
【Cancer cell】2025年4月-2025年5月刊论文导读
期刊介绍:
Cancer Cell创刊于2002年,由CELL PRESS出版商出版,收稿方向涵盖医学-肿瘤学全领域,在行业领域中学术影响力很大,属于TOP期刊,国际一流期刊。审议手稿的主要标准是研究是否在回答与自然发生的癌症有关的重要问题方面取得重大进展。影响因子指数48.8。
2025年4-5月一共发表36篇,包括Commentary 9篇,Preview 5篇,Review 5篇,Article 13篇,Report 1篇,Correction 3篇。

Apr 14, 2025 Volume 43 Issue 4
2025年4月一共发表17篇,包括Editorial 1篇,Commentary 7篇,Review 5篇,Article 4篇。
On the cover: Cancer Cell celebrates five years of transformative progress in bridging foundational cancer biology and clinical oncology (see the editorial by Editor-in-Chief Steve Mao). This issue features insightful reviews, commentaries, and opinion pieces that integrate basic science, translational insights, and clinical advances to unravel the complexities of cancer and drive innovative therapies. Together, we are advancing a multidisciplinary approach to understanding cancer as a systemic disease, fostering collaboration between bench and bedside. Join us in this endeavor as we connect discovery to patient impact and shape the future of cancer research. Cover art by Phillip Krzeminski.
封面介绍:本期《Cancer Cell》庆祝在推动基础癌症生物学与临床肿瘤学融合方面取得的五年重要进展(参见主编Steve Mao的社论)。本期刊登了多篇深具洞见的综述、评论和观点文章,融合基础科学、转化医学和临床进展,致力于揭示癌症的复杂本质并推动创新疗法的诞生。我们正共同推进一种多学科交叉的研究方法,将癌症作为一种系统性疾病进行深入探索,促进实验室与临床的紧密合作。欢迎加入我们的行列,将科学发现转化为患者福祉,共同塑造癌症研究的未来。封面艺术由Phillip Krzeminski创作。
1. Fragmentomics profiling and quantification of plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA enhance prediction of future nasopharyngeal carcinoma
血浆EB病毒DNA的片段组学特征分析与定量有助于提升鼻咽癌未来发病风险的预测能力

香港中文大学
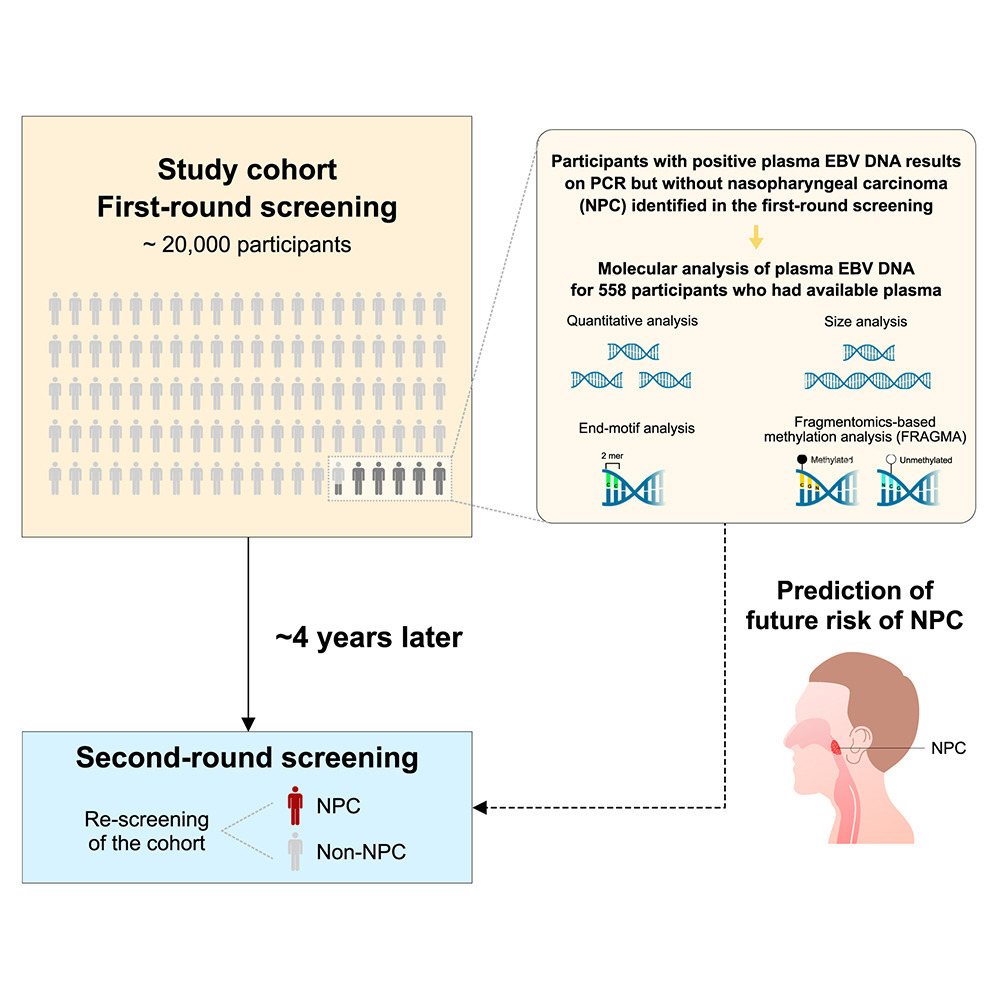
Fragmentomics analysis of plasma autosomal DNA has shown promise in cancer diagnostics. Here we evaluated the clinical utility of plasma Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA fragmentomics analysis for nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) screening. Among our prospective cohort of approximately 20,000 subjects that underwent two rounds of screening, we analyzed the first-round blood samples of subjects who tested positive for EBV DNA via polymerase chain reaction (PCR) (n = 558). We found that those who subsequently developed NPC in the second round exhibited a distinctive mononucleosomal size pattern, an NPC-associated end motif (specifically, a depletion of CC-motif) and aberrations in methylation identified through fragmentomics-based methylation analysis (FRAGMA). Subjects with these aberrant fragmentomics features and higher quantity of EBV DNA had a relative risk of 87.1 times greater for developing NPC in the second round compared to subjects tested negative for EBV DNA on PCR. These results demonstrate plasma DNA fragmentomics could predict future cancer risk.
血浆常染色体DNA的片段组学分析在癌症诊断中展现出良好前景。本研究评估了血浆EB病毒(EBV)DNA片段组学分析在鼻咽癌(NPC)筛查中的临床应用价值。在一项前瞻性队列研究中,约有2万人接受了两轮筛查。该研究对第一轮筛查中通过聚合酶链式反应(PCR)检测EBV DNA阳性的受试者(n = 558)进行了分析。结果发现,在第二轮中发展为鼻咽癌的个体,其血浆中EBV DNA呈现出特征性的单核小体片段分布模式,出现与NPC相关的末端基序(特别是CC基序的缺失),以及在片段组学甲基化分析(FRAGMA)中检测到的异常甲基化特征。具备这些异常片段组学特征且EBV DNA含量较高的个体,其在第二轮发展为鼻咽癌的相对风险比PCR检测为EBV阴性的个体高出87.1倍。研究结果表明,血浆DNA片段组学可用于预测未来罹患癌症的风险。
2. Effective targeting of PDGFRA-altered high-grade glioma with avapritinib
阿伐普替尼靶向治疗PDGFRA突变高级别神经胶质瘤的疗效研究

