【Cell】2024年4月-2024年5月论文导读(187卷,8-10期)
期刊介绍:
Cell是Cell Press细胞出版社旗下的旗舰刊,创办于1974年,由Elsevier公司出版发行。这是一本多学科期刊,包括但不限于细胞生物学、分子生物学、神经科学、免疫学、病毒学和微生物学、癌症、人类遗传学、系统生物学、信号传导和疾病机制和疾病治疗。该期刊为双周刊,最新影响因子为64.5。
本期文献导读将呈现2024年4月和2024年5月的主要刊物内容。

Apr 11, 2024 Volume 187 Issue 8 p1819-2028
在2024年4月11日,共发表15篇文章,其中包括1篇讣告,1篇Bench to Bedside,2篇Commentary,8篇Articles,3篇Resources。
1、Gut microbiome and metabolome profiling in Framingham heart study reveals cholesterol-metabolizing bacteria
弗雷明汉心脏研究中的肠道微生物组和代谢组分析揭示了胆固醇代谢细菌

Accumulating evidence suggests that cardiovascular disease (CVD) is associated with an altered gut microbiome. Our understanding of the underlying mechanisms has been hindered by lack of matched multi-omic data with diagnostic biomarkers. To comprehensively profile gut microbiome contributions to CVD, we generated stool metagenomics and metabolomics from 1,429 Framingham Heart Study participants. We identified blood lipids and cardiovascular health measurements associated with microbiome and metabolome composition. Integrated analysis revealed microbial pathways implicated in CVD, including flavonoid, γ-butyrobetaine, and cholesterol metabolism. Species from the Oscillibacter genus were associated with decreased fecal and plasma cholesterol levels. Using functional prediction and in vitro characterization of multiple representative human gut Oscillibacter isolates, we uncovered conserved cholesterol-metabolizing capabilities, including glycosylation and dehydrogenation. These findings suggest that cholesterol metabolism is a broad property of phylogenetically diverse Oscillibacter spp., with potential benefits for lipid homeostasis and cardiovascular health.
越来越多的证据表明心血管疾病(CVD)与肠道微生物组的改变有关。由于缺乏与诊断生物标志物相匹配的多组学数据,我们对潜在机制的理解受到了阻碍。为了全面分析肠道微生物组对CVD的贡献,我们从1,429名Framingham心脏研究参与者中生成了粪便宏基因组学和代谢组学数据。我们鉴定了与微生物组和代谢组组成相关的血脂和心血管健康测量值。综合分析揭示了与CVD相关的微生物途径,包括类黄酮、γ-丁基甜菜碱和胆固醇代谢。来自颤杆菌克属的物种与粪便和血浆胆固醇水平降低有关。通过对多种代表性人类肠道颤杆菌克属分离株的功能预测和体外表征,我们发现了保守的胆固醇代谢能力,包括糖基化和脱氢。这些发现表明,胆固醇代谢是系统发育多样化的颤杆菌克属的一个广泛特性,对脂质稳态和心血管健康具有潜在益处。
2.Infant microbes and metabolites point to childhood neurodevelopmental disorders
婴儿微生物和代谢物导致儿童神经发育障碍

This study has followed a birth cohort for over 20 years to find factors associated with neurodevelopmental disorder (ND) diagnosis. Detailed, early-life longitudinal questionnaires captured infection and antibiotic events, stress, prenatal factors, family history, and more. Biomarkers including cord serum metabolome and lipidome, human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genotype, infant microbiota, and stool metabolome were assessed. Among the 16,440 Swedish children followed across time, 1,197 developed an ND. Significant associations emerged for future ND diagnosis in general and for specific ND subtypes, spanning intellectual disability, speech disorder, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and autism. This investigation revealed microbiome connections to future diagnosis as well as early emerging mood and gastrointestinal problems. The findings suggest links to immunodysregulation and metabolism, compounded by stress, early-life infection, and antibiotics. The convergence of infant biomarkers and risk factors in this prospective, longitudinal study on a large-scale population establishes a foundation for early-life prediction and intervention in neurodevelopment.
本研究对出生队列进行了20多年的跟踪,以寻找与神经发育障碍(ND)诊断相关的因素。详细的早期生命纵向调查问卷记录了感染和抗生素事件、压力、产前因素、家族史等。评估了包括脐带血清代谢物和脂质组、人类白细胞抗原(HLA)基因型、婴儿微生物群和粪便代谢物组在内的生物标志物。在长期追踪的16,440名瑞典儿童中,有1,197名患有ND。未来的一般ND诊断和特定ND亚型(包括智力障碍、言语障碍、注意力缺陷/多动障碍和自闭症)诊断之间存在显著关联。这项研究揭示了微生物组与未来ND诊断的强相关性以及与早期情绪和胃肠道问题的关联。研究结果表明,ND与免疫失调和新陈代谢有关,再加上压力、早期感染和抗生素的影响。在这项针对大规模人群的前瞻性纵向研究中,婴儿生物标志物和危险因素的融合为早期生命预测和神经发育干预奠定了基础。
3、Biofilm exopolysaccharides alter sensory-neuron-mediated sickness during lung infection
生物膜胞外多糖改变肺部感染期间感觉神经元介导的疾病

Infections of the lung cause observable sickness thought to be secondary to inflammation. Signs of sickness are crucial to alert others via behavioral-immune responses to limit contact with contagious individuals. Gram-negative bacteria produce exopolysaccharide (EPS) that provides microbial protection; however, the impact of EPS on sickness remains uncertain. Using genome-engineered Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) strains, we compared EPS-producers versus non-producers and a virulent Escherichia coli (E. coli) lung infection model in male and female mice. EPS-negative P. aeruginosa and virulent E. coli infection caused severe sickness, behavioral alterations, inflammation, and hypothermia mediated by TLR4 detection of the exposed lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in lung TRPV1+ sensory neurons. However, inflammation did not account for sickness. Stimulation of lung nociceptors induced acute stress responses in the paraventricular hypothalamic nuclei by activating corticotropin-releasing hormone neurons responsible for sickness behavior and hypothermia. Thus, EPS-producing biofilm pathogens evade initiating a lung-brain sensory neuronal response that results in sickness.
肺部感染会引起明显可观察的疾病,被认为是继发于炎症。疾病迹象对于通过行为免疫反应提醒他人以限制与传染性个体的接触至关重要。革兰氏阴性细菌产生的胞外多糖(EPS)给微生物提供保护;然而,EPS对疾病的影响仍不确定。使用基因组工程铜绿假单胞菌(P.aeruginosa)菌株,我们在雄性和雌性小鼠中比较了EPS生产者与非生产者以及强毒大肠杆菌(E.coli)肺部感染模型。EPS阴性铜绿假单胞菌和强毒力大肠杆菌感染导致严重疾病、行为改变、炎症和体温过低,这是由TLR4检测到的肺TRPV1+感觉神经元中暴露的脂多糖(LPS)介导的。然而,炎症并不能解释疾病。肺部伤害感受器受到刺激后通过激活负责疾病行为和体温过低的促肾上腺皮质激素释放激素神经元,诱导室旁下丘脑核团的急性应激反应。因此,产生EPS的生物膜病原体会避免启动肺-脑感觉神经元反应,从而导致疾病。
4.Macromolecular condensation organizes nucleolar sub-phases to set up a pH gradient
大分子聚合组织核仁亚相以建立 pH 梯度

