质性,考虑了肿瘤的基因组/转录组特征及其对七种临床相关药物的敏感性,以及临床相关性。药物基因组学分析鉴定和验证了多基因表达特征,可用于预测药物反应,有助于患者分层。此外,研究还发现c-Jun能通过JNK和β-连环蛋白信号通路介导乐伐替尼的耐药,并合成筛选了一种化合物(PKUF-01),它结合了乐伐替尼和维拉特拉明(c-Jun抑制剂)的成分,展现出了两种成分显著的协同效应。总的来说,该研究描绘了PLC的异质性景观,建立了一套预测生物标志物的方法,并发现了乐伐替尼耐药机制,为联合治疗提供了重要线索。 2.Single-cell systems pharmacology identifies development-driven drug response and combination therapy in B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia 通过单细胞系统药理学在B细胞急性淋巴细胞白血病中发现了由肿瘤发展驱动的药物反应和对应的联合治疗方案
美国圣犹达儿童研究医院计算生物系
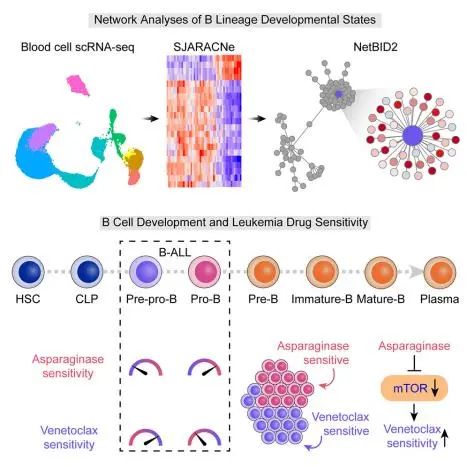
Leukemia can arise at various stages of the hematopoietic differentiation hierarchy, but the impact of developmental arrest on drug sensitivity is unclear. Applying network-based analyses to single-cell transcriptomes of human B cells, we define genome-wide signaling circuitry for each B cell differentiation stage. Using this reference, we comprehensively map the developmental states of B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), revealing its strong correlation with sensitivity to asparaginase, a commonly used chemotherapeutic agent. Single-cell multi-omics analyses of primary B-ALL blasts reveal marked intra-leukemia heterogeneity in asparaginase response: resistance is linked to pre-pro-B-like cells, with sensitivity associated with the pro-B-like population. By targeting BCL2, a driver within the pre-pro-B like cell signaling network, we find that venetoclax significantly potentiates asparaginase efficacy in vitro and in vivo. These findings demonstrate a single-cell systems pharmacology framework to predict effective combination therapies based on intra-leukemia heterogeneity in developmental state, with potentially broad applications beyond B-ALL.
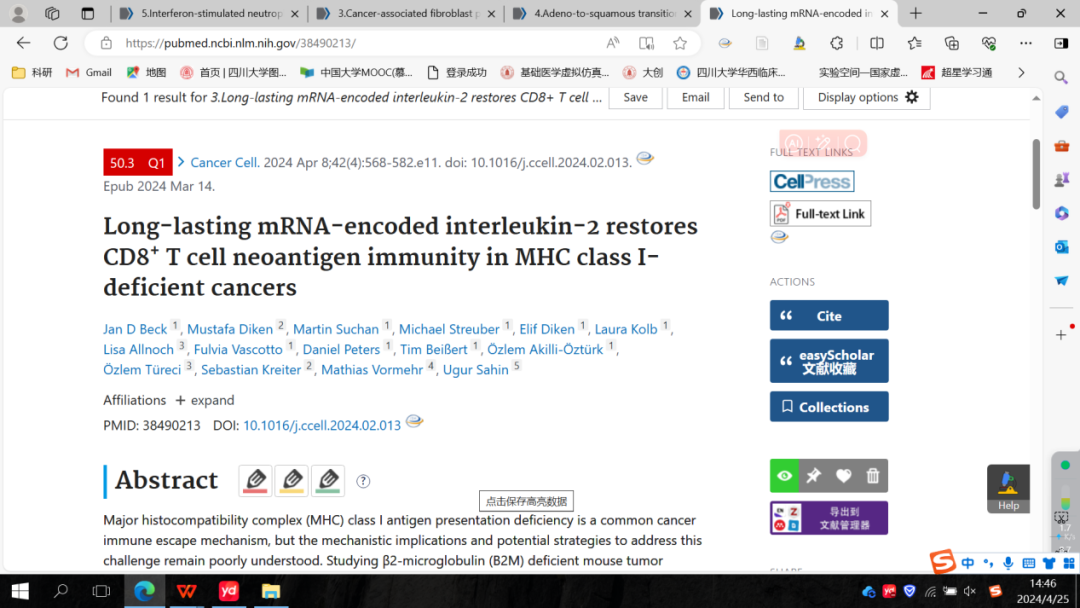