哈佛大学、麻省总医院、加州大学旧金山分校等
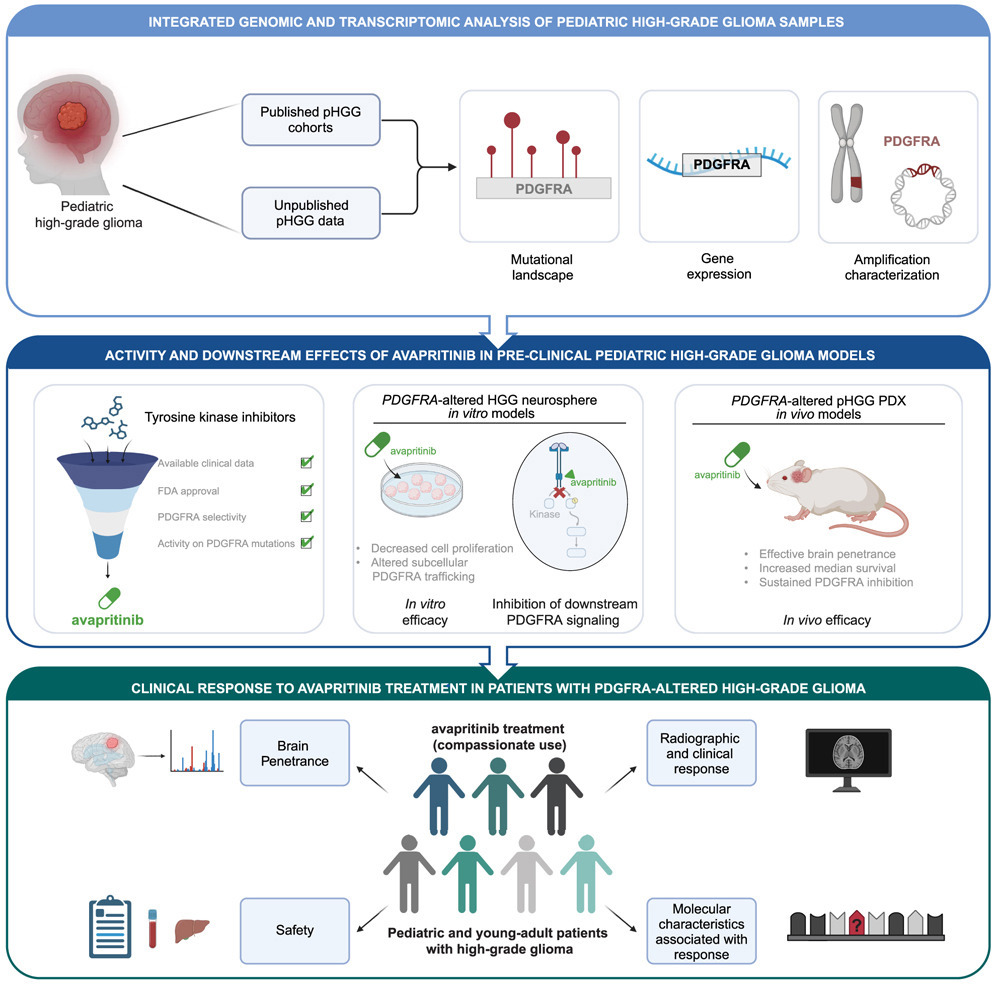
PDGFRA is crucial to tumorigenesis and frequently genomically altered in high-grade glioma (HGG). In a comprehensive dataset of pediatric HGG (n = 261), we detect PDGFRA mutations and/or amplifications in 15% of cases, suggesting PDGFRA as a therapeutic target. We reveal that the PDGFRA/KIT inhibitor avapritinib shows (1) selectivity for PDGFRA inhibition, (2) distinct patterns of subcellular effects, (3) in vitro and in vivo activity in patient-derived HGG models, and (4) effective blood-brain barrier penetration in mice and humans. Furthermore, we report preliminary clinical real-world experience using avapritinib in pediatric and young adult patients with predominantly recurrent/refractory PDGFRA-altered HGG (n = 8). Our early data demonstrate that avapritinib is well tolerated and results in radiographic response in 3/7 cases, suggesting a potential role for avapritinib in the treatment of HGG with specific PDGFRA alterations. Overall, these translational results underscore the therapeutic potential of PDGFRA inhibition with avapritinib in HGG.
PDGFRA在肿瘤发生中发挥关键作用,并在高级别神经胶质瘤(HGG)中常见基因改变。该研究对261例儿童HGG的综合数据集中进行分析,发现15%的病例存在PDGFRA突变和/或扩增,提示PDGFRA是一个具有潜力的治疗靶点。研究显示,PDGFRA/KIT抑制剂阿伐普替尼具有以下特征:(1)对PDGFRA具备高度选择性抑制作用;(2)展现出独特的亚细胞效应模式;(3)在来源于患者的HGG模型中展现出体外和体内活性;(4)在小鼠和人类中均表现出良好的血脑屏障穿透能力。此外,还报告了阿伐普替尼在真实世界中用于治疗以PDGFRA改变为主的复发或难治性儿童及青少年HGG患者(n = 8)的初步临床应用经验。早期数据显示,阿伐普替尼耐受性良好,在7例可评估患者中有3例出现影像学缓解,提示其在治疗特定PDGFRA异常的HGG中具有潜在疗效。总体而言,这些转化研究结果强调了靶向PDGFRA治疗在HGG中的应用前景。
3. Distinct CD8+ T cell dynamics associate with response to neoadjuvant cancer immunotherapies
CD8⁺ T细胞特异性动态变化与新辅助癌症免疫治疗反应相关联

匹兹堡大学等
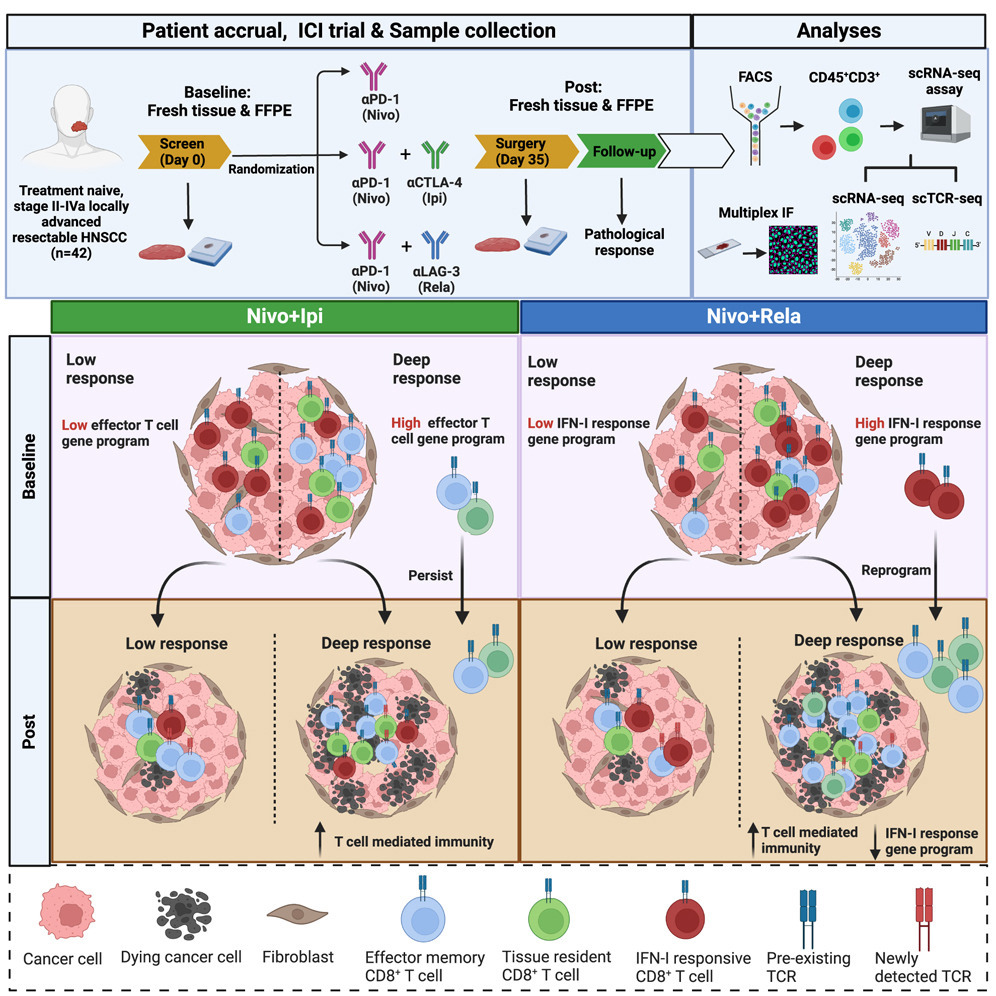
We leverage a clinical trial (NCT04080804) that compared neoadjuvant anti-PD-1, anti-PD-1+CTLA-4, and anti-PD-1+LAG-3 therapies in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients. Combination therapies promote higher pathologic response rates versus monotherapy, and major pathologic response is associated with better survival. To address whether successful immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) regimens act through similar or distinct pathways, we robustly and longitudinally characterize transcriptional and proteomic dynamics of CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) in a clonal manner. Anti-PD-1+LAG-3 reprograms CD8+ TIL with type-I interferon response and exhaustion gene programs into effector memory and resident memory (TEM/TRM). In contrast, anti-PD-1+CTLA-4 activates and expands pre-existing TEM/TRM CD8+ TIL, but does not rejuvenate exhausted phenotypes into T effector cells. Anti-PD-1+LAG-3, but not anti-PD-1+CTLA-4, induces widespread TCR sharing among the different transcriptional states, as well as increased TCR diversity in responding patients. Our data suggest doublet regimen-specific transcriptional and clonal dynamics of tumor-reactive CD8+ T cells.
该研究利用一项临床试验(NCT04080804),比较了新辅助抗PD-1、抗PD-1+CTLA-4、抗PD-1+LAG-3治疗在头颈鳞状细胞癌患者中的效果。联合治疗较单药治疗能显著提高病理反应率,且主要病理反应(MPR)与更佳生存相关。为探究不同免疫检查点抑制剂(ICI)联合方案是否通过相似或不同机制发挥作用,对CD8⁺肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞(TIL)的转录和蛋白组特征进行了克隆水平的纵向分析。研究发现,抗PD-1+LAG-3可将具有I型干扰素应答和耗竭基因特征的CD8⁺ TIL重塑为效应记忆及组织驻留记忆(TEM/TRM)亚型;而抗PD-1+CTLA-4则激活并扩增原有的TEM/TRM亚群,但无法使耗竭表型转化为效应T细胞。值得注意的是,仅抗PD-1+LAG-3能诱导不同转录状态间广泛的TCR克隆共享,并在应答患者中提升TCR多样性。我们的研究表明,不同ICI双联方案在诱导肿瘤反应性CD8⁺ T细胞方面呈现出特异性的转录与克隆动态变化。
4. Proteogenomic characterization of non-functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors unravels clinically relevant subgroups
非功能性胰腺神经内分泌肿瘤的蛋白质组学-基因组学特征揭示具有临床意义的分子亚型