Nucleoli are multicomponent condensates defined by coexisting sub-phases. We identified distinct intrinsically disordered regions (IDRs), including acidic (D/E) tracts and K-blocks interspersed by E-rich regions, as defining features of nucleolar proteins. We show that the localization preferences of nucleolar proteins are determined by their IDRs and the types of RNA or DNA binding domains they encompass. In vitro reconstitutions and studies in cells showed how condensation, which combines binding and complex coacervation of nucleolar components, contributes to nucleolar organization. D/E tracts of nucleolar proteins contribute to lowering the pH of co-condensates formed with nucleolar RNAs in vitro. In cells, this sets up a pH gradient between nucleoli and the nucleoplasm. By contrast, juxta-nucleolar bodies, which have different macromolecular compositions, featuring protein IDRs with very different charge profiles, have pH values that are equivalent to or higher than the nucleoplasm. Our findings show that distinct compositional specificities generate distinct physicochemical properties for condensates.
核仁是由共存子相定义的多组分凝聚物。我们鉴定了不同的固有无序区域(IDR),包括酸性(D/E)区域,和夹杂着富含E区域的K区,作为核仁蛋白的定义特征。我们发现核仁蛋白的定位偏好是由它们的IDR以及它们所包含的RNA或DNA结合域的类型决定的。细胞的体外重建和研究表明了包括结合以及核仁成分的复杂凝聚的凝聚过程如何有助于核仁组织。核仁蛋白的D/E束有助于降低体外与核仁RNA形成的共缩合物的pH值。在细胞中,这会在核仁和核质之间建立pH梯度。相比之下,核仁旁体具有不同的大分子组成,其蛋白质IDR具有非常不同的电荷分布,并且pH值等于或高于核质。我们的研究结果表明,不同的组成特异性会产生不同的凝聚物物理化学性质。
5.Mastigoneme structure reveals insights into the O-linked glycosylation code of native hydroxyproline-rich helices
鞭毛丝结构揭示了对天然富含羟脯氨酸螺旋的O-连接糖基化密码的见解
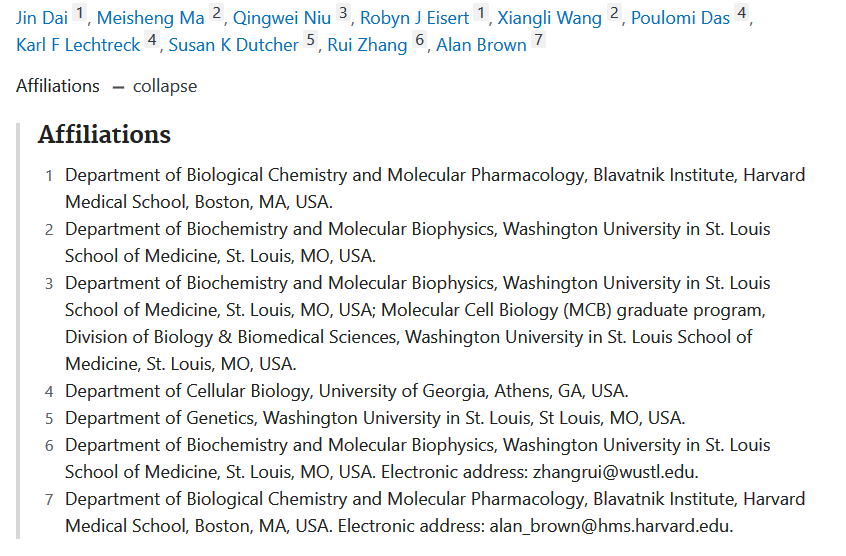
Hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins (HRGPs) are a ubiquitous class of protein in the extracellular matrices and cell walls of plants and algae, yet little is known of their native structures or interactions. Here, we used electron cryomicroscopy (cryo-EM) to determine the structure of the hydroxyproline-rich mastigoneme, an extracellular filament isolated from the cilia of the alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. The structure demonstrates that mastigonemes are formed from two HRGPs (a filament of MST1 wrapped around a single copy of MST3) that both have hyperglycosylated poly(hydroxyproline) helices. Within the helices, O-linked glycosylation of the hydroxyproline residues and O-galactosylation of interspersed serine residues create a carbohydrate casing. Analysis of the associated glycans reveals how the pattern of hydroxyproline repetition determines the type and extent of glycosylation. MST3 possesses a PKD2-like transmembrane domain that forms a heteromeric polycystin-like cation channel with PKD2 and SIP, explaining how mastigonemes are tethered to ciliary membranes.
富含羟脯氨酸的糖蛋白(HRGP)是植物和藻类的细胞外基质和细胞壁中普遍存在的一类蛋白质,但对其天然结构或相互作用知之甚少。本研究使用电子冷冻显微镜(cryo-EM)来确定富含羟脯氨酸的藻类鞭丝体(一种从藻类莱茵衣藻纤毛中分离出来的细胞外丝)的结构。该结构表明,鞭丝体由两个HRGP(一条MST1细丝包裹在一个MST3拷贝周围)形成,两者都具有高糖基化的聚(羟脯氨酸)螺旋。在螺旋内,羟脯氨酸残基的O-连接糖基化和散布的丝氨酸残基的O-半乳糖基化形成碳水化合物外壳。对相关聚糖的分析揭示了羟脯氨酸重复模式如何决定糖基化的类型和程度。MST3具有类似PKD2的跨膜结构域,可与PKD2和SIP形成异聚多囊蛋白样阳离子通道,解释了鞭毛体如何与纤毛膜相连。
6.Barcoding of episodic memories in the hippocampus of a food-caching bird
储存食物的鸟类海马体中情境记忆的“条形码”神经活动

The hippocampus is critical for episodic memory. Although hippocampal activity represents place and other behaviorally relevant variables, it is unclear how it encodes numerous memories of specific events in life. To study episodic coding, we leveraged the specialized behavior of chickadees—food-caching birds that form memories at well-defined moments in time whenever they cache food for subsequent retrieval. Our recordings during caching revealed very sparse, transient barcode-like patterns of firing across hippocampal neurons. Each “barcode” uniquely represented a caching event and transiently reactivated during the retrieval of that specific cache. Barcodes co-occurred with the conventional activity of place cells but were uncorrelated even for nearby cache locations that had similar place codes. We propose that animals recall episodic memories by reactivating hippocampal barcodes. Similarly to computer hash codes, these patterns assign unique identifiers to different events and could be a mechanism for rapid formation and storage of many non-interfering memories.
海马体对于情境记忆至关重要。尽管海马体活动代表了地点和其他行为相关变量,但尚不清楚它如何编码生活中特定事件的大量记忆。为了研究情境编码,我们利用了山雀(储存食物的鸟类)的特殊行为,每当它们储存食物以供后续食用时,它们都会在明确的时刻形成记忆。我们在对贮藏食物的记忆“缓存”期间的记录显示,海马神经元的放电模式非常稀疏、短暂,类似于条形码。每个“条形码”唯一地代表一个缓存事件,并在检索该特定缓存期间短暂重新激活。条形码与位置细胞的传统活动同时出现,但即使对于具有相似位置代码的附近缓存位置也是不相关的。我们认为,动物通过重新激活海马条形码来回忆情境记忆。与计算机哈希码类似,这些模式为不同的事件分配唯一的标识符,并且可以成为快速形成和存储许多互不干扰的记忆的机制。
7.Type-I-interferon-responsive microglia shape cortical development and behavior
I型干扰素反应性小胶质细胞塑造大脑皮层发育和行为

Microglia are brain-resident macrophages that shape neural circuit development and are implicated in neurodevelopmental diseases. Multiple microglial transcriptional states have been defined, but their functional significance is unclear. Here, we identify a type I interferon (IFN-I)-responsive microglial state in the developing somatosensory cortex (postnatal day 5) that is actively engulfing whole neurons. This population expands during cortical remodeling induced by partial whisker deprivation. Global or microglial-specific loss of the IFN-I receptor resulted in microglia with phagolysosomal dysfunction and an accumulation of neurons with nuclear DNA damage. IFN-I gain of function increased neuronal engulfment by microglia in both mouse and zebrafish and restricted the accumulation of DNA-damaged neurons. Finally, IFN-I deficiency resulted in excess cortical excitatory neurons and tactile hypersensitivity. These data define a role for neuron-engulfing microglia during a critical window of brain development and reveal homeostatic functions of a canonical antiviral signaling pathway in the brain.
小胶质细胞是大脑驻留的巨噬细胞,影响神经回路的发育并与神经发育疾病有关。多种小胶质细胞转录状态已被定义,但其功能意义尚不清楚。本研究在发育中的躯体感觉皮层(出生后第5天)中发现了I型干扰素(IFN-I)反应性小胶质细胞状态,该状态会主动吞噬整个神经元。在部分胡须剥夺(whisker deprivation)引起的皮质重塑过程中,这个群体会扩大。IFN-I受体的整体或小胶质细胞特异性缺失导致小胶质细胞吞噬溶酶体功能障碍以及核DNA损伤的神经元积聚。IFN-I的功能增益增加了小鼠和斑马鱼中小胶质细胞对神经元的吞噬,并限制了DNA损伤神经元的积累。最后,IFN-I缺乏导致皮质兴奋性神经元过多和触觉超敏反应。这些数据确定了神经元吞噬小胶质细胞在大脑发育的关键窗口期间的作用,并揭示了大脑中典型抗病毒信号通路的稳态功能。
8.Contrasting somatic mutation patterns in aging human neurons and oligodendrocytes
衰老人类神经元和少突胶质细胞的体细胞突变模式对比