白血病可在造血过程的不同阶段发生,但白血病中造血细胞的发育阻碍对药物敏感性的影响尚不清楚。因此,该研究利用单细胞转录组数据对人类B细胞进行了网络分析,为B细胞的每个分化阶段定义了基因信号网络。以此为参考,该研究全面地描绘了B细胞急性淋巴细胞白血病(B-ALL)的发育状态,并发现其与门冬酰胺酶敏感性强相关,这是一种常用的化疗药物。对原发性B细胞急性淋巴白血病的原始细胞的单细胞多组学分析显示,肿瘤细胞对门冬酰胺酶的反应存在明显的内部异质性,比如抗性与前祖B细胞样细胞相关联,而敏感性与祖B细胞样细胞群体相关。通过针对前祖B细胞样细胞信号传导网络中的关键因子BCL2,该研究发现维奈托克(BCL2抑制剂)可以在体内和体外显著地提高门冬酰胺酶的疗效。这些发现展示了一种单细胞系统药理学框架,可根据白血病内部的发育状态异质性来预测有效的联合治疗方案,这种框架不仅限于B-ALL,具有广泛的应用前景。 3.Long-lasting mRNA-encoded interleukin-2 restores CD8+ T cell neoantigen immunity in MHC class I-deficient cancers 长效mRNA编码的IL-2可以在MHC-I缺陷型癌症中恢复CD8+ T细胞对新抗原的免疫能力
德国约翰内斯古腾堡大学医学中心转化肿瘤学
Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I antigen presentation deficiency is a common cancer immune escape mechanism, but the mechanistic implications and potential strategies to address this challenge remain poorly understood. Studying β2-microglobulin (β2M) deficient mouse tumor models, we find that MHC class I loss leads to a substantial immune desertification of the tumor microenvironment (TME) and broad resistance to immune-, chemo-, and radiotherapy. We show that treatment with long-lasting mRNA-encoded interleukin-2 (IL-2) restores an immune cell infiltrated, IFNγ-promoted, highly proinflammatory TME signature, and when combined with a tumor-targeting monoclonal antibody (mAB), can overcome therapeutic resistance. Unexpectedly, the effectiveness of this treatment is driven by IFNγ-releasing CD8+ T cells that recognize neoantigens cross-presented by TME-resident activated macrophages. These macrophages acquire augmented antigen presentation proficiency and other M1-phenotype-associated features under IL-2 treatment. Our findings highlight the importance of restoring neoantigen-specific immune responses in the treatment of cancers with MHC class I deficiencies.