复旦大学附属肿瘤医院、上海药物研究所及生化所等
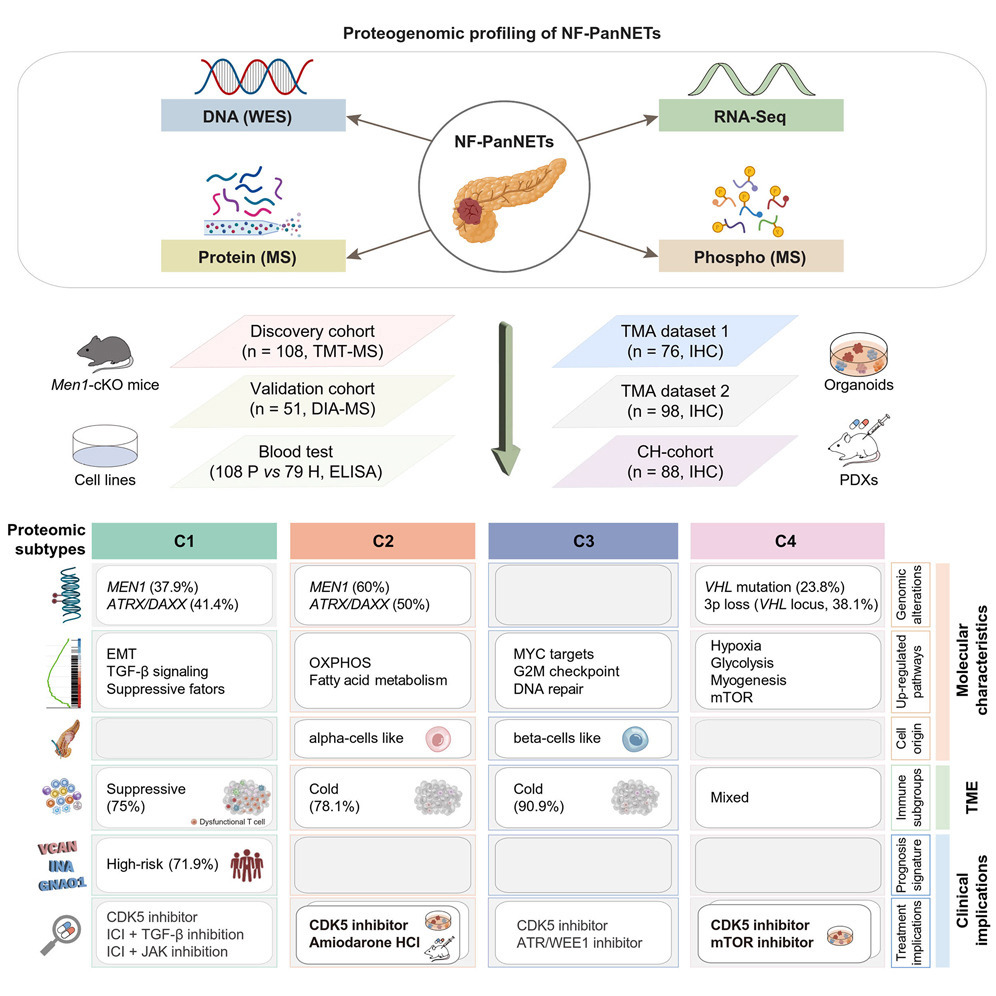
The majority of neuroendocrine neoplasms in pancreas are non-functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (NF-PanNETs), which exhibit a high occurrence of distant metastases with limited therapeutic options. Here, we perform a comprehensive molecular characterization of 108 NF-PanNETs through integrative analysis of genomic, transcriptomic, proteomic, and phosphoproteomic profiles. Proteogenomic analysis provides functional insights into the genomic driver alterations of NF-PanNETs, revealing a potential mediator of MEN1 alterations using Men1-conditional knockout mice. Machine-learning-based modeling uncovers a three-protein signature as an independent prognostic factor, which is validated by an independent external cohort. Proteomic and phosphoproteomic-based stratification identifies four subtypes with distinct molecular characteristics, immune microenvironments, and clinicopathological features. Drug screening using patient-derived tumor organoids identifies cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 5 and Calcium Voltage-Gated Channel Subunit Alpha1 D (CACNA1D) as ubiquitous and subtype-specific targets, respectively, with in vivo validation using xenograft models. Together, our proteogenomic analyses illustrate a comprehensive molecular landscape of NF-PanNETs, revealing biological insights and therapeutic vulnerabilities.
多数胰腺神经内分泌肿瘤(PanNETs)为非功能性类型(NF-PanNETs),其具有较高的远处转移发生率,且有效治疗手段有限。本研究对108例NF-PanNETs进行了全方位分子特征分析,整合了基因组、转录组、蛋白质组及磷酸化蛋白质组的数据。蛋白质组-基因组联合分析揭示了NF-PanNETs中驱动性基因改变的功能机制,并利用MEN1条件性敲除小鼠模型,识别出MEN1突变的潜在调控因子。基于机器学习的模型构建发现了一个由三个蛋白组成的预后特征组合,且该模型在独立外部队列中获得验证。进一步基于蛋白质组和磷酸化组的分型分析将NF-PanNETs划分为四个具有不同分子特征、免疫微环境和临床病理表现的亚型。利用来源于患者的肿瘤类器官进行药物筛选,发现细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶5(CDK5)是广谱靶点,而钙电压门控通道亚单位α1D(CACNA1D)则为特异性亚型靶点,二者均通过异种移植模型获得体内验证。综上,本研究通过蛋白质组-基因组联合分析描绘了NF-PanNETs的全面分子图谱,揭示了其生物学特征与治疗易感性。

May 12, 2025 Volume 43 Issue 5
2025年5月一共发表16篇,包括Commentary 2篇,Preview 5篇,Article 9篇。
On the cover: A traditional Peking opera performance serves as a powerful allegory for nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) treatment. In this artistic representation, four actors symbolize the standard treatment modalities: radiotherapy (RT), induction chemotherapy (GP), immunotherapy (anti-PD-1), and concurrent cisplatin (CC). In a pivotal new act, the CC actor prepares to take a final bow, symbolizing the progression of NPC therapies as CC gives way to innovative strategies. This artistic portrayal highlights a study by Xu et al., which demonstrates that incorporating PD-1 blockade into cisplatin-sparing regimens achieves potent anti-tumor efficacy with reduced toxicity, heralding a new era in NPC treatment. Image credit: Coloring Guangzhou.
封面图:一场传统的京剧表演成为鼻咽癌(NPC)治疗的生动隐喻。在这幅艺术化的演绎中,四位演员象征着标准的治疗手段:放疗(RT)、诱导化疗(GP方案)、免疫治疗(抗PD-1疗法)以及同步顺铂治疗(CC)。在这一关键的新篇章中,扮演CC的演员正准备谢幕,寓意鼻咽癌治疗正从传统的CC方案迈向更具创新性的策略。这一艺术呈现呼应了Xu等人的研究成果:在不含顺铂的治疗方案中引入PD-1抑制剂,能够在显著降低毒性的同时,维持甚至增强抗肿瘤疗效,预示着鼻咽癌治疗新时代的到来。
图片来源:Coloring Guangzhou。
5. Translation dysregulation in cancer as a source for targetable antigens
癌症中的蛋白质翻译失调可作为可靶向抗原的新来源

以色列韦茨曼科学研究、美国斯坦福大学等
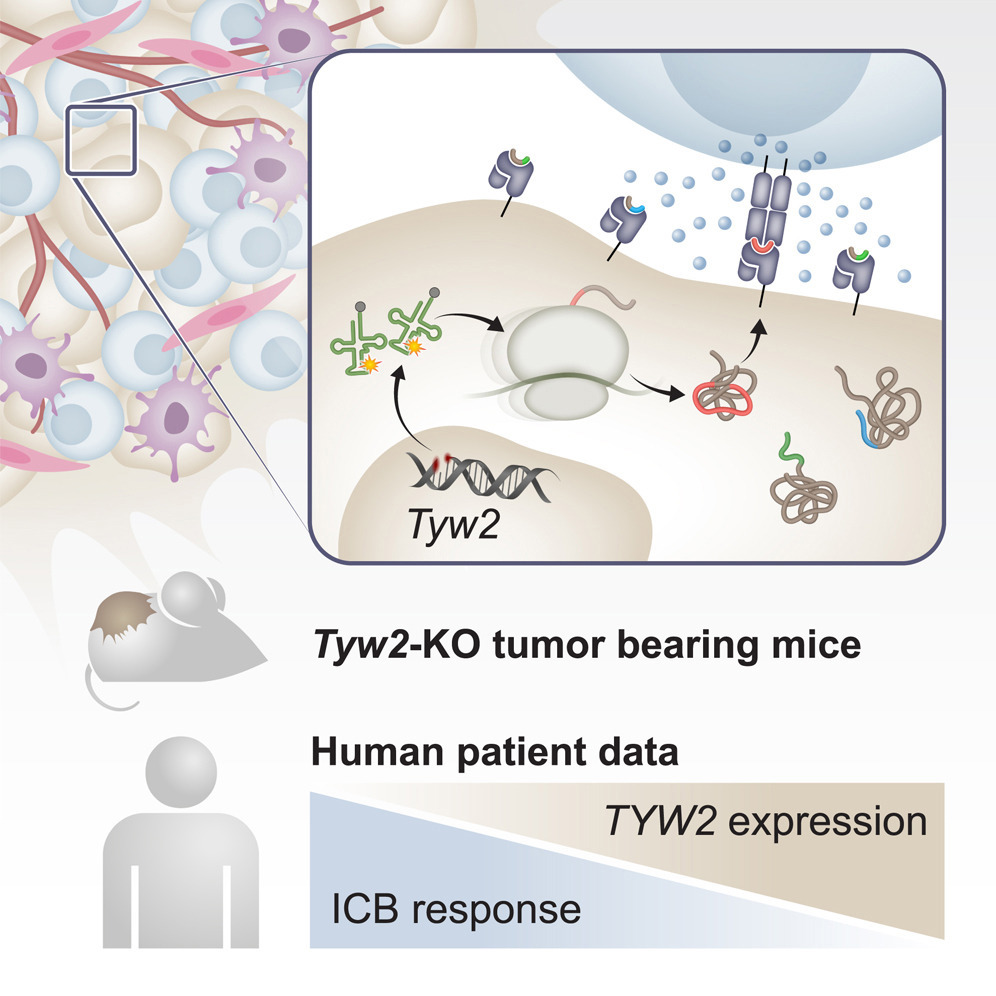
Aberrant peptides presented by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules are targets for tumor eradication, as these peptides can be recognized as foreign by T cells. Protein synthesis in malignant cells is dysregulated, which may result in the generation and presentation of aberrant peptides that can be exploited for T cell-based therapies. To investigate the role of translational dysregulation in immunological tumor control, we disrupt translation fidelity by deleting tRNA wybutosine (yW)-synthesizing protein 2 (TYW2) in tumor cells and characterize the downstream impact on translation fidelity and immunogenicity using immunopeptidomics, genomics, and functional assays. These analyses reveal that TYW2 knockout (KO) cells generate immunogenic out-of-frame peptides. Furthermore, Tyw2 loss increases tumor immunogenicity and leads to anti-programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) checkpoint blockade sensitivity in vivo. Importantly, reduced TYW2 expression is associated with increased response to checkpoint blockade in patients. Together, we demonstrate that defects in translation fidelity drive tumor immunogenicity and may be leveraged for cancer immunotherapy.
由主要组织相容性复合体(MHC)分子呈递的异常肽段可作为肿瘤清除的靶点,因为这些肽段可被T细胞识别为“外来”成分。恶性细胞的蛋白质合成过程通常存在失调,可能导致异常肽段的生成与呈递,从而为T细胞治疗提供潜在靶标。为探究翻译失调在肿瘤免疫控制中的作用,本研究通过敲除编码tRNA wybutosine(yW)合成蛋白的基因 TYW2,人为破坏肿瘤细胞的翻译保真性,并结合免疫肽组学、基因组学及功能实验,评估其对翻译保真性及免疫原性的影响。结果显示,TYW2敲除细胞能产生具有免疫原性的移码(out-of-frame)肽段。此外,Tyw2的缺失增强了肿瘤的免疫原性,并提高其对抗PD-1免疫检查点抑制治疗的敏感性。更重要的是,临床数据表明TYW2表达降低与免疫检查点抑制治疗的更好应答相关。综上,本研究揭示了翻译保真性缺陷可驱动肿瘤免疫原性,并可能成为癌症免疫治疗的新靶点。
6. Small-molecule RNA therapeutics to target prostate cancer
靶向前列腺癌的小分子RNA治疗策略