Characterizing somatic mutations in the brain is important for disentangling the complex mechanisms of aging, yet little is known about mutational patterns in different brain cell types. Here, we performed whole-genome sequencing (WGS) of 86 single oligodendrocytes, 20 mixed glia, and 56 single neurons from neurotypical individuals spanning 0.4-104 years of age and identified >92,000 somatic single-nucleotide variants (sSNVs) and small insertions/deletions (indels). Although both cell types accumulate somatic mutations linearly with age, oligodendrocytes accumulated sSNVs 81% faster than neurons and indels 28% slower than neurons. Correlation of mutations with single-nucleus RNA profiles and chromatin accessibility from the same brains revealed that oligodendrocyte mutations are enriched in inactive genomic regions and are distributed across the genome similarly to mutations in brain cancers. In contrast, neuronal mutations are enriched in open, transcriptionally active chromatin. These stark differences suggest an assortment of active mutagenic processes in oligodendrocytes and neurons.
表征大脑中的体细胞突变对于解开衰老的复杂机制非常重要,但人们对不同类型脑细胞的突变模式知之甚少。本研究对来自0.4-104岁的神经典型个体的86个单个少突胶质细胞、20个混合神经胶质细胞和56个单个神经元进行了全基因组测序(WGS),并鉴定了超过92,000个体细胞单核苷酸变异(sSNV)和小插入/删除(插入缺失)。尽管两种细胞类型都随着年龄线性积累体细胞突变,但少突胶质细胞积累sSNV的速度比神经元快81%,而积累插入缺失的速度比神经元慢28%。突变与单核RNA谱和来自同一大脑的染色质可及性的相关性表明,少突胶质细胞突变在不活跃的基因组区域中富集,并且分布在整个基因组中,类似于脑癌中的突变。相比之下,神经元突变在开放的转录活性染色质中富集。这些明显的差异表明少突胶质细胞和神经元中存在多种活跃的突变过程。
Apr 25, 2024 Volume 187 Issue 9 p2029-2342
在2024年4月25日,共发表22篇文章,其中包括6篇leading edge的50周年专栏,2篇previews,12篇Articles,2篇Resources。
1、Generation of rat forebrain tissues in mice
小鼠前脑组织的生成

Interspecies blastocyst complementation (IBC) provides a unique platform to study development and holds the potential to overcome worldwide organ shortages. Despite recent successes, brain tissue has not been achieved through IBC. Here, we developed an optimized IBC strategy based on C-CRISPR, which facilitated rapid screening of candidate genes and identified that Hesx1 deficiency supported the generation of rat forebrain tissue in mice via IBC. Xenogeneic rat forebrain tissues in adult mice were structurally and functionally intact. Cross-species comparative analyses revealed that rat forebrain tissues developed at the same pace as the mouse host but maintained rat-like transcriptome profiles. The chimeric rate of rat cells gradually decreased as development progressed, suggesting xenogeneic barriers during mid-to-late pre-natal development. Interspecies forebrain complementation opens the door for studying evolutionarily conserved and divergent mechanisms underlying brain development and cognitive function. The C-CRISPR-based IBC strategy holds great potential to broaden the study and application of interspecies organogenesis.
异种囊胚互补(IBC)提供了一个独特的发育研究平台,并具有克服全球器官短缺的潜力。尽管最近取得了一些成功,但脑组织尚未通过IBC获得。本研究开发了一种基于C-CRISPR的优化IBC策略,该策略有助于快速筛选候选基因,并确定Hesx1缺陷支持通过IBC在小鼠中生成大鼠前脑组织。成年小鼠中的异种大鼠前脑组织结构和功能完整。跨物种比较分析表明,大鼠前脑组织的发育速度与小鼠宿主相同,但保持了与大鼠相似的转录组特征。大鼠细胞的嵌合率随着发育的进展逐渐降低,提示产前发育中后期存在异种障碍。异种前脑互补为研究大脑发育和认知功能背后的进化保守和差异机制打开了大门。基于C-CRISPR的IBC策略在拓宽异种器官发生的研究和应用方面具有巨大的潜力。
2.Functional sensory circuits built from neurons of two species
由两个物种的神经元构建的功能感觉回路

A central question for regenerative neuroscience is whether synthetic neural circuits, such as those built from two species, can function in an intact brain. Here, we apply blastocyst complementation to selectively build and test interspecies neural circuits. Despite approximately 10–20 million years of evolution, and prominent species differences in brain size, rat pluripotent stem cells injected into mouse blastocysts develop and persist throughout the mouse brain. Unexpectedly, the mouse niche reprograms the birth dates of rat neurons in the cortex and hippocampus, supporting rat-mouse synaptic activity. When mouse olfactory neurons are genetically silenced or killed, rat neurons restore information flow to odor processing circuits. Moreover, they rescue the primal behavior of food seeking, although less well than mouse neurons. By revealing that a mouse can sense the world using neurons from another species, we establish neural blastocyst complementation as a powerful tool to identify conserved mechanisms of brain development, plasticity, and repair.
再生神经科学的一个核心问题是合成的神经回路(例如由两个物种构建的神经回路)是否可以在完整的大脑中发挥作用。本研究应用囊胚互补来选择性地构建和测试种间神经回路。尽管经历了大约10-2000万年的进化,并且大脑大小存在显着的物种差异,但注射到小鼠囊胚中的大鼠多能干细胞在整个小鼠大脑中发育并持续存在。出乎意料的是,小鼠生态位重新编程了大脑皮层和海马体中大鼠神经元的出生日期,支持大鼠-小鼠突触活动。当小鼠嗅觉神经元被基因沉默或杀死时,大鼠神经元会恢复气味处理回路的信息流。此外,它们还挽救了寻找食物的原始行为,尽管效果不如小鼠神经元。通过揭示小鼠可以利用来自另一个物种的神经元感知世界,我们将神经囊胚互补建立为识别大脑发育、可塑性和修复的保守机制的强大工具。
3.Time-series reconstruction of the molecular architecture of human centriole assembly
人类中心粒组装分子结构的时间序列重建

Centriole biogenesis, as in most organelle assemblies, involves the sequential recruitment of sub-structural elements that will support its function. To uncover this process, we correlated the spatial location of 24 centriolar proteins with structural features using expansion microscopy. A time-series reconstruction of protein distributions throughout human procentriole assembly unveiled the molecular architecture of the centriole biogenesis steps. We found that the process initiates with the formation of a naked cartwheel devoid of microtubules. Next, the bloom phase progresses with microtubule blade assembly, concomitantly with radial separation and rapid cartwheel growth. In the subsequent elongation phase, the tubulin backbone grows linearly with the recruitment of the A-C linker, followed by proteins of the inner scaffold (IS). By following six structural modules, we modeled 4D assembly of the human centriole. Collectively, this work provides a framework to investigate the spatial and temporal assembly of large macromolecules.
与大多数细胞器组装一样,中心粒的生物发生涉及支持其功能的亚结构元件的顺序募集。为了揭示这一过程,我们使用膨胀显微成像技术将24个中心粒蛋白的空间位置与结构特征相关联。对整个人类原中心粒组装过程中蛋白质分布的时间序列重建揭示了中心粒生物发生步骤的分子结构。我们发现这个过程起始于没有微管的裸侧齿轮的形成。接下来,随着微管叶片组装,伴随着径向分离和快速轮状生长,形成阶段继续进行。在随后的延伸阶段,微管蛋白主链随着A-C连接子的招募而线性增长,随后是内部支架(IS)蛋白质的加入。通过遵循六个结构模块,我们对人类中心粒的4D组装进行了建模。总的来说,这项工作提供了一个研究大分子的空间和时间组装的框架。
4.Short-distance vesicle transport via phase separation
通过相分离进行短距离囊泡运输