MHC I类抗原呈递缺失是一种常见的癌症免疫逃逸机制,但我们对其中的机制和解决这一问题的方法仍知之甚少。由此,该研究通过研究β2-微球蛋白(β2M)缺陷的小鼠肿瘤模型,发现MHC I类分子的丢失会导致肿瘤微环境(TME)的免疫荒漠化以及对免疫、化疗和放疗的广泛抵抗。研究发现,用长效mRNA编码的白细胞介素-2(IL-2)来治疗可以恢复TME免疫细胞浸润的、IFNγ促进的高度炎症性的特征,并且当IL-2与肿瘤靶向的单克隆抗体(mAB)联合使用时,可以克服单用的治疗抵抗。出人意料的是,这种治疗是由释放IFNγ的CD8+ T细胞驱动的,它们能识别由TME中激活的巨噬细胞交叉呈递的新抗原。因为这些巨噬细胞在IL-2的治疗下获得了增强的抗原呈递能力和M1型巨噬细胞的相关特征。总的来说,该研究强调了在治疗MHC I类缺陷的癌症中恢复新抗原特异性免疫应答的重要性。
4.ARID1A orchestrates SWI/SNF-mediated sequential binding of transcription factors with ARID1A loss driving pre-memory B cell fate and lymphomagenesis ARID1A是调控SWI/SNF介导的转录因子顺序结合的亚基,ARID1A的缺失会影响前记忆B细胞的命运和驱动淋巴瘤的发生
美国纽约康奈尔大学威尔康奈尔医学院血液学和肿瘤学研究室
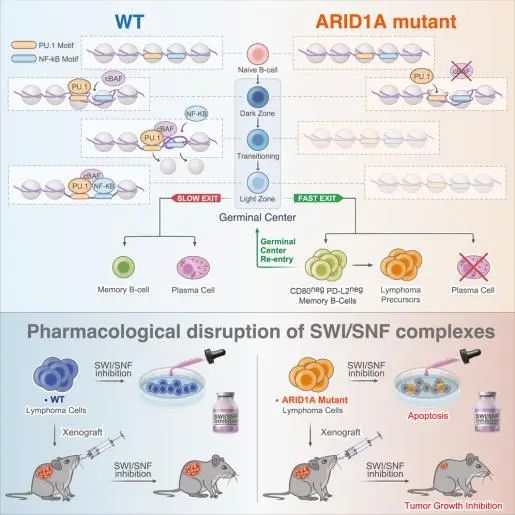
ARID1A, a subunit of the canonical BAF nucleosome remodeling complex, is commonly mutated in lymphomas. We show that ARID1A orchestrates B cell fate during the germinal center (GC) response, facilitating cooperative and sequential binding of PU.1 and NF-kB at crucial genes for cytokine and CD40 signaling. The absence of ARID1A tilts GC cell fate toward immature IgM+CD80-PD-L2- memory B cells, known for their potential to re-enter new GCs. When combined with BCL2 oncogene, ARID1A haploinsufficiency hastens the progression of aggressive follicular lymphomas (FLs) in mice. Patients with FL with ARID1A-inactivating mutations preferentially display an immature memory B cell-like state with increased transformation risk to aggressive disease. These observations offer mechanistic understanding into the emergence of both indolent and aggressive ARID1A-mutant lymphomas through the formation of immature memory-like clonal precursors. Lastly, we demonstrate that ARID1A mutation induces synthetic lethality to SMARCA2/4 inhibition, paving the way for potential precision therapy for high-risk patients.
ARID1A是经典BAF核小体重塑复合物的一个亚基,常在淋巴瘤中发生突变。该研究发现ARID1A会在生发中心(GC)反应期间调控B细胞的命运,促进PU.1和NF-kB在细胞因子和CD40信号通路的关键基因上的合作和顺序结合。而ARID1A的缺失会使GC的B细胞命运倾向于不成熟的IgM+CD80PD-L2记忆B细胞,这些细胞往往能够重新进入新的GC。另外,当ARID1A与BCL2致癌基因相结合时,ARID1A的半失效加速了小鼠中侵袭性滤泡性淋巴瘤(FL)的进展。研究还发现,有ARID1A失活突变的FL患者优先表现出类似不成熟记忆B细胞的状态,并且这类患者转化为侵袭性疾病的风险更高。总的来说,上述观察结果发现,不成熟的记忆样克隆前体B细胞的形成,是ARID1A突变引起侵袭性的淋巴瘤的关键机制。最后,该研究证明了ARID1A突变和SMARCA2/4抑制剂有合成致死作用,这为高风险患者提供了潜在的精准治疗途径。
5.SMARCA4 is a haploinsufficient B cell lymphoma tumor suppressor that fine-tunes centrocyte cell fate decisions SMARCA4是一个半失效的B细胞淋巴瘤抑癌基因,能调控中心细胞的命运走向。
美国德州大学安德森癌症中心淋巴瘤与骨髓瘤科
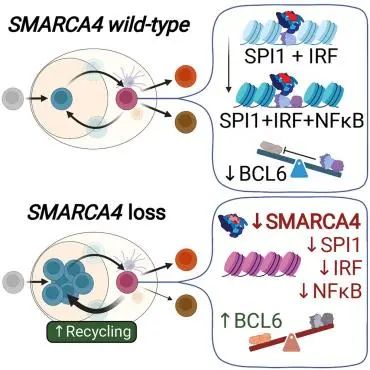
SMARCA4 encodes one of two mutually exclusive ATPase subunits in the BRG/BRM associated factor (BAF) complex that is recruited by transcription factors (TFs) to drive chromatin accessibility and transcriptional activation. SMARCA4 is among the most recurrently mutated genes in human cancer, including 30% of germinal center (GC)-derived Burkitt lymphomas. In mice, GC-specific Smarca4 haploinsufficiency cooperated with MYC over-expression to drive lymphomagenesis. Furthermore, monoallelic Smarca4 deletion drove GC hyperplasia with centroblast polarization via significantly increased rates of centrocyte recycling to the dark zone. Mechanistically, Smarca4 loss reduced the activity of TFs that are activated in centrocytes to drive GC-exit, including SPI1 (PU.1), IRF family, and NF-kB. Loss of activity for these factors phenocopied aberrant BCL6 activity within murine centrocytes and human Burkitt lymphoma cells. SMARCA4 therefore facilitates chromatin accessibility for TFs that shape centrocyte trajectories, and loss of fine-control of these programs biases toward centroblast cell-fate, GC hyperplasia and lymphoma.