美国加州大学旧金山分校(UCSF)等
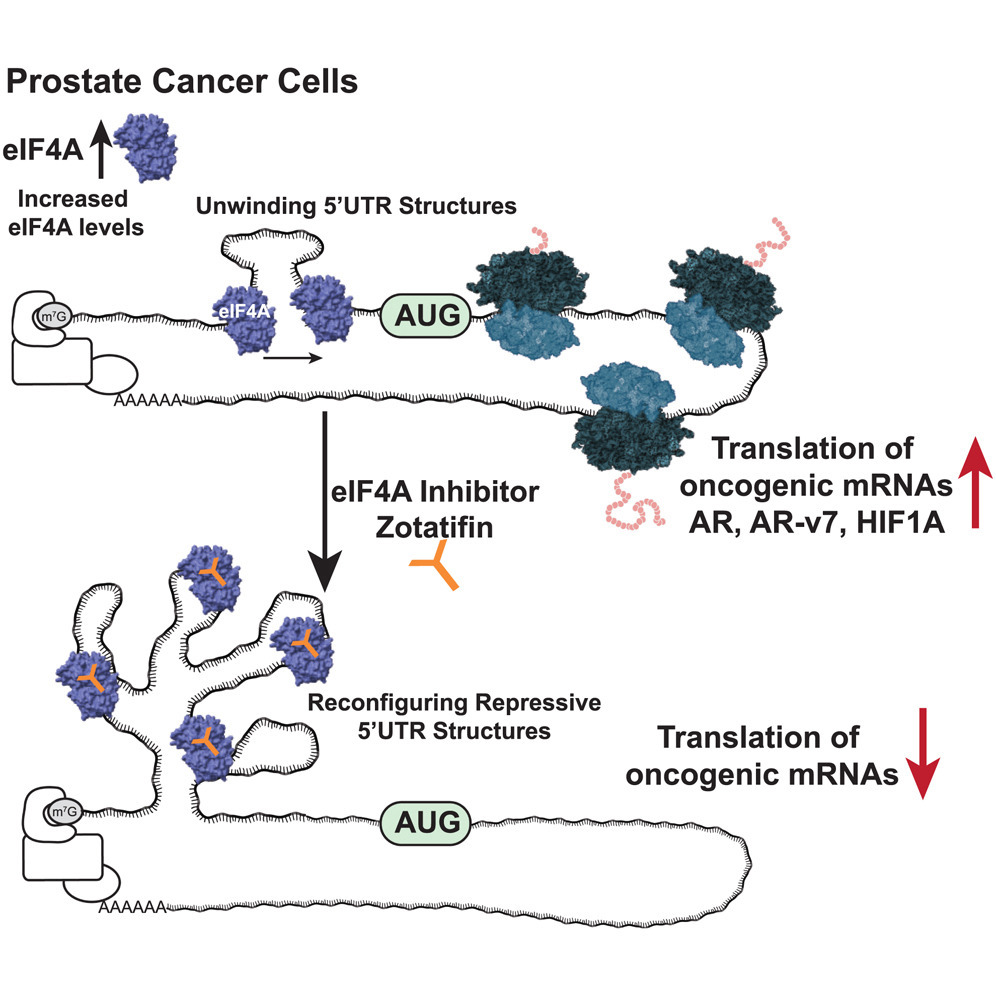
Tuning protein expression by targeting RNA structure using small molecules is an unexplored avenue for cancer treatment. To understand whether this vulnerability could be therapeutically targeted in the most lethal form of prostate cancer, castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC), we use a clinical small molecule, zotatifin, that targets the RNA helicase and translation factor eukaryotic initiation factor 4A (eIF4A). Zotatifin represses tumorigenesis in patient-derived and xenograft models and prolonged survival in vivo alongside hormone therapy. Genome-wide transcriptome, translatome, and proteomic analysis reveals two important translational targets: androgen receptor (AR), a key oncogene in CRPC, and hypoxia-inducible factor 1A (HIF1A), an essential cancer modulator in hypoxia. We solve the structure of the 5′ UTRs of these oncogenic mRNAs and strikingly observe complex structural remodeling of these select mRNAs by this small molecule. Remarkably, tumors treated with zotatifin become more sensitive to anti-androgen therapy and radiotherapy. Therefore, “translatome therapy” provides additional strategies to treat the deadliest cancers.
由通过靶向RNA结构调控蛋白表达的小分子治疗,为癌症治疗开辟了一条尚未深入探索的新途径。为验证这种机制在最具致死性的前列腺癌亚型——去势抵抗性前列腺癌(CRPC)中的治疗潜力,本研究采用临床级小分子药物 zotatifin,其作用靶点为RNA解旋酶兼翻译起始因子 eIF4A。研究发现,zotatifin能够抑制患者来源及异种移植模型中的肿瘤发生,并在联合激素治疗时延长小鼠存活期。通过全基因组转录组、转译组及蛋白质组的联合分析,识别出两个关键的转译调控靶标:雄激素受体(AR) —— CRPC的核心致癌基因,以及缺氧诱导因子1A(HIF1A) —— 缺氧环境中关键的癌症调控因子。研究进一步解析了这些致癌mRNA的5′ UTR结构,并发现zotatifin可引发其结构发生复杂重塑,从而影响其转译效率。值得注意的是,zotatifin处理后的肿瘤对抗雄激素治疗和放疗表现出更高的敏感性。综上所述,本研究提出了“转译组治疗”(translatome therapy)的新概念,为治疗高度致死性的癌症提供了全新的策略。
7. PAI-1-driven SFRP2high cancer-associated fibroblasts hijack the abscopal effect of radioimmunotherapy
PAI-1驱动的SFRP2高表达癌相关成纤维细胞劫持了放射免疫治疗的远隔效应