In addition to long-distance molecular motor-mediated transport, cellular vesicles also need to be moved at short distances with defined directions to meet functional needs in subcellular compartments but with unknown mechanisms. Such short-distance vesicle transport does not involve molecular motors. Here, we demonstrate, using synaptic vesicle (SV) transport as a paradigm, that phase separation of synaptic proteins with vesicles can facilitate regulated, directional vesicle transport between different presynaptic bouton sub-compartments. Specifically, a large coiled-coil scaffold protein Piccolo, in response to Ca2+ and via its C2A domain-mediated Ca2+ sensing, can extract SVs from the synapsin-clustered reserve pool condensate and deposit the extracted SVs onto the surface of the active zone protein condensate. We further show that the Trk-fused gene, TFG, also participates in COPII vesicle trafficking from ER to the ER-Golgi intermediate compartment via phase separation. Thus, phase separation may play a general role in short-distance, directional vesicle transport in cells.
除了分子马达介导的长距离运输外,细胞囊泡还需要以明确的方向进行短距离移动,以满足亚细胞区室的功能需求,但机制未知。这种短距离囊泡运输不涉及分子马达。本研究证明,使用突触囊泡(SV)运输作为范例,突触蛋白与囊泡的相分离可以促进不同突触前布顿子区室之间受调节的定向囊泡运输。具体来说,一个大的卷曲螺旋支架蛋白Piccolo,响应Ca2+并通过其C2A结构域介导的Ca2+感应,可以从突触蛋白簇的储备池凝结物中提取SV,并将提取的SV沉积到活性区蛋白凝结物的表面上。我们进一步表明,Trk融合基因TFG也参与通过相分离从ER到ER-高尔基体中间室的COPII囊泡运输。因此,相分离可能在细胞内短距离定向囊泡运输中发挥普遍作用。
5.Flexible scaffold-based cheminformatics approach for polypharmacological drug design
用于多药理学药物设计的基于灵活支架的化学信息学方法

Effective treatments for complex central nervous system (CNS) disorders require drugs with polypharmacology and multifunctionality, yet designing such drugs remains a challenge. Here, we present a flexible scaffold-based cheminformatics approach (FSCA) for the rational design of polypharmacological drugs. FSCA involves fitting a flexible scaffold to different receptors using different binding poses, as exemplified by IHCH-7179, which adopted a “bending-down” binding pose at 5-HT2AR to act as an antagonist and a “stretching-up” binding pose at 5-HT1AR to function as an agonist. IHCH-7179 demonstrated promising results in alleviating cognitive deficits and psychoactive symptoms in mice by blocking 5-HT2AR for psychoactive symptoms and activating 5-HT1AR to alleviate cognitive deficits. By analyzing aminergic receptor structures, we identified two featured motifs, the “agonist filter” and “conformation shaper,” which determine ligand binding pose and predict activity at aminergic receptors. With these motifs, FSCA can be applied to the design of polypharmacological ligands at other receptors.
复杂中枢神经系统(CNS)疾病的有效治疗需要具有多药理学和多功能性的药物,但设计此类药物仍然是一个挑战。本研究提出了一种灵活的基于支架的化学信息学方法(FSCA),用于合理设计多药理学药物。FSCA涉及使用不同的结合姿势将灵活支架安装到不同的受体上,例如IHCH-7179,它在5-HT2AR处采用“向下弯曲”的结合姿势作为拮抗剂,在5-HT1AR处采用“向上伸展”的结合姿势而作为激动剂发挥作用。IHCH-7179通过阻断5-HT2AR治疗精神症状并激活5-HT1AR缓解认知缺陷,在缓解小鼠认知缺陷和精神症状方面取得了可喜的结果。通过分析胺能受体结构,我们确定了两个特征基序,“激动剂过滤器”和“构象塑造器”,它们决定配体结合姿势并预测胺能受体的活性。有了这些基序,FSCA可应用于其他受体的多药理学配体的设计。
6.Positive selection CRISPR screens reveal a druggable pocket in an oligosaccharyltransferase required for inflammatory signaling to NF-κB
正向选择 CRISPR 筛选揭示了向 NF-κB 发出炎症信号所需的寡糖转移酶中的可药物口袋

Nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) plays roles in various diseases. Many inflammatory signals, such as circulating lipopolysaccharides (LPSs), activate NF-κB via specific receptors. Using whole-genome CRISPR-Cas9 screens of LPS-treated cells that express an NF-κB-driven suicide gene, we discovered that the LPS receptor Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) is specifically dependent on the oligosaccharyltransferase complex OST-A for N-glycosylation and cell-surface localization. The tool compound NGI-1 inhibits OST complexes in vivo, but the underlying molecular mechanism remained unknown. We did a CRISPR base-editor screen for NGI-1-resistant variants of STT3A, the catalytic subunit of OST-A. These variants, in conjunction with cryoelectron microscopy studies, revealed that NGI-1 binds the catalytic site of STT3A, where it traps a molecule of the donor substrate dolichyl-PP-GlcNAc2-Man9-Glc3, suggesting an uncompetitive inhibition mechanism. Our results provide a rationale for and an initial step toward the development of STT3A-specific inhibitors and illustrate the power of contemporaneous base-editor and structural studies to define drug mechanism of action.
核因子κB(NF-κB)在多种疾病中发挥作用。许多炎症信号,例如循环脂多糖(LPS),通过特定受体激活NF-κB。通过对表达NF-κB驱动自杀基因的LPS处理细胞进行全基因组CRISPR-Cas9筛选,我们发现LPS受体Toll样受体4(TLR4)特异性依赖于寡糖转移酶复合物OST-A以进行N-糖基化和细胞表面定位。工具化合物NGI-1在体内抑制OST复合物,但潜在的分子机制仍不清楚。我们对STT3A(OST-A的催化亚基)的NGI-1抗性变体进行了CRISPR碱基编辑器筛选。这些变体与冷冻电子显微镜研究相结合,揭示了NGI-1结合了STT3A的催化位点,它在该位点捕获了供体底物dolichyl-PP-GlcNAc2-Man9-Glc3的分子,表明了一种非竞争性抑制机制。我们的结果为开发STT3A特异性抑制剂提供了基本原理并迈出了第一步,并说明了同期碱基编辑器和结构研究在定义药物作用机制方面的作用。
7.NINJ1 mediates plasma membrane rupture by cutting and releasing membrane disks
NINJ1通过切割和释放膜盘介导质膜破裂

The membrane protein NINJ1 mediates plasma membrane rupture in pyroptosis and other lytic cell death pathways. Here, we report the cryo-EM structure of a NINJ1 oligomer segmented from NINJ1 rings. Each NINJ1 subunit comprises amphipathic (⍺1, ⍺2) and transmembrane (TM) helices (⍺3, ⍺4) and forms a chain of subunits, mainly by the TM helices and ⍺1. ⍺3 and ⍺4 are kinked, and the Gly residues are important for function. The NINJ1 oligomer possesses a concave hydrophobic side that should face the membrane and a convex hydrophilic side formed by ⍺1 and ⍺2, presumably upon activation. This structural observation suggests that NINJ1 can form membrane disks, consistent with membrane fragmentation by recombinant NINJ1. Live-cell and super-resolution imaging uncover ring-like structures on the plasma membrane that are released into the culture supernatant. Released NINJ1 encircles a membrane inside, as shown by lipid staining. Therefore, NINJ1-mediated membrane disk formation is different from gasdermin-mediated pore formation, resulting in membrane loss and plasma membrane rupture.
膜蛋白NINJ1在焦亡和其他裂解细胞死亡途径中介导质膜破裂。本研究报告了从NINJ1环切割的NINJ1寡聚物的冷冻电镜结构。每个NINJ1亚基均包含两性螺旋(⍺1、⍺2)和跨膜(TM)螺旋(⍺3、⍺4),并形成亚基链,主要由TM螺旋和⍺1组成。⍺3和⍺4是扭结的,甘氨酸残基对于功能很重要。NINJ1寡聚物具有应面向膜的凹疏水侧和由⍺1和⍺2形成的凸亲水侧(可能是在激活后)。这一结构观察表明NINJ1可以形成膜盘,与重组NINJ1的膜破裂作用一致。活细胞和超分辨率成像揭示了质膜上的环状结构,这些结构被释放到培养物上清液中。脂质染色显示,释放的NINJ1包围内部膜。因此,NINJ1介导的膜盘形成不同会导致膜损失和质膜破裂的gasdermin家族蛋白介导的孔形成。
8.RNA genome packaging and capsid assembly of bluetongue virus visualized in host cells
在宿主细胞中可视化蓝舌病毒的 RNA 基因组包装和衣壳组装