SMARCA4编码BRG/BRM相关因子(BAF)复合物中的两个互斥的ATP酶亚基之一,该复合物被转录因子(TFs)招募以推动染色质可及性和转录激活。SMARCA4是人类癌症中最常见的突变基因之一,30%的生发中心(GC)来源的伯基特淋巴瘤都有该基因的突变。在小鼠中,GC特异性的Smarca4半失效联合MYC的过表达,会促进淋巴瘤的发生。此外,单等位基因的Smara4缺失会通过显著增加中心母细胞重新循环到暗区的速率,驱动GC增生并使中心母细胞极化。从机制上讲,Smarca4的丢失降低了在中心细胞中激活的转录因子的活性,这些转录因子通常能驱动B细胞从GC离开,包括SPI1(PU.1)、IRF家族和NF-kB。这些因子在小鼠中的中心细胞和人类伯基特淋巴瘤细胞中的活性丧失,使细胞的BCL6表现出异常的活性。总的来说,SMARCA4提高了调控中心细胞发育轨迹的转录因子的染色质可及性,这些调控程序的失控会使中心母细胞的命运发生偏移、导致GC增生和淋巴瘤。
6.Multimodal stimulation screens reveal unique and shared genes limiting T cell fitness 多模式刺激筛选揭示了限制T细胞适应性的特异性和共同基因
荷兰癌症研究所分子肿瘤学和免疫学分部
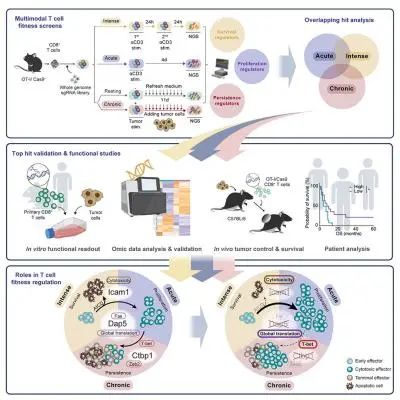
Genes limiting T cell antitumor activity may serve as therapeutic targets. It has not been systematically studied whether there are regulators that uniquely or broadly contribute to T cell fitness. We perform genomescale CRISPR-Cas9 knockout screens in primary CD8 T cells to uncover genes negatively impacting fitness upon three modes of stimulation: (1) intense, triggering activation-induced cell death (AICD); (2) acute, triggering expansion; (3) chronic, causing dysfunction. Besides established regulators, we uncover genes controlling T cell fitness either specifically or commonly upon differential stimulation. Dap5 ablation, ranking highly in all three screens, increases translation while enhancing tumor killing. Loss of Icam1-mediated homotypic T cell clustering amplifies cell expansion and effector functions after both acute and intense stimulation. Lastly, Ctbp1 inactivation induces functional T cell persistence exclusively upon chronic stimulation. Our results functionally annotate fitness regulators based on their unique or shared contribution to traits limiting T cell antitumor activity.