南方医科大学南方医院等
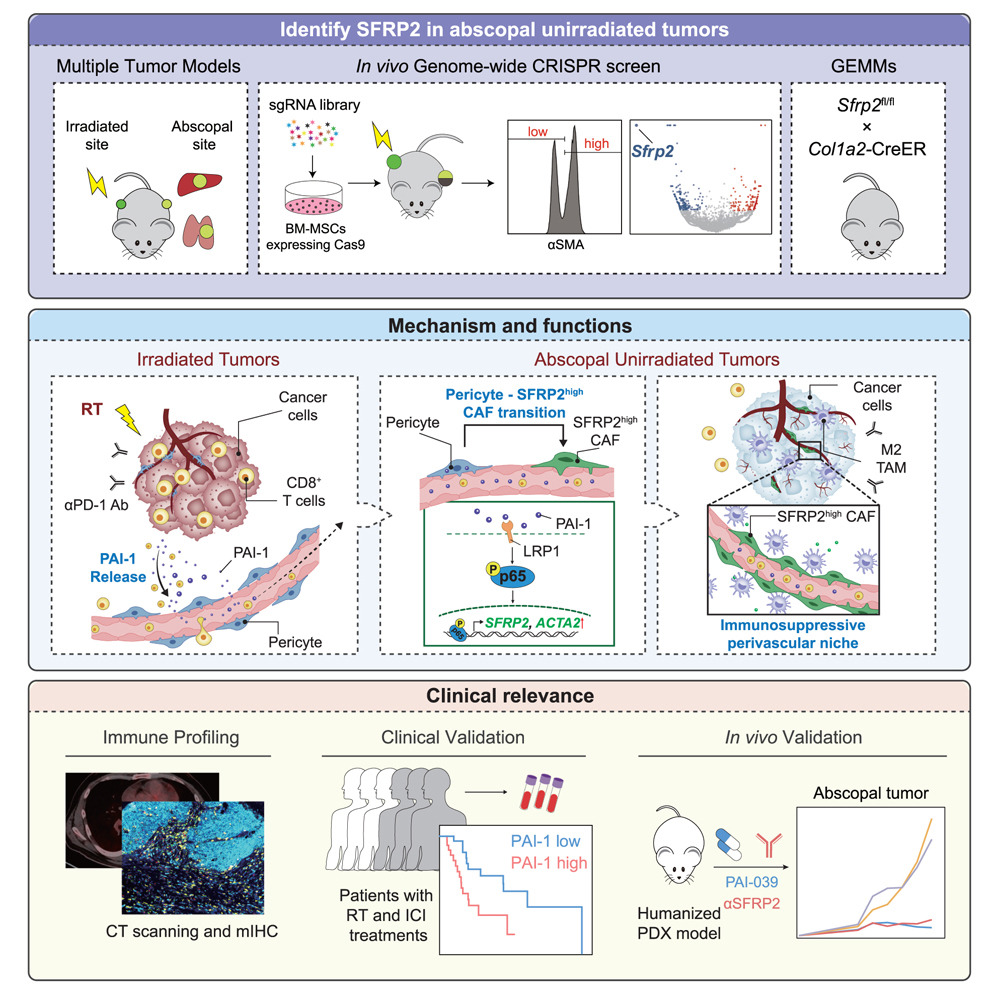
The abscopal effect of radioimmunotherapy, wherein tumor shrinkage occurs beyond the irradiated field, is therapeutically promising but clinically rare. The mechanisms underlying this effect remain elusive. Here, in vivo genome-wide CRISPR screening identifies SFRP2 as a potential stromal regulator of the abscopal effect. SFRP2 exhibits cancer-associated fibroblast (CAF)-specific expression and radioimmunotherapy-mediated upregulation in unirradiated tumors. Conditional Sfrp2 knockout in CAFs boosts the abscopal effect by rewiring the vascular-immune microenvironment to promote CD8+ T cell recruitment to unirradiated tumors. In vivo lineage tracing reveals that elevated SFRP2 correlates with radioimmunotherapy-driven pericyte lineage commitment. Serum proteomics reveals that irradiated-tumor-secreted PAI-1 triggers distant tumor pericyte cell-fate transition into SFRP2high CAFs via the LRP1/p65 axis. Pharmacologically blocking SFRP2 or PAI-1 enhances the abscopal effect in humanized patient-derived xenograft models. Our findings collectively illustrate that PAI-1-induced SFRP2high CAFs serve as critical stromal regulator to hijack the abscopal effect, providing promising targets for enhancing radioimmunotherapy effectiveness.
由放射免疫治疗(radioimmunotherapy)可引发“远隔效应”(abscopal effect),即照射区域外的肿瘤也发生缩小,这一现象在治疗上具有巨大潜力,但临床上却极为罕见,其潜在机制尚不明确。本研究通过体内全基因组CRISPR筛选,鉴定出 SFRP2 是调控远隔效应的重要间质因子。SFRP2在癌相关成纤维细胞(CAF)中呈特异性表达,且在未照射的肿瘤中可被放射免疫治疗诱导上调。条件性敲除CAF中的 Sfrp2 可增强远隔效应,通过重塑血管-免疫微环境,促进CD8⁺ T细胞向未照射肿瘤的募集。体内谱系追踪实验显示,SFRP2升高与放射免疫治疗诱导的周细胞(pericyte)向CAF分化密切相关。血清蛋白质组学分析进一步揭示,被照射肿瘤分泌的PAI-1 可通过 LRP1/p65通路 促使远处肿瘤的周细胞向**SFRP2高表达CAF(SFRP2^high CAFs)**转化。药物抑制SFRP2或PAI-1信号,在人源化患者来源异种移植模型中显著增强远隔效应。综上,该研究发现:PAI-1诱导的SFRP2^high癌相关成纤维细胞是劫持远隔效应的关键间质调控因子,为提高放射免疫治疗疗效提供了新的治疗靶点。
8. AI-driven predictive biomarker discovery with contrastive learning to improve clinical trial outcomes
基于对比学习的AI驱动预测性生物标志物发现助力提升临床试验效果

阿斯利康公司肿瘤研发部肿瘤数据科学团队、坦普斯公司生命科学部门等
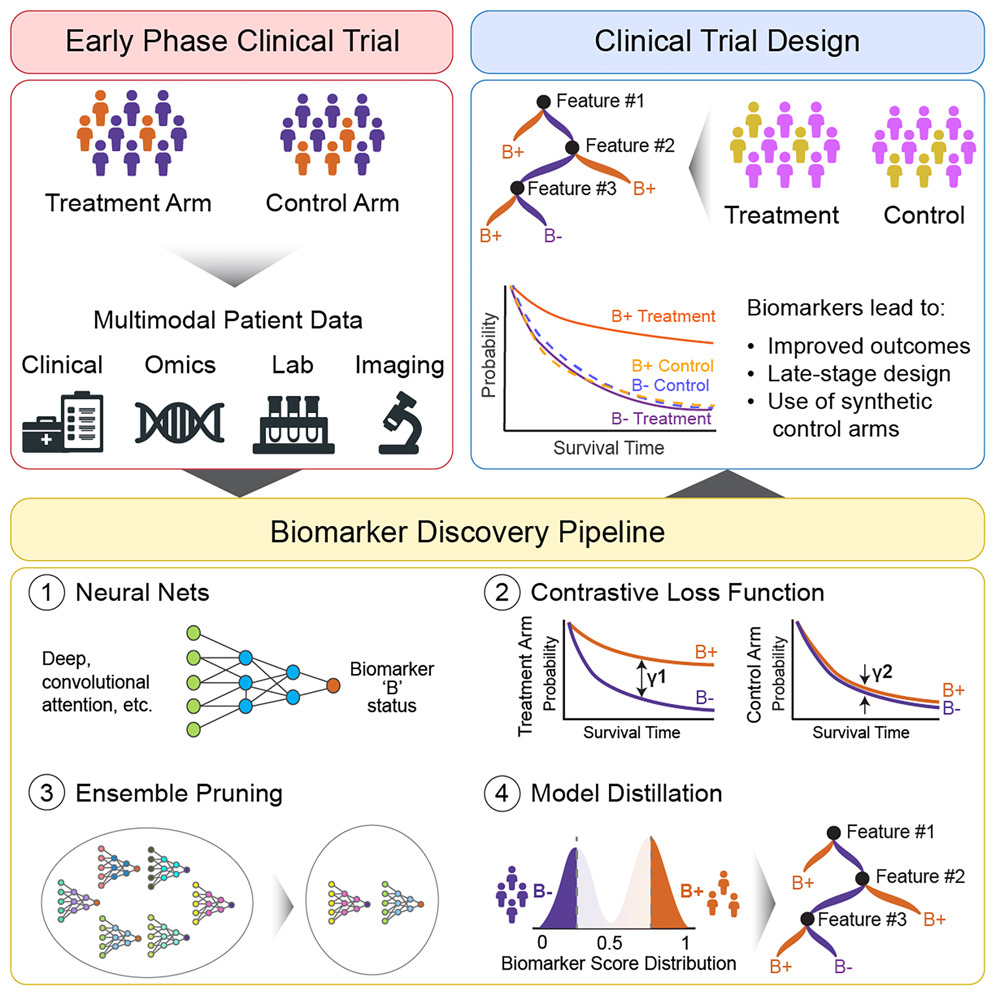
Modern clinical trials can capture tens of thousands of clinicogenomic measurements per individual. Discovering predictive biomarkers, as opposed to prognostic markers, remains challenging. To address this, we present a neural network framework based on contrastive learning—the Predictive Biomarker Modeling Framework (PBMF)—that explores potential predictive biomarkers in an automated, systematic, and unbiased manner. Applied retrospectively to real clinicogenomic datasets, particularly for immuno-oncology (IO) trials, our algorithm identifies biomarkers of IO-treated individuals who survive longer than those treated with other therapies. We demonstrate how our framework retrospectively contributes to a phase 3 clinical trial by uncovering a predictive, interpretable biomarker based solely on early study data. Patients identified with this predictive biomarker show a 15% improvement in survival risk compared to those in the original trial. The PBMF offers a general-purpose, rapid, and robust approach to inform biomarker strategy, providing actionable outcomes for clinical decision-making.
由现代临床试验可为每位受试者收集成千上万条临床-基因组学数据,但与预后标志物相比,预测性生物标志物的发现仍面临重大挑战。为此,该研究提出了一种基于对比学习的神经网络框架——预测性生物标志物建模框架(PBMF),该方法可自动化、系统性、无偏地探索潜在的预测性生物标志物。该研究将该框架回顾性地应用于真实的临床-基因组数据集,尤其是免疫肿瘤治疗(IO)临床试验,成功识别出在接受IO治疗后生存期显著长于其他治疗方式的患者所特有的预测性标志物。进一步研究表明,该方法可在III期临床试验的早期阶段即识别出具有解释性的预测性标志物。具有该标志物的患者,其生存风险相较原始试验人群改善了15%。PBMF框架为生物标志物策略提供了一种通用、高效、稳健的研究工具,可为临床决策带来明确的指导价值。
9. Circular RMST cooperates with lineage-driving transcription factors to govern neuroendocrine transdifferentiation
环状RNA RMST与谱系决定性转录因子协同调控神经内分泌表型转分化
加拿大多伦多大学及附属玛格丽特公主癌症中心、中国科学院等
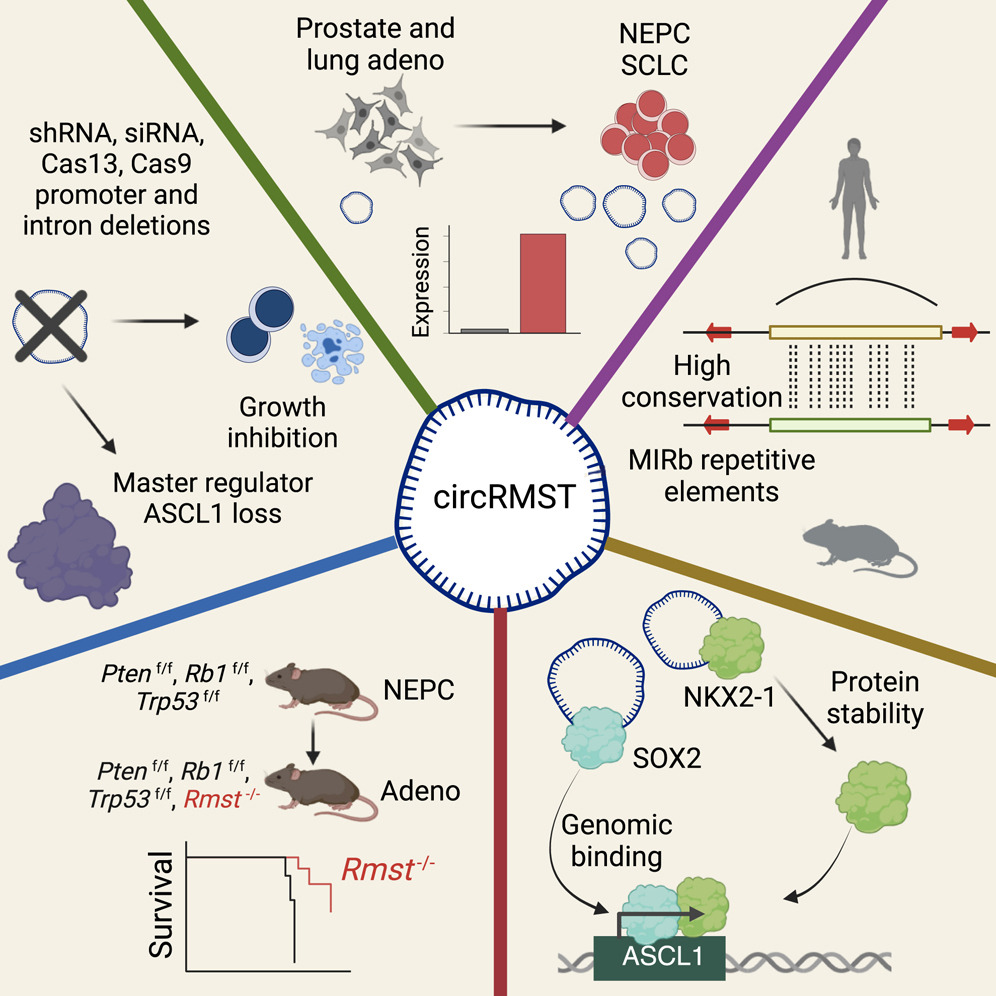
Circular RNA (circRNA) is a class of noncoding RNA with regulatory potentials. Its role in the transdifferentiation of prostate and lung adenocarcinoma into neuroendocrine prostate cancer (NEPC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC) remains unexplored. Here, we identified circRMST as an exceptionally abundant circRNA predominantly expressed in NEPC and SCLC, with strong conservation between humans and mice. Functional studies using shRNA, siRNA, CRISPR-Cas13, and Cas9 consistently demonstrate that circRMST is essential for tumor growth and the expression of ASCL1, a master regulator of neuroendocrine fate. Genetic knockout of Rmst in NEPC genetic engineered mouse models prevents neuroendocrine transdifferentiation, maintaining tumors in an adenocarcinoma state. Mechanistically, circRMST physically interacts with lineage transcription factors NKX2-1 and SOX2. Loss of circRMST induces NKX2-1 protein degradation through autophagy-lysosomal pathway and alters the genomic binding of SOX2, collectively leading to the loss of ASCL1 transcription.
环状RNA(circRNA)是一类具有调控功能的非编码RNA,其在前列腺癌和肺腺癌向神经内分泌前列腺癌(NEPC)和小细胞肺癌(SCLC)转分化过程中的作用尚未被充分研究。本研究鉴定出circRMST作为一种在NEPC和SCLC中高度富集的环状RNA,且在人与小鼠之间具有高度保守性。功能研究通过shRNA、siRNA、CRISPR-Cas13及Cas9等多种手段一致证实,circRMST对于肿瘤生长及神经内分泌命运主控转录因子ASCL1的表达至关重要。在NEPC基因工程小鼠模型中敲除Rmst基因可显著阻断神经内分泌转分化,使肿瘤维持在腺癌状态。机制上,circRMST可与谱系决定性转录因子NKX2-1和SOX2发生直接相互作用;其缺失会通过自噬-溶酶体通路诱导NKX2-1蛋白降解,并改变SOX2的基因组结合模式,最终导致ASCL1转录活性的丧失。综上,circRMST 是驱动神经内分泌转分化的关键环状RNA,并通过调控关键转录因子网络发挥作用。
10. Conserved spatial subtypes and cellular neighborhoods of cancer-associated fibroblasts revealed by single-cell spatial multi-omics
单细胞空间多组学揭示癌相关成纤维细胞的保守性空间亚型与细胞邻域结构