Unlike those of double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), single-stranded DNA (ssDNA), and ssRNA viruses, the mechanism of genome packaging of dsRNA viruses is poorly understood. Here, we combined the techniques of high-resolution cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM), cellular cryoelectron tomography (cryo-ET), and structure-guided mutagenesis to investigate genome packaging and capsid assembly of bluetongue virus (BTV), a member of the Reoviridae family of dsRNA viruses. A total of eleven assembly states of BTV capsid were captured, with resolutions up to 2.8 Å, with most visualized in the host cytoplasm. ATPase VP6 was found underneath the vertices of capsid shell protein VP3 as an RNA-harboring pentamer, facilitating RNA packaging. RNA packaging expands the VP3 shell, which then engages middle- and outer-layer proteins to generate infectious virions. These revealed “duality” characteristics of the BTV assembly mechanism reconcile previous contradictory co-assembly and core-filling models and provide insights into the mysterious RNA packaging and capsid assembly of Reoviridae members and beyond.
与双链DNA(dsDNA)、单链DNA(ssDNA)和ssRNA病毒不同,dsRNA病毒的基因组包装机制知之甚少。本研究结合了高分辨率冷冻电子显微镜(cryo-EM)、细胞冷冻电子断层扫描(cryo-ET)和结构引导诱变技术来研究蓝舌病毒(BTV,dsRNA病毒呼肠孤病毒科的成员)的基因组包装和衣壳组装。总共捕获了BTV衣壳的11种组装状态,分辨率高达2.8Å,大部分在宿主细胞质中可见。在衣壳蛋白VP3的顶点下方发现了APT酶VP6,它是一种含有RNA的五聚体,有助于RNA包装。RNA包装扩展了VP3外壳,其随后与中层和外层蛋白质结合以产生感染性病毒粒子。这些揭示的BTV组装机制的“二元性”特征调和了先前相互矛盾的共组装和核心填充模型,并为呼肠孤病毒科成员及其他成员的神秘RNA包装和衣壳组装提供了见解。
9.The SPATA5-SPATA5L1 ATPase complex directs replisome proteostasis to ensure genome integrity
SPATA5-SPATA5L1 ATP酶复合物指导复制体蛋白稳态以确保基因组完整性

Ubiquitin-dependent unfolding of the CMG helicase by VCP/p97 is required to terminate DNA replication. Other replisome components are not processed in the same fashion, suggesting that additional mechanisms underlie replication protein turnover. Here, we identify replisome factor interactions with a protein complex composed of AAA+ ATPases SPATA5-SPATA5L1 together with heterodimeric partners C1orf109-CINP (55LCC). An integrative structural biology approach revealed a molecular architecture of SPATA5-SPATA5L1 N-terminal domains interacting with C1orf109-CINP to form a funnel-like structure above a cylindrically shaped ATPase motor. Deficiency in the 55LCC complex elicited ubiquitin-independent proteotoxicity, replication stress, and severe chromosome instability. 55LCC showed ATPase activity that was specifically enhanced by replication fork DNA and was coupled to cysteine protease-dependent cleavage of replisome substrates in response to replication fork damage. These findings define 55LCC-mediated proteostasis as critical for replication fork progression and genome stability and provide a rationale for pathogenic variants seen in associated human neurodevelopmental disorders.
VCP/p97引起的CMG解旋酶的泛素依赖性解折叠是终止DNA复制所必需的。其他复制体成分的加工方式不同,这表明复制蛋白周转背后有其他机制。本研究确定了复制体因子与由AAA+ATP酶SPATA5-SPATA5L1以及异二聚体伙伴C1orf109-CINP(55LCC)组成的蛋白质复合物的相互作用。综合结构生物学方法揭示了SPATA5-SPATA5L1的N末端结构域与C1orf109-CINP相互作用以在圆柱形ATP酶马达上方形成漏斗状结构的分子结构。55LCC复合体的缺陷会引发不依赖于泛素的蛋白毒性、复制应激和严重的染色体不稳定。55LCC显示出通过复制叉DNA特异性增强的ATP酶活性,并与复制叉损伤响应的复制体底物的半胱氨酸蛋白酶依赖性裂解相结合,以应对复制叉损伤。这些发现将55LCC介导的蛋白质稳态定义为复制叉进展和基因组稳定性的关键,并为相关人类神经发育障碍中发现的致病变异提供了基本原理。
10.A glycolytic metabolite bypasses “two-hit” tumor suppression by BRCA2
一种糖酵解代谢物可绕过 BRCA2 对肿瘤的的“二次打击”抑制

Knudson's "two-hit" paradigm posits that carcinogenesis requires inactivation of both copies of an autosomal tumor suppressor gene. Here, we report that the glycolytic metabolite methylglyoxal (MGO) transiently bypasses Knudson's paradigm by inactivating the breast cancer suppressor protein BRCA2 to elicit a cancer-associated, mutational single-base substitution (SBS) signature in nonmalignant mammary cells or patient-derived organoids. Germline monoallelic BRCA2 mutations predispose to these changes. An analogous SBS signature, again without biallelic BRCA2 inactivation, accompanies MGO accumulation and DNA damage in Kras-driven, Brca2-mutant murine pancreatic cancers and human breast cancers. MGO triggers BRCA2 proteolysis, temporarily disabling BRCA2's tumor suppressive functions in DNA repair and replication, causing functional haploinsufficiency. Intermittent MGO exposure incites episodic SBS mutations without permanent BRCA2 inactivation. Thus, a metabolic mechanism wherein MGO-induced BRCA2 haploinsufficiency transiently bypasses Knudson's two-hit requirement could link glycolysis activation by oncogenes, metabolic disorders, or dietary challenges to mutational signatures implicated in cancer evolution.
Knudson的“双重打击”(二次突变)范式认为,致癌需要常染色体肿瘤抑制基因的两个拷贝都失活。在此,我们报告糖酵解代谢物甲基乙二醛(MGO)通过灭活乳腺癌抑制蛋白BRCA2暂时绕过Knudson的范式,从而在非恶性乳腺细胞或患者来源的类器官中引发癌症相关的突变单碱基替换(SBS)特征。生殖系单等位基因BRCA2突变易导致这些变化。在Kras驱动的Brca2突变小鼠胰腺癌和人类乳腺癌中,类似的SBS特征(同样没有双等位基因BRCA2失活)伴随着MGO积累和DNA损伤。MGO触发BRCA2蛋白水解,暂时禁用BRCA2在DNA修复和复制中的肿瘤抑制功能,导致功能性单倍体剂量不足。间歇性MGO暴露会引发偶发性SBS突变,但不会导致BRCA2永久失活。因此,MGO诱导的BRCA2单倍体剂量不足暂时绕过Knudson的两次打击要求的代谢机制可能会将癌基因、代谢紊乱或饮食挑战引起的糖酵解激活与癌症进化中涉及的突变特征联系起来。
11.Cancer SLC6A6-mediated taurine uptake transactivates immune checkpoint genes and induces exhaustion in CD8+ T cells
癌症 SLC6A6 介导的牛磺酸摄取反式激活免疫检查点基因并诱导 CD8+ T 细胞耗竭

Taurine is used to bolster immunity, but its effects on antitumor immunity are unclear. Here, we report that cancer-related taurine consumption causes T cell exhaustion and tumor progression. The taurine transporter SLC6A6 is correlated with aggressiveness and poor outcomes in multiple cancers. SLC6A6-mediated taurine uptake promotes the malignant behaviors of tumor cells but also increases the survival and effector function of CD8+ T cells. Tumor cells outcompete CD8+ T cells for taurine by overexpressing SLC6A6, which induces T cell death and malfunction, thereby fueling tumor progression. Mechanistically, taurine deficiency in CD8+ T cells increases ER stress, promoting ATF4 transcription in a PERK-JAK1-STAT3 signaling-dependent manner. Increased ATF4 transactivates multiple immune checkpoint genes and induces T cell exhaustion. In gastric cancer, we identify a chemotherapy-induced SP1-SLC6A6 regulatory axis. Our findings suggest that tumoral-SLC6A6-mediated taurine deficiency promotes immune evasion and that taurine supplementation reinvigorates exhausted CD8+ T cells and increases the efficacy of cancer therapies.
牛磺酸用于增强免疫力,但其对抗肿瘤免疫力的影响尚不清楚。在此,我们报告与癌症相关的牛磺酸消耗会导致T细胞耗竭和肿瘤进展。牛磺酸转运蛋白SLC6A6与多种癌症的侵袭性和不良预后相关。SLC6A6介导的牛磺酸摄取促进肿瘤细胞的恶性行为,但也增加CD8+T细胞的存活和效应功能。肿瘤细胞通过过度表达SLC6A6来与CD8+T细胞争夺牛磺酸,从而诱导T细胞死亡和功能障碍,促进肿瘤进展。从机制上讲,CD8+T细胞中的牛磺酸缺乏会增加ER应激,以PERK-JAK1-STAT3信号依赖的方式促进ATF4转录。ATF4增加会反式激活多个免疫检查点基因并诱导T细胞耗竭。在胃癌中,我们发现了化疗诱导的SP1-SLC6A6调节轴。我们的研究结果表明,肿瘤SLC6A6介导的牛磺酸缺乏会促进免疫逃避,而补充牛磺酸可以重振耗竭的CD8+T细胞并提高癌症治疗的功效。
12.ITPRIPL1 binds CD3ε to impede T cell activation and enable tumor immune evasion
ITPRIPL1 结合 CD3ε 阻止 T 细胞激活并实现肿瘤免疫逃避