限制T细胞抗肿瘤活性的基因可能成为抗肿瘤的治疗靶点。但目前还不清楚是否存在特异或广泛调控T细胞适应性的基因。因此,该研究在原代CD8 T细胞中进行了基因组规模的CRISPR-Cas9敲除筛选,以揭示在三种刺激模式下对细胞适应性产生负性影响的基因:(1)强烈刺激,引起T细胞的激活诱导细胞死亡(AICD);(2)急性刺激,诱导T细胞扩增;(3)慢性刺激,导致T细胞功能失调。结果发现,除了已知的调节因子外,该研究发现了一些新的能在不同刺激下调控T细胞适应性的基因,包括刺激特异性的和共同的。其中,Dap5的消除在三种筛选中排名较高,提高了T细胞的翻译能力并增强了肿瘤杀伤作用。另外,当时失去Icam1介导的同种型T细胞聚集时,急性和强烈刺激都会刺激T细胞扩增和增强T细胞的功能效应。最后,Ctbp1失活仅在慢性刺激下能诱导功能性T细胞的持久性。总的来说,该研究的结果根据这些适应性调节因子对限制T细胞抗肿瘤活性的贡献,对它们进行了功能注释。
7.Retinoic acid receptor activation reprograms senescence response and enhances anti-tumor activity of natural killer cells 激活视黄酸受体能重编程衰老反应并增强自然杀伤细胞的抗肿瘤活性
瑞士肿瘤研究所
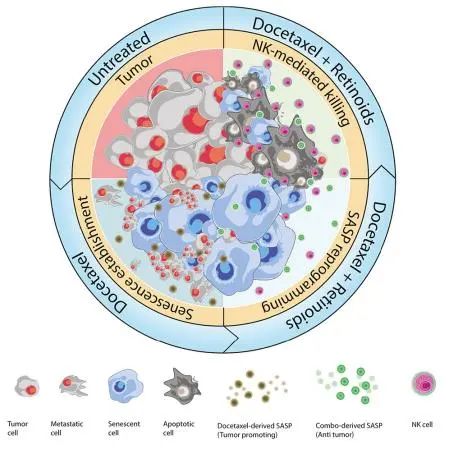
Cellular senescence can exert dual effects in tumors, either suppressing or promoting tumor progression. The senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP), released by senescent cells, plays a crucial role in this dichotomy. Consequently, the clinical challenge lies in developing therapies that safely enhance senescence in cancer, favoring tumor-suppressive SASP factors over tumor-promoting ones. Here, we identify the retinoic-acid-receptor (RAR) agonist adapalene as an effective pro-senescence compound in prostate cancer (PCa). Reactivation of RARs triggers a robust senescence response and a tumor-suppressive SASP. In preclinical mouse models of PCa, the combination of adapalene and docetaxel promotes a tumor-suppressive SASP that enhances natural killer (NK) cell-mediated tumor clearance more effectively than either agent alone. This approach increases the efficacy of the allogenic infusion of human NK cells in mice injected with human PCa cells, suggesting an alternative therapeutic strategy to stimulate the anti-tumor immune response in "immunologically cold" tumors.
细胞衰老在肿瘤中可能产生双重效应,既可以抑制肿瘤的发展,也可能促进其进展。衰老细胞释放会释放一系列生物分子(包括细胞因子,生长因子等),称为衰老相关的分泌表型(SASP),它们在其中起着至关重要的作用。因此,临床上的挑战在于开发能够安全促进肿瘤细胞衰老,有利于肿瘤抑制的SASP,而不是促进肿瘤进展的SASP。因此,在这项研究中,研究者发现视黄酸受体(RAR)激动剂阿达博林是一种在前列腺癌(PCa)中有效的促肿瘤衰老化合物。RAR的重新激活能引发肿瘤强烈的衰老反应和并产生抑制肿瘤的SASP。在临床前的PCa小鼠模型中,阿达博林和多西他赛的联合使用促进了一种抑制肿瘤的SASP的产生,这种SASP比单独使用任何一种药物更能有效地增强自然杀伤(NK)细胞介导的肿瘤清除作用。研究在注射了人类PCa细胞的小鼠体内验证了这种方法的疗效,为刺激“免疫冷”肿瘤的抗肿瘤免疫反应提供了一种替代治疗方法。
8.Mapping functional to morphological variation reveals the basis of regional extracellular matrix subversion and nerve invasion in pancreatic cancer 通过将肿瘤细胞的功能变异映射到形态学变异,揭示了胰腺癌中区域性细胞外基质转变和神经侵袭的基础。
意大利欧洲肿瘤研究所(IRCCS)
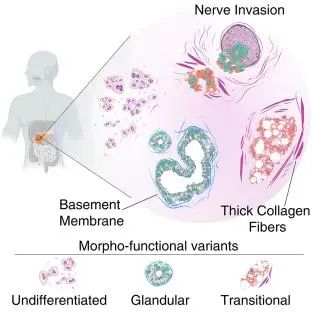
Intratumor morphological heterogeneity of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) predicts clinical outcomes but is only partially understood at the molecular level. To elucidate the gene expression programs underpinning intratumor morphological variation in PDAC, we investigated and deconvoluted at single cell level the molecular profiles of histologically distinct clusters of PDAC cells. We identified three major morphological and functional variants that co-exist in varying proportions in all PDACs, display limited genetic diversity, and are associated with a distinct organization of the extracellular matrix: a glandular variant with classical ductal features; a transitional variant displaying abortive ductal structures and mixed endodermal and myofibroblast-like gene expression; and a poorly differentiated variant lacking ductal features and basement membrane, and showing neuronal lineage priming. Ex vivo and in vitro evidence supports the occurrence of dynamic transitions among these variants in part influenced by extracellular matrix composition and stiffness and associated with local, specifically neural, invasion.