美国德克萨斯大学MD安德森癌症中心等
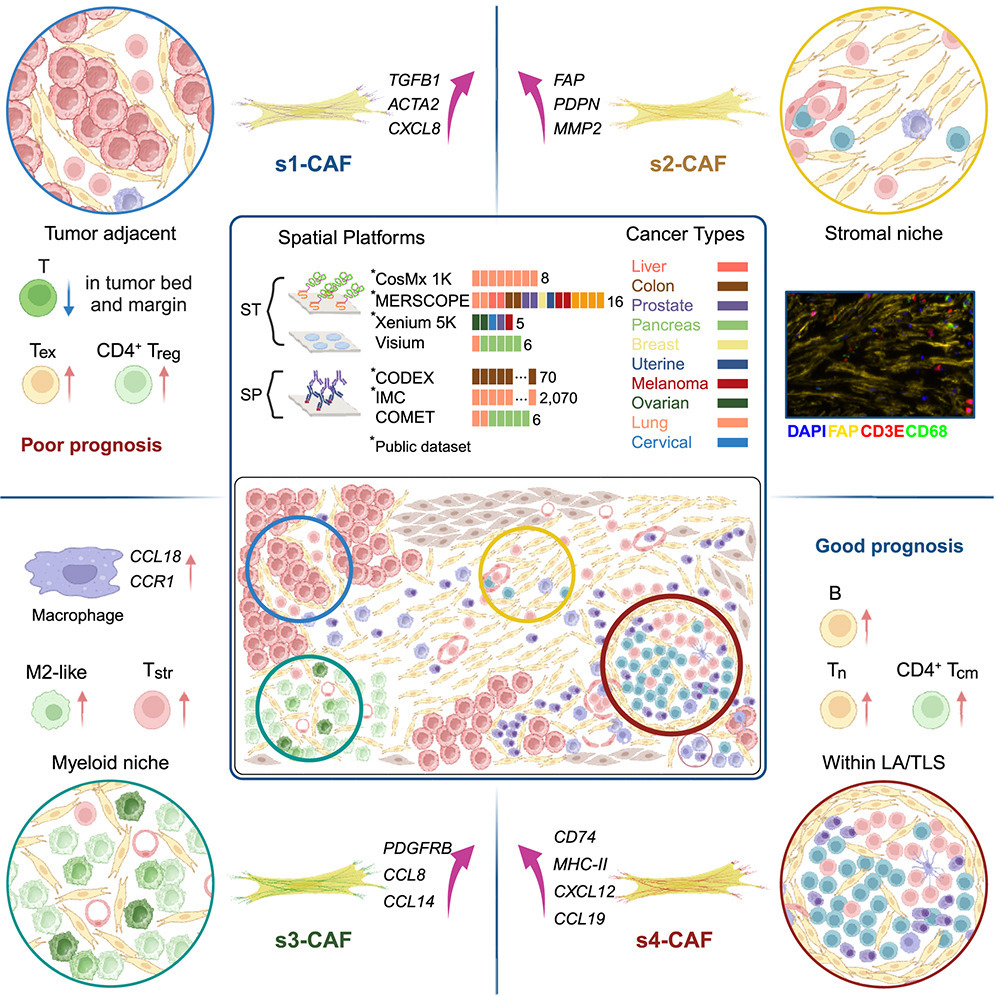
Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) are a multifaceted cell population essential for shaping the tumor microenvironment (TME) and influencing therapy responses. Characterizing the spatial organization and interactions of CAFs within complex tissue environments provides critical insights into tumor biology and immunobiology. In this study, through integrative analyses of over 14 million cells from 10 cancer types across 7 spatial transcriptomics and proteomics platforms, we discover, validate, and characterize four distinct spatial CAF subtypes. These subtypes are conserved across cancer types and independent of spatial omics platforms. Notably, they exhibit distinct spatial organizational patterns, neighboring cell compositions, interaction networks, and transcriptomic profiles. Their abundance and composition vary across tissues, shaping TME characteristics, such as levels, distribution, and state composition of tumor-infiltrating immune cells, tumor immune phenotypes, and patient survival. This study enriches our understanding of CAF spatial heterogeneity in cancer and paves the way for novel approaches to target and modulate CAFs.
癌相关成纤维细胞(CAF)是肿瘤微环境(TME)中的关键组成,具有多重功能,能够重塑微环境并影响治疗反应。深入解析CAF在复杂组织中的空间分布及其与其他细胞的相互作用,对于理解肿瘤生物学和免疫学具有重要意义。本研究整合分析了来自10种癌症、超过1400万个细胞,覆盖7种空间转录组和蛋白组平台,系统发现并验证了4种保守性CAF空间亚型,并对其特征进行了深入描绘。这些亚型在不同癌种之间高度保守,且不受平台差异影响。它们展现出彼此不同的空间组织模式、邻近细胞组成、相互作用网络及转录组特征。不同CAF亚型在组织中的丰度与组合差异,对TME特征产生深远影响,包括肿瘤浸润免疫细胞的水平、分布和状态构成,肿瘤的免疫表型以及患者生存结局。本研究显著拓展了对CAF空间异质性的理解,为靶向CAF进行精准调控提供了新的方向和策略。
11. Nivolumab combined with induction chemotherapy and radiotherapy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A multicenter phase 2 PLATINUM trial
Nivolumab联合诱导化疗与放疗治疗鼻咽癌:多中心II期PLATINUM临床试验