Cancer immunotherapy has transformed treatment possibilities, but its effectiveness differs significantly among patients, indicating the presence of alternative pathways for immune evasion. Here, we show that ITPRIPL1 functions as an inhibitory ligand of CD3ε, and its expression inhibits T cells in the tumor microenvironment. The binding of ITPRIPL1 extracellular domain to CD3ε on T cells significantly decreased calcium influx and ZAP70 phosphorylation, impeding initial T cell activation. Treatment with a neutralizing antibody against ITPRIPL1 restrained tumor growth and promoted T cell infiltration in mouse models across various solid tumor types. The antibody targeting canine ITPRIPL1 exhibited notable therapeutic efficacy against naturally occurring tumors in pet clinics. These findings highlight the role of ITPRIPL1 (or CD3L1, CD3ε ligand 1) in impeding T cell activation during the critical “signal one” phase. This discovery positions ITPRIPL1 as a promising therapeutic target against multiple tumor types.
癌症免疫疗法改变了治疗的可能性,但其有效性在患者之间存在显着差异,表明存在免疫逃避的替代途径。本研究证明ITPRIPL1作为CD3ε的抑制性配体发挥作用,其表达可以抑制肿瘤微环境中的T细胞。ITPRIPL1胞外结构域与T细胞上CD3ε的结合显著降低了钙流入和ZAP70磷酸化,从而阻碍了初始T细胞激活。在各种类型的实体瘤小鼠模型中,使用针对ITPRIPL1的中和抗体进行治疗可抑制肿瘤生长并促进T细胞浸润。针对犬类ITPRIPL1的抗体在宠物诊所中对自然发生的肿瘤表现出显著的治疗效果。这些发现强调了ITPRIPL1(或CD3L1、CD3ε配体1)在关键的“信号一”阶段阻碍T细胞激活的作用。这一发现使ITPRIPL1成为针对多种肿瘤类型的有前景的治疗靶点。
May 09, 2024 Volume 187 Issue 10 p2343-2598
在2024年5月9日,共发表22篇文章,其中包括1篇perspective,10篇Articles,3篇Resources, 1篇correction。
1.BCAA-nitrogen flux in brown fat controls metabolic health independent of thermogenesis
棕色脂肪中的BCAA氮通量控制代谢健康且与产热无关

Brown adipose tissue (BAT) is best known for thermogenesis. Rodent studies demonstrated that enhanced BAT thermogenesis is tightly associated with increased energy expenditure, reduced body weight, and improved glucose homeostasis. However, human BAT is protective against type 2 diabetes, independent of body weight. The mechanism underlying this dissociation remains unclear. Here, we report that impaired mitochondrial catabolism of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) in BAT, by deleting mitochondrial BCAA carriers (MBCs), caused systemic insulin resistance without affecting energy expenditure and body weight. Brown adipocytes catabolized BCAA in the mitochondria as nitrogen donors for the biosynthesis of non-essential amino acids and glutathione. Impaired mitochondrial BCAA-nitrogen flux in BAT resulted in increased oxidative stress, decreased hepatic insulin signaling, and decreased circulating BCAA-derived metabolites. A high-fat diet attenuated BCAA-nitrogen flux and metabolite synthesis in BAT, whereas cold-activated BAT enhanced the synthesis. This work uncovers a metabolite-mediated pathway through which BAT controls metabolic health beyond thermogenesis.
棕色脂肪组织(BAT)以产热作用而闻名。啮齿动物研究表明,BAT产热作用的增强与能量消耗的增加、体重的减轻和葡萄糖稳态的改善密切相关。然而,人类BAT具有预防2型糖尿病的作用,与体重无关。这种BAT与体重解离的机制尚不清楚。本研究发现通过删除线粒体BCAA载体(MBC)引起的BAT中支链氨基酸(BCAA)的线粒体分解代谢受损,会导致全身胰岛素抵抗,而不影响能量消耗和体重。棕色脂肪细胞在线粒体中分解代谢支链氨基酸,作为非必需氨基酸和谷胱甘肽生物合成的氮供体。BAT中线粒体BCAA氮通量受损会导致氧化应激增加、肝脏胰岛素信号传导减少以及循环BCAA衍生代谢物减少。高脂肪饮食减弱了BAT中的BCAA氮通量和代谢物合成,而冷刺激激活的BAT则增强了合成。这项工作揭示了代谢物介导的途径,BAT通过该途径控制产热之外的代谢健康。
2.Alanyl-tRNA synthetase, AARS1, is a lactate sensor and lactyltransferase that lactylates p53 and contributes to tumorigenesis
丙氨酰-tRNA 合成酶 (AARS1) 是一种乳酸传感器和乳酰转移酶,可乳酰化 p53 并有助于肿瘤发生

Lysine lactylation is a post-translational modification that links cellular metabolism to protein function. Here, we find that AARS1 functions as a lactate sensor that mediates global lysine lacylation in tumor cells. AARS1 binds to lactate and catalyzes the formation of lactate-AMP, followed by transfer of lactate to the lysince acceptor residue. Proteomics studies reveal a large number of AARS1 targets, including p53 where lysine 120 and lysine 139 in the DNA binding domain are lactylated. Generation and utilization of p53 variants carrying constitutively lactylated lysine residues revealed that AARS1 lactylation of p53 hinders its liquid-liquid phase separation, DNA binding, and transcriptional activation. AARS1 expression and p53 lacylation correlate with poor prognosis among cancer patients carrying wild type p53. β-alanine disrupts lactate binding to AARS1, reduces p53 lacylation, and mitigates tumorigenesis in animal models. We propose that AARS1 contributes to tumorigenesis by coupling tumor cell metabolism to proteome alteration.
赖氨酸乳酰化是一种翻译后修饰,可以将细胞代谢与蛋白质功能联系起来。本研究发现AARS1作为乳酸传感器发挥作用,介导肿瘤细胞中的整体赖氨酸酰化。AARS1与乳酸结合并催化乳酸-AMP的形成,然后将乳酸转移至赖氨酸受体残基。蛋白质组学研究揭示了大量AARS1靶标,包括p53,其DNA结合域中的赖氨酸120和赖氨酸139被乳酰化。构建携带组成型乳酰化赖氨酸残基的p53变体,随后用其进行实验,结果显示p53的AARS1乳酰化阻碍了其液-液相分离、DNA结合和转录激活。在携带野生型p53的癌症患者中,AARS1表达和p53乳酰化与不良预后相关。β-丙氨酸破坏乳酸与AARS1的结合,减少p53乳酰化,并减轻动物模型中的肿瘤发生。我们认为AARS1通过将肿瘤细胞代谢与蛋白质组改变耦合起来而促进肿瘤发生。
3.Evasion of NKG2D-mediated cytotoxic immunity by sarbecoviruses
沙贝病毒逃避 NKG2D 介导的细胞毒性免疫