胰腺导管腺癌(PDAC)的肿瘤内形态异质性可以用来预测临床结局,但我们对PDAC肿瘤内分子水平上的异质性了解很少。为了阐明PDAC肿瘤内形态变异的基因表达程序,该研究在单细胞水平上解析了PDAC的不同组织学细胞簇的分子特征。结果显示,该研究一共鉴定出了三种主要的形态和功能细胞群,它们在所有PDAC组织中以不同比例共存,显示有限的遗传多样性,并与细胞外基质的不同结构相关联,比如,具有经典导管特征的腺体细胞;有未成熟导管结构和混合内胚层并且有肌纤维母细胞样基因表达的过渡细胞;缺乏导管特征和基底膜,并表现出神经细胞谱系的初步特征的未分化细胞。体外和体内的证据支持了这些细胞之间会发生动态转变,这些转变会在一定程度上受到细胞外基质的组成和刚度的影响,并与肿瘤的局部侵袭,特别是神经侵袭相关。
9.PDGFRα+ITGA11+ fibroblasts foster early-stage cancer lymphovascular invasion and lymphatic metastasis via ITGA11-SELE interplay PDGFRα+ITGA11+成纤维细胞通过ITGA11-SELE相互作用促进早期癌症的淋巴血管侵袭和淋巴转移
中山大学孙逸仙纪念医院
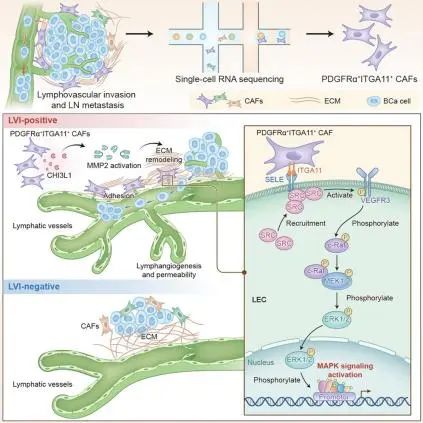
Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) exhibit considerable heterogeneity in advanced cancers; however, the functional annotation and mechanism of CAFs in early-stage cancers remain elusive. Utilizing single-cell RNA sequencing and spatial transcriptomic, we identify a previously unknown PDGFRa+ITGA11+ CAF subset in early-stage bladder cancer (BCa). Multicenter clinical analysis of a 910-case cohort confirms that PDGFRa+ITGA11+ CAFs are associated with lymphovascular invasion (LVI) and poor prognosis in early-stage BCa. These CAFs facilitate LVI and lymph node (LN) metastasis in early-stage BCa, as evidenced in a PDGFRa+ITGA11+ CAFs-specific deficient mouse model. Mechanistically, PDGFRa+ITGA11+ CAFs promote lymphangiogenesis via recognizing ITGA11 surface receptor SELE on lymphatic endothelial cells to activate SRC-p-VEGFR3-MAPK pathway. Further, CHI3L1 from PDGFRa+ITGA11+ CAFs aligns the surrounding matrix to assist cancer cell intravasation, fostering early-stage BCa LVI and LN metastasis. Collectively, our study reveals the crucial role of PDGFRa+ITGA11+ CAFs in shaping metastatic landscape, informing the treatment of early-stage BCa LVI.