中山大学肿瘤防治中心及其临床试验中心等
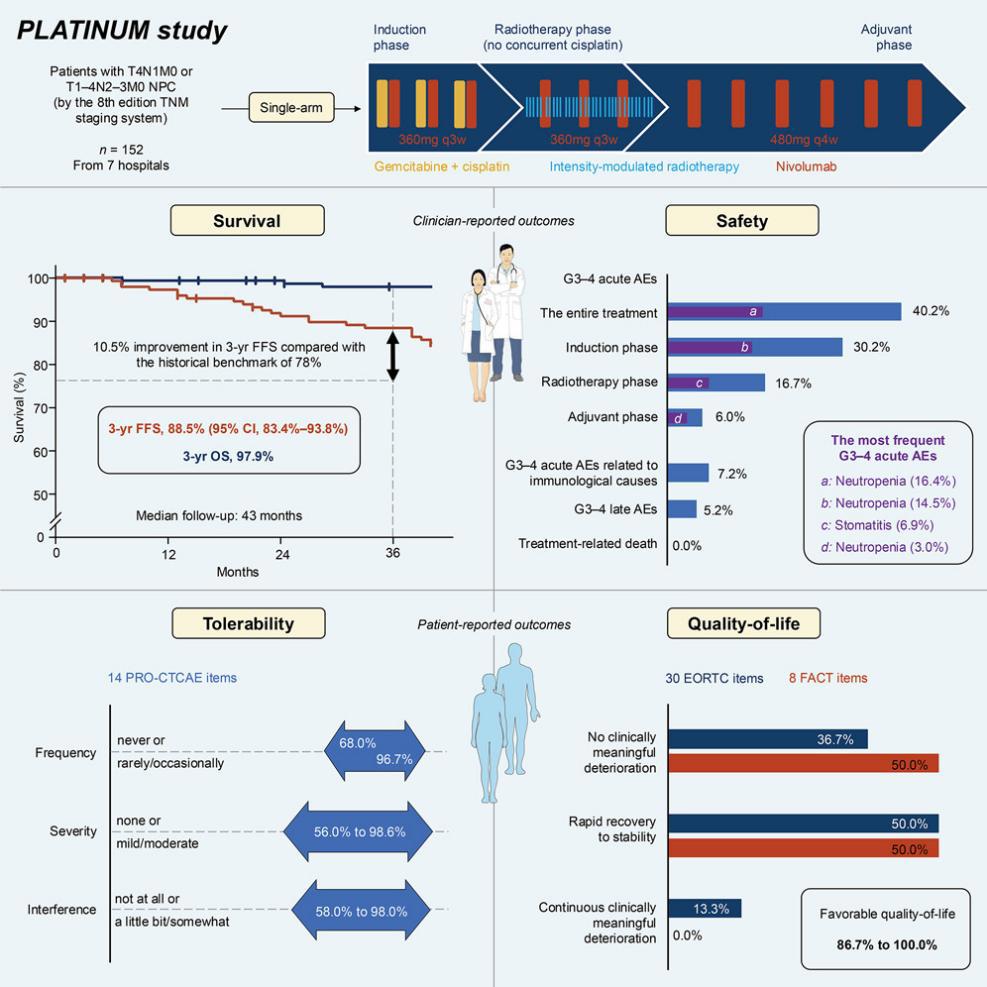
Severe toxicities caused by concurrent cisplatin are a critical problem in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) treatment. In this phase 2 multicenter PLATINUM trial (NCT03984357), we recruited 152 NPC patients who received 12-cycle nivolumab plus induction chemotherapy and radiotherapy without concurrent cisplatin. After a median follow-up of 43 months, the 3-year failure-free survival (FFS) was 88.5% (95% confidence interval [CI], 83.4%–93.8%) and the 3-year overall survival was 97.9%. An early clearance of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA after induction-phase treatment was associated with FFS benefit. Sixty (40.2%) and eight (5.2%) patients had acute and late grade 3–4 adverse events (AEs), respectively. Most patients had good tolerance to AE-associated frequency (68.0%–96.7%), severity (56.0%–98.6%), and interference (58.0%–98.0%); 86.7%–100.0% of quality-of-life domains showed either no clinically meaningful deterioration or a rapid recovery. Nivolumab plus induction chemotherapy and radiotherapy demonstrated efficacious anti-tumor activity, low toxicity, and favorable tolerability and quality-of-life for NPC patients.
在鼻咽癌(NPC)治疗中,同时应用顺铂(cisplatin)所引发的严重毒副作用是临床面临的重要难题。在本项II期多中心PLATINUM临床试验(NCT03984357)中,共纳入152名接受12周期纳武利尤单抗(nivolumab)联合诱导化疗与放疗、且不含同步顺铂的NPC患者。中位随访时间为43个月,结果显示3年无失败生存率(FFS)为88.5%(95%置信区间:83.4%–93.8%),3年总生存率(OS)高达97.9%。研究还发现,诱导治疗阶段后EB病毒(EBV)DNA的早期清除与更好的FFS获益显著相关。共有60例(40.2%)患者出现急性3–4级不良事件,8例(5.2%)出现晚期3–4级不良事件。大多数患者对治疗相关不良事件的频率(68.0%–96.7%)、严重程度(56.0%–98.6%)和干扰程度(58.0%–98.0%)表现出良好耐受性;86.7%–100.0%的生活质量各项指标未见明显下降或可迅速恢复。总体而言,纳武利尤单抗联合诱导化疗与放疗在NPC患者中展现出良好的抗肿瘤活性、低毒性、良好的耐受性及生活质量保障,为替代同步顺铂方案提供了有前景的治疗策略。
12. Hypoxia inducible factor-1α drives cancer resistance to cuproptosis
缺氧诱导因子-1α(HIF-1α)驱动癌症对铜死亡(cuproptosis)的耐受机制

复旦大学上海癌症中心及上海医学院多个肿瘤相关科室等
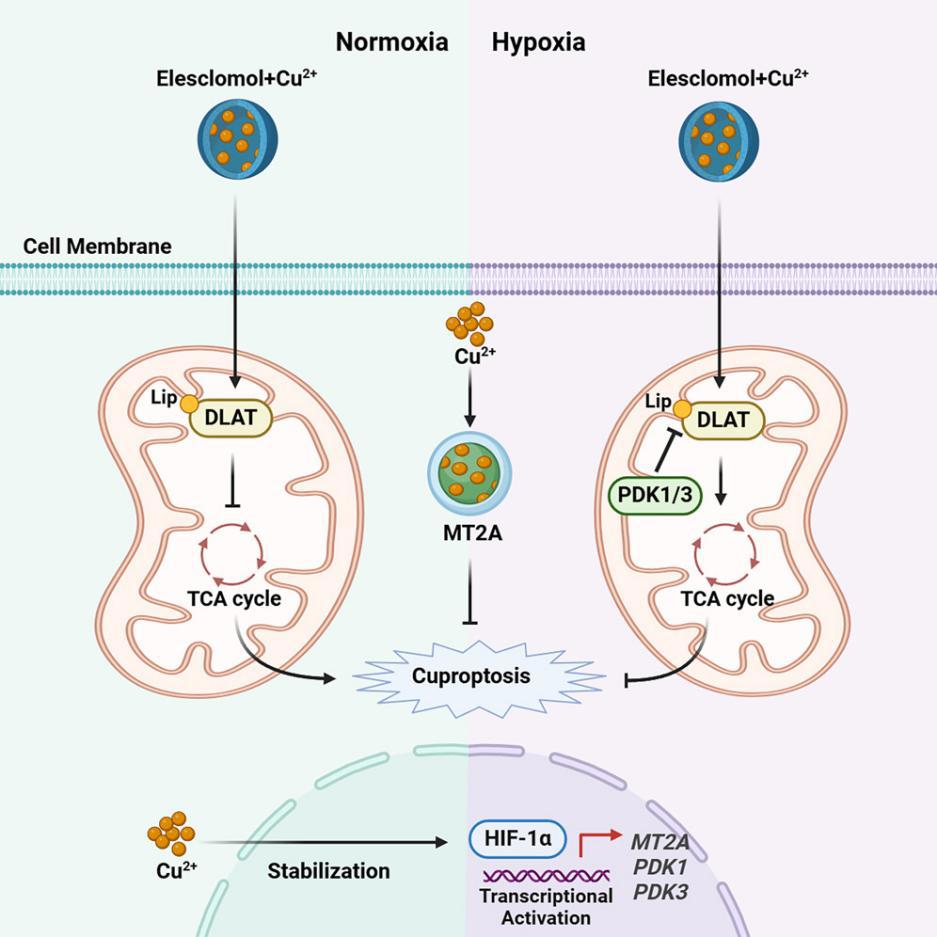
Cuproptosis represents a new type of cell death that intricately associated with copper homeostasis and protein lipoylation. The cuproptosis suppression has been characterized in the hypoxic tumor microenvironment (TME). Here we reveal that hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) is a driver of cuproptosis resistance in solid tumor. We found that HIF-1α activates pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 and 3 (PDK1/3), resulting in decreased expression of dihydrolipoamide S-acetyltransferase (DLAT) (target of copper), and promotes the accumulation of metallothionein, which sequesters mitochondrial copper, leading to resistance to cuproptosis under hypoxic conditions. Furthermore, we discovered that high levels of copper reduce ubiquitination and increase the stability of HIF-1α protein without affecting its mRNA levels. Inhibition of HIF-1α increases the susceptibility of cancer to cuproptosis in vivo. This study unveils the multifaceted role of HIF-1α in cuproptosis and demonstrates the molecular mechanism of hypoxia-promoted carcinogenesis.
铜死亡(cuproptosis)是一种新型的细胞死亡方式,与铜离子稳态及蛋白脂酰化密切相关。已有研究表明,低氧肿瘤微环境(TME)中铜死亡受到抑制。本研究进一步揭示,缺氧诱导因子-1α(HIF-1α)是实体瘤中铜死亡耐受的关键驱动因子。该研究发现,HIF-1α通过激活丙酮酸脱氢酶激酶1和3(PDK1/3),抑制了铜死亡靶蛋白DLAT(二氢硫辛酰胺S-乙酰转移酶)的表达,并促进金属硫蛋白(metallothionein)的积聚,从而将线粒体铜隔离,导致在低氧条件下肿瘤细胞对铜死亡产生耐受。此外,高浓度铜可通过抑制HIF-1α蛋白的泛素化、增加其稳定性,增强该因子的活性,而不影响其mRNA水平。更重要的是,抑制HIF-1α可在体内显著提高肿瘤对铜死亡的敏感性。本研究揭示了HIF-1α在铜死亡中的多重调控作用,明确了低氧状态促进肿瘤发生的分子机制,为靶向铜死亡耐受提供了潜在策略。
13. Lymph node macrophages drive immune tolerance and resistance to cancer therapy by induction of the immune-regulatory cytokine IL-33
淋巴结巨噬细胞通过诱导免疫调节因子IL-33,促进免疫耐受并驱动肿瘤对治疗的抗性