SARS-CoV-2 and other sarbecoviruses continue to threaten humanity, highlighting the need to characterize common mechanisms of viral immune evasion for pandemic preparedness. Cytotoxic lymphocytes are vital for antiviral immunity and express NKG2D, an activating receptor conserved among mammals that recognizes infection-induced stress ligands (e.g., MIC-A/B). We found that SARS-CoV-2 evades NKG2D recognition by surface downregulation of MIC-A/B via shedding, observed in human lung tissue and COVID-19 patient serum. Systematic testing of SARS-CoV-2 proteins revealed that ORF6, an accessory protein uniquely conserved among sarbecoviruses, was responsible for MIC-A/B downregulation via shedding. Further investigation demonstrated that natural killer (NK) cells efficiently killed SARS-CoV-2-infected cells and limited viral spread. However, inhibition of MIC-A/B shedding with a monoclonal antibody, 7C6, further enhanced NK-cell activity toward SARS-CoV-2-infected cells. Our findings unveil a strategy employed by SARS-CoV-2 to evade cytotoxic immunity, identify the culprit immunevasin shared among sarbecoviruses, and suggest a potential novel antiviral immunotherapy.
SARS-CoV-2和其他沙贝病毒继续威胁着人类,提示需要确定病毒免疫逃避的常见机制,以防备大流行。细胞毒性淋巴细胞对于抗病毒免疫至关重要,其可以表达NKG2D,是哺乳动物中保守的一种激活受体,可识别感染诱导的应激配体(例如MIC-A/B)。我们在人肺组织和COVID-19患者血清中观察到,SARS-CoV-2通过脱落而下调表面MIC-A/B的表达来逃避NKG2D识别。对SARS-CoV-2蛋白的系统分析表明,ORF6(一种在冠状病毒中独特保守的辅助蛋白)通过脱落而导致MIC-A/B下调。进一步的研究表明,自然杀伤(NK)细胞可以有效杀死SARS-CoV-2感染的细胞并限制病毒传播。然而,用单克隆抗体7C6抑制MIC-A/B脱落,进一步增强了NK细胞对SARS-CoV-2感染细胞的活性。我们的研究结果揭示了SARS-CoV-2用来逃避细胞毒性免疫的策略,识别了沙贝病毒之间共有的罪魁祸首免疫血管素,并提出了一种潜在的新型抗病毒免疫疗法。
4.Chromatin context-dependent regulation and epigenetic manipulation of prime editing
染色质上下文依赖性调控和先导编辑的表观遗传操作

We set out to exhaustively characterize the impact of the cis-chromatin environment on prime editing, a precise genome engineering tool. Using a highly sensitive method for mapping the genomic locations of randomly integrated reporters, we discover massive position effects, exemplified by editing efficiencies ranging from ∼0% to 94% for an identical target site and edit. Position effects on prime editing efficiency are well predicted by chromatin marks, e.g., positively by H3K79me2 and negatively by H3K9me3. Next, we developed a multiplex perturbational framework to assess the interaction of trans-acting factors with the cis-chromatin environment on editing outcomes. Applying this framework to DNA repair factors, we identify HLTF as a context-dependent repressor of prime editing. Finally, several lines of evidence suggest that active transcriptional elongation enhances prime editing. Consistent with this, we show we can robustly decrease or increase the efficiency of prime editing by preceding it with CRISPR-mediated silencing or activation, respectively.
我们着手详尽地描述顺式染色质环境对先导编辑(一种精确的基因组工程工具)的影响。使用高度灵敏的方法来绘制随机整合报告基因的基因组位置,我们发现了大量的位置效应,例如对于相同的目标位点和编辑,编辑效率范围从~0%到94%。染色质标记可以很好地预测位置对先导编辑效率的影响,例如H3K79me2的正效应和H3K9me3的负效应。接下来,我们开发了一个多重扰动框架来评估反式作用因子与顺式染色质环境对编辑结果的相互作用。将此框架应用于DNA修复因子,我们将HLTF确定为先导编辑的上下文依赖性抑制因子。最后,一些证据表明主动转录延伸增强了先导编辑。与此一致的是,我们表明,通过在先导编辑之前分别进行CRISPR介导的沉默或激活,可以显著降低或提高引物编辑的效率。
5.Tracing the origin of alveolar stem cells in lung repair and regeneration
追踪肺泡干细胞在肺修复和再生中的起源

Alveolar type 2 (AT2) cells are stem cells of the alveolar epithelia. Previous genetic lineage tracing studies reported multiple cellular origins for AT2 cells after injury. However, conventional lineage tracing based on Cre-loxP has the limitation of non-specific labeling. Here, we introduced a dual recombinase-mediated intersectional genetic lineage tracing approach, enabling precise investigation of AT2 cellular origins during lung homeostasis, injury, and repair. We found AT1 cells, being terminally differentiated, did not contribute to AT2 cells after lung injury and repair. Distinctive yet simultaneous labeling of club cells, bronchioalveolar stem cells (BASCs), and existing AT2 cells revealed the exact contribution of each to AT2 cells post-injury. Mechanistically, Notch signaling inhibition promotes BASCs but impairs club cells' ability to generate AT2 cells during lung repair. This intersectional genetic lineage tracing strategy with enhanced precision allowed us to elucidate the physiological role of various epithelial cell types in alveolar regeneration following injury.
肺泡2型(AT2)细胞是肺泡上皮的干细胞。先前的遗传谱系追踪研究报告了损伤后的AT2细胞有多个细胞起源。然而,基于Cre-loxP的传统谱系追踪存在非特异性标记的局限性。本研究引入了一种双重组酶介导的交叉遗传谱系追踪方法,能够在肺稳态、损伤和修复过程中精确研究AT2细胞起源。我们发现,终末分化的AT1细胞在肺损伤和修复后对AT2细胞生成没有贡献。对棒状细胞(club cell)、支气管肺泡干细胞(BASC)和现有AT2细胞进行独特但同时的标记,揭示了每种细胞对损伤后AT2细胞的确切贡献。从机制上讲,Notch信号传导抑制会促进BASC,但会削弱棒状细胞(club cell)在肺修复过程中生成AT2细胞的能力。这种具有更高精确度的交叉遗传谱系追踪策略使我们能够阐明各种上皮细胞类型在损伤后肺泡再生中的生理作用。
6.Human iPSC 4R tauopathy model uncovers modifiers of tau propagation
人类 iPSC 4R tau 病模型揭示了 tau 增殖的修饰因子

Tauopathies are age-associated neurodegenerative diseases whose mechanistic underpinnings remain elusive, partially due to a lack of appropriate human models. Here, we engineered human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC)-derived neuronal lines to express 4R Tau and 4R Tau carrying the P301S MAPT mutation when differentiated into neurons. 4R-P301S neurons display progressive Tau inclusions upon seeding with Tau fibrils and recapitulate features of tauopathy phenotypes including shared transcriptomic signatures, autophagic body accumulation, and reduced neuronal activity. A CRISPRi screen of genes associated with Tau pathobiology identified over 500 genetic modifiers of seeding-induced Tau propagation, including retromer VPS29 and genes in the UFMylation cascade. In progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) and Alzheimer's Disease (AD) brains, the UFMylation cascade is altered in neurofibrillary-tangle-bearing neurons. Inhibiting the UFMylation cascade in vitro and in vivo suppressed seeding-induced Tau propagation. This model provides a robust platform to identify novel therapeutic strategies for 4R tauopathy.
Tau蛋白病是一种年龄相关的神经退行性疾病,其机制仍然难以捉摸,部分原因是缺乏合适的人类模型。本研究设计了人类诱导多能干细胞(hiPSC)衍生的神经元系,使其在分化为神经元时表达4RTau和携带P301SMAPT突变的4RTau。4R-P301S神经元在接种Tau原纤维后表现出渐进的Tau包涵体,并表现出了tau蛋白病的表型特征,包括共享转录组特征、自噬体积累和神经元活性降低。对与Tau病理生物学相关的基因进行CRISPRi筛选,发现了超过500个播种诱导Tau进展的遗传修饰因子,包括逆转录酶VPS29和UFMylation级联中的基因。在进行性核上性麻痹(PSP)和阿尔茨海默病(AD)大脑中,带有神经原纤维缠结的神经元中的UFMylation级联发生改变。体外和体内抑制UFMylation级联可抑制播种诱导的Tau增殖。该模型提供了一个强大的平台来确定4R tau蛋白病的新治疗策略。
7.Small-molecule-induced epigenetic rejuvenation promotes SREBP condensation and overcomes barriers to CNS myelin regeneration
小分子诱导的表观遗传学年轻化促进SREBP浓缩并克服中枢神经系统髓磷脂再生的障碍