在晚期癌症中,肿瘤相关的成纤维细胞(CAFs)展现出相当大的异质性;然而,在早期癌症中,CAFs的功能和机制仍然不为人知。因此,该研究通过单细胞RNA测序和空间转录组学,在早期膀胱癌(BCa)中发现了一个未报道过的PDGFRa+ITGA11+ CAF亚群。通过对910例病例的多中心临床分析,证实了PDGFRa+ITGA11+ CAF与早期BCa中的淋巴血管侵袭(LVI)和不良预后相关。这些CAFs促进了早期BCa的LVI和淋巴结(LN)转移,并在PDGFRa+ITGA11+ CAF特异性缺失的小鼠模型中得到了证实。机制上,PDGFRa+ITGA11+ CAF通过识别淋巴内皮细胞上的ITGA11表面受体SELE来激活SRC-p-VEGFR3-MAPK通路,从而促进淋巴管新生。此外,来自PDGFRa+ITGA11+ CAF的CHI3L1重塑了癌细胞周围的基质,协助癌细胞内皮化,促进早期BCa的LVI和LN转移。综上所述,该研究揭示了PDGFRa+ITGA11+ CAF在形成转移性肿瘤景观中的关键作用,并为早期BCa的LVI治疗提供了重要信息。
10.Genetic interactions reveal distinct biological and therapeutic implications in breast cancer 基因相互作用揭示了乳腺癌中不同的生物学和治疗启示
复旦大学上海肿瘤中心乳腺外科乳腺癌重点实验室
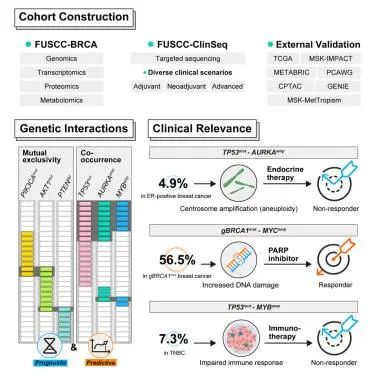
Co-occurrence and mutual exclusivity of genomic alterations may reflect the existence of genetic interactions, potentially shaping distinct biological phenotypes and impacting therapeutic response in breast cancer. However, our understanding of them remains limited. Herein, we investigate a large-scale multi-omics cohort (n=873) and a real-world clinical sequencing cohort (n=4,405) including several clinical trials with detailed treatment outcomes and perform functional validation in patient-derived organoids, tumor fragments, and in vivo models. Through this comprehensive approach, we construct a network comprising co-alterations and mutually exclusive events and characterize their therapeutic potential and underlying biological basis. Notably, we identify associations between TP53mut-AURKAamp and endocrine therapy resistance, germline BRCA1mut-MYCamp and improved sensitivity to PARP inhibitors, and TP53mut-MYBamp and immunotherapy resistance. Furthermore, we reveal that precision treatment strategies informed by co-alterations hold promise to improve patient outcomes. Our study highlights the significance of genetic interactions in guiding genome-informed treatment decisions beyond single driver alterations.
乳腺癌中基因组改变的共同发生和互斥可能反映了基因相互作用的存在,这些相互作用可能塑造了不同的生物学表型,并影响了治疗反应。然而,我们对它们的理解仍然有限。在这项研究中,研究者调查了一个大规模多组学队列(n = 873)和一个现实世界的临床测序队列(n = 4,405),其中包括几项具有详细治疗结果的临床试验,并在患者来源的类器官、肿瘤组织碎片和体内模型中进行功能验证。通过这种全面的方法,该研究构建了一个包括基因共同改变和互斥事件的网络,并表征了基因共同改变和互斥对治疗潜力的影响和潜在的生物学基础。值得注意的是,研究发现了TP53突变-AURKA扩增与肿瘤的内分泌治疗抵抗、BRCA1突变-MYC扩增与肿瘤对PARP抑制剂的敏感性提高以及TP53突变-MYB扩增与肿瘤的免疫治疗抵抗之间的关联。此外,该研究还发现根据基因共同改变制定的精准治疗策略有望改善患者预后。总的来说,该研究凸显了基因相互作用对于指导治疗决策的重要性,甚至超越了单一驱动基因改变对治疗决策的影响。 汇报人: 夏晓旭 导师:赵宇 任建君 审核:任建君 邱轲