Remyelination failure in diseases like multiple sclerosis (MS) was thought to involve suppressed maturation of oligodendrocyte precursors; however, oligodendrocytes are present in MS lesions yet lack myelin production. We found that oligodendrocytes in the lesions are epigenetically silenced. Developing a transgenic reporter labeling differentiated oligodendrocytes for phenotypic screening, we identified a small-molecule epigenetic-silencing-inhibitor (ESI1) that enhances myelin production and ensheathment. ESI1 promotes remyelination in animal models of demyelination and enables de novo myelinogenesis on regenerated CNS axons. ESI1 treatment lengthened myelin sheaths in human iPSC-derived organoids and augmented (re)myelination in aged mice while reversing age-related cognitive decline. Multi-omics revealed that ESI1 induces an active chromatin landscape that activates myelinogenic pathways and reprograms metabolism. Notably, ESI1 triggered nuclear condensate formation of master lipid-metabolic regulators SREBP1/2, concentrating transcriptional co-activators to drive lipid/cholesterol biosynthesis. Our study highlights the potential of targeting epigenetic silencing to enable CNS myelin regeneration in demyelinating diseases and aging.
多发性硬化症(MS)等疾病中的髓鞘再生失败被认为与少突胶质细胞前体成熟受抑制有关。然而,多发性硬化症病变中存在少突胶质细胞,但缺乏髓鞘生成。我们发现病变中的少突胶质细胞在表观遗传上被沉默。我们开发了一种标记分化少突胶质细胞的转基因报告基因用于表型筛选,并鉴定出一种可以增强髓磷脂的产生和鞘层形成的小分子表观遗传沉默抑制剂(ESI1)。ESI1促进脱髓鞘动物模型中的髓鞘再生,并使再生中枢神经系统轴突从头开始髓鞘形成。ESI1治疗延长了人类iPSC衍生类器官中的髓鞘,并增强了老年小鼠的髓鞘(再)形成,同时逆转了与年龄相关的认知能力下降。多组学研究表明,ESI1会诱导活跃的染色质景观图,从而激活髓鞘形成途径并重新编程代谢。值得注意的是,ESI1触发了主要脂质代谢调节因子SREBP1/2的核凝聚体形成,集中转录共激活因子来驱动脂质/胆固醇生物合成。我们的研究强调了以表观遗传沉默为靶点,在脱髓鞘疾病和衰老过程中使中枢神经系统髓鞘再生的潜力。
8.Integrative spatial analysis reveals a multi-layered organization of glioblastoma
综合空间分析揭示了胶质母细胞瘤的多层组织结构

Glioma contains malignant cells in diverse states. Here, we combine spatial transcriptomics, spatial proteomics, and computational approaches to define glioma cellular states and uncover their organization. We find three prominent modes of organization. First, gliomas are composed of small local environments, each typically enriched with one major cellular state. Second, specific pairs of states preferentially reside in proximity across multiple scales. This pairing of states is consistent across tumors. Third, these pairwise interactions collectively define a global architecture composed of five layers. Hypoxia appears to drive the layers, as it is associated with a long-range organization that includes all cancer cell states. Accordingly, tumor regions distant from any hypoxic/necrotic foci and tumors that lack hypoxia such as low-grade IDH-mutant glioma are less organized. In summary, we provide a conceptual framework for the organization of cellular states in glioma, highlighting hypoxia as a long-range tissue organizer.
神经胶质瘤包含不同状态的恶性细胞。本研究结合空间转录组学、空间蛋白质组学和计算方法来定义神经胶质瘤细胞状态并揭示其组织结构。我们发现了三种突出的组织模式。首先,神经胶质瘤由小的局部环境组成,每个环境通常富含一种主要的细胞状态。其次,特定的状态对在多个尺度上优先位于邻近区域。这种状态配对在(多个)肿瘤中是一致的。第三,这些成对的相互作用共同定义了一个由五层组成的全局架构。缺氧似乎会驱动细胞层,因为它与包括所有癌细胞状态的远程组织有关。因此,远离任何缺氧/坏死病灶的肿瘤区域和缺乏缺氧的肿瘤(例如低级别IDH突变神经胶质瘤)的组织性较差。总之,我们为神经胶质瘤中细胞状态的组织提供了一个概念框架,强调缺氧作为一种远程组织组织者。
9.Analysis of 3D pathology samples using weakly supervised AI
使用弱监督 AI 分析 3D 病理样本

Human tissue, which is inherently three-dimensional (3D), is traditionally examined through standard-of-care histopathology as limited two-dimensional (2D) cross-sections that can insufficiently represent the tissue due to sampling bias. To holistically characterize histomorphology, 3D imaging modalities have been developed, but clinical translation is hampered by complex manual evaluation and lack of computational platforms to distill clinical insights from large, high-resolution datasets. We present TriPath, a deep-learning platform for processing tissue volumes and efficiently predicting clinical outcomes based on 3D morphological features. Recurrence risk-stratification models were trained on prostate cancer specimens imaged with open-top light-sheet microscopy or microcomputed tomography. By comprehensively capturing 3D morphologies, 3D volume-based prognostication achieves superior performance to traditional 2D slice-based approaches, including clinical/histopathological baselines from six certified genitourinary pathologists. Incorporating greater tissue volume improves prognostic performance and mitigates risk prediction variability from sampling bias, further emphasizing the value of capturing larger extents of heterogeneous morphology.
人体组织本质上是三维 (3D) 的,传统的标准组织病理学检查方法,使用有限的二维 (2D) 横截面进行检查。由于采样偏差,这些横截面不能充分代表人体组织。为了全面表征组织形态学,已经开发了 3D 成像模式,但临床转化受到复杂的人工评估和缺乏从大型高分辨率数据集中提取临床见解的计算平台的阻碍。我们推出了 TriPath,这是一个深度学习平台,用于处理组织体积并根据 3D 形态特征有效预测临床结果。复发风险分层模型是在使用开顶光片显微镜或微型计算机断层扫描成像的前列腺癌标本上进行训练的。通过全面捕获 3D 形态,基于 3D 体积的预测实现了优于传统 2D 切片方法的性能,包括来自六位经过认证的泌尿生殖病理学家的临床/组织病理学基线。纳入更大的组织量可以改善预后性能,并减轻采样偏差造成的风险预测变异性,进一步强调捕获更大范围的异质形态的价值。
10.RNA aggregates harness the danger response for potent cancer immunotherapy
RNA聚集体利用危险反应进行强效的癌症免疫治疗

Cancer immunotherapy remains limited by poor antigenicity and a regulatory tumor microenvironment (TME). Here, we create “onion-like” multi-lamellar RNA lipid particle aggregates (LPAs) to substantially enhance the payload packaging and immunogenicity of tumor mRNA antigens. Unlike current mRNA vaccine designs that rely on payload packaging into nanoparticle cores for Toll-like receptor engagement in immune cells, systemically administered RNA-LPAs activate RIG-I in stromal cells, eliciting massive cytokine/chemokine response and dendritic cell/lymphocyte trafficking that provokes cancer immunogenicity and mediates rejection of both early- and late-stage murine tumor models. In client-owned canines with terminal gliomas, RNA-LPAs improved survivorship and reprogrammed the TME, which became “hot” within days of a single infusion. In a first-in-human trial, RNA-LPAs elicited rapid cytokine/chemokine release, immune activation/trafficking, tissue-confirmed pseudoprogression, and glioma-specific immune responses in glioblastoma patients. These data support RNA-LPAs as a new technology that simultaneously reprograms the TME while eliciting rapid and enduring cancer immunotherapy.
癌症免疫疗法仍然受到抗原性差和调节性肿瘤微环境(TME)的限制。本研究创建了“洋葱状”多层RNA脂质颗粒聚集体(LPAs),以显著增强肿瘤mRNA抗原的有效负载包装和免疫原性。目前的mRNA疫苗设计依赖于将有效负载包装到纳米颗粒核心中以与免疫细胞中的Toll样受体结合,而不同的是,系统全身给药的RNA-LPAs会激活基质细胞中的RIG-I,引发大量细胞因子/趋化因子反应和树突状细胞/淋巴细胞运输,从而引发癌症免疫原性并介导早期和晚期小鼠肿瘤模型的排斥。在客户拥有的患有晚期神经胶质瘤的犬中,RNA-LPAs提高了存活率,并对TME进行了重新编程,使其在单次输注后几天内就变得“热”(热肿瘤)。在一项首次人体试验中,RNA-LPAs在胶质母细胞瘤患者中引发快速细胞因子/趋化因子释放、免疫激活/运输、组织证实的假性进展和胶质瘤特异性免疫反应。这些数据支持RNA-LPAs作为一种新技术,可以在重新编程TME的同时引发快速且持久的癌症免疫治疗。

汇报人: 李俊虹
导师:赵宇教授
审核:任建君 吴桂儀