加拿大多伦多大学及其附属的玛格丽特公主癌症中心等
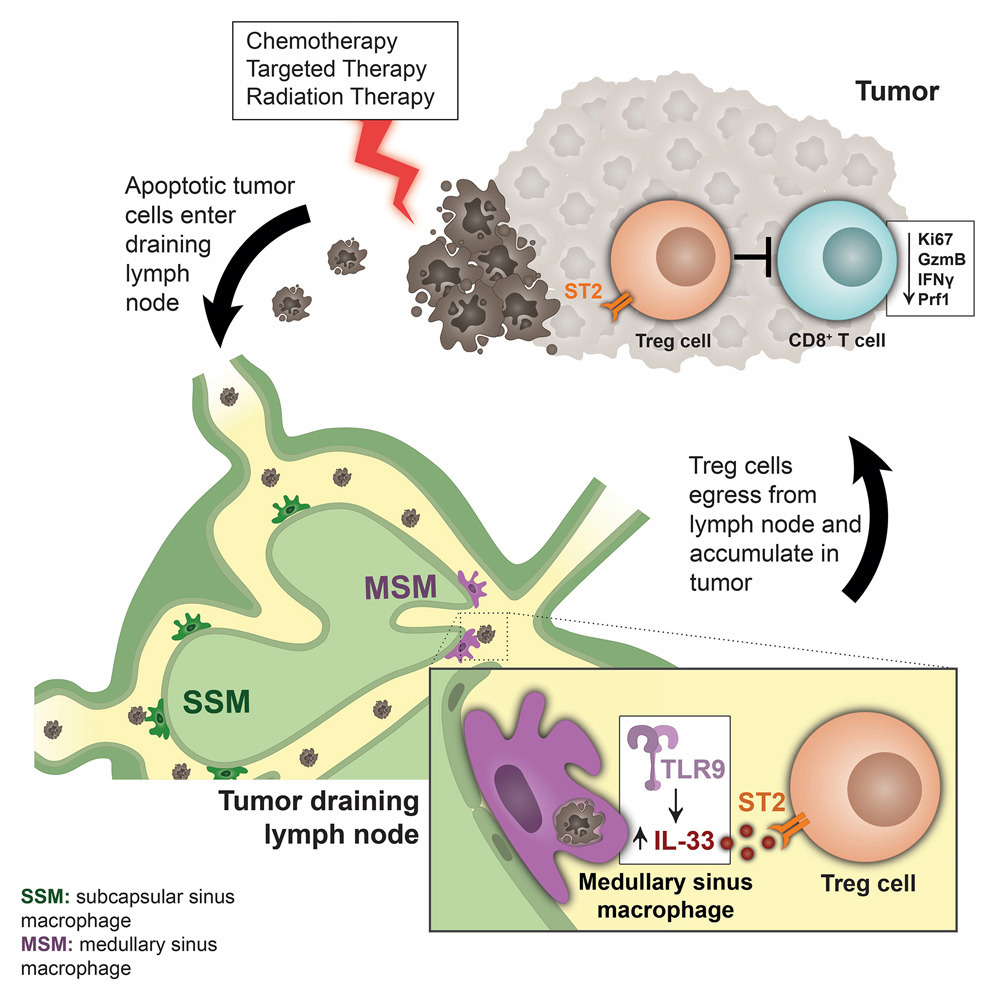
Apoptotic cells are immunosuppressive, creating a barrier in cancer treatment. Thus, we investigated immune responses to dying tumor cells after therapy in the tumor draining lymph node (TDLN). A key population responsible for clearing tumor material in the TDLN was medullary sinus macrophages (MSMs). Tumor debris phagocytosis by MSMs induces the cytokine IL-33, and blocking the IL-33 receptor (ST2) or deletion of Il33 in MSMs enhances therapy responses. Mechanistically, IL-33 activates T regulatory cells in TDLNs that migrate to the tumor to suppress CD8+ T cells. Therapeutically combining ST2 blockade, targeted kinase inhibitors, and anti-PD-1 immunotherapy increases CD8+ T cell activity promoting tumor regression. Importantly, we observe similar activity in human macrophages, and IL-33 expression in sentinel lymph nodes correlates with disease stage and survival in melanoma. Thus, our data identifies an IL-33-dependent immune response to therapy that attenuates therapy-induced anti-tumor immunity.
凋亡细胞具有免疫抑制作用,是癌症治疗中的重要障碍之一。本研究聚焦治疗后肿瘤引流淋巴结(TDLN)中对死亡肿瘤细胞的免疫反应,发现髓窦巨噬细胞(medullary sinus macrophages, MSMs)是清除肿瘤残留物的关键细胞群体。MSMs吞噬肿瘤碎片后会诱导分泌免疫调节性细胞因子IL-33,而阻断IL-33受体ST2或特异性敲除MSMs中的Il33基因,可显著增强治疗应答。机制上,IL-33在TDLN中激活调节性T细胞(Tregs),这些Tregs随后迁移至肿瘤部位,抑制CD8⁺ T细胞的抗肿瘤功能。在治疗策略上,联合使用ST2阻断剂、靶向激酶抑制剂与抗PD-1免疫治疗,可增强CD8⁺ T细胞活性,显著促进肿瘤缩小。更重要的是,在人类巨噬细胞中也观察到类似机制,且哨点淋巴结中IL-33表达水平与黑色素瘤的疾病分期和患者生存期呈相关性。综上,本研究揭示了一种由IL-33介导的治疗反应性免疫通路,该通路在一定程度上削弱了治疗诱导的抗肿瘤免疫反应,为提升癌症免疫治疗疗效提供了新的干预靶点。
Online articles
May 8, 2025: Article 3篇
April 24, 2025: Article 3篇
April 10, 2025: Article 4篇
April 3, 2025: Article 2篇
March 27, 2025: Article 1篇
合计13篇。
14. Understanding and reversing mammary tumor-driven reprogramming of myelopoiesis to reduce metastatic spread
理解并逆转乳腺肿瘤驱动的髓系造血重编程以减少转移扩散

荷兰癌症研究所等
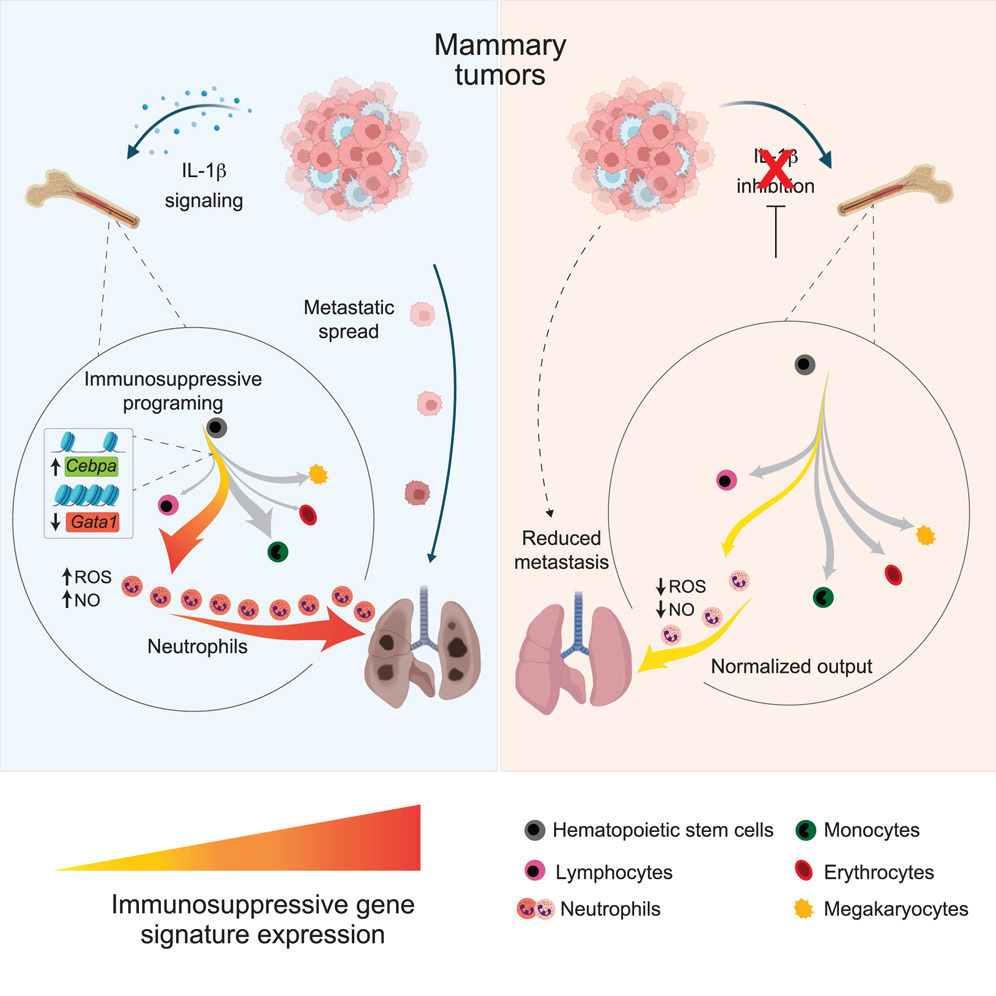
Tumor-induced systemic accumulation and polarization of neutrophils to an immunosuppressive phenotype is a potent driver of metastasis formation. Yet, how mammary tumors reprogram granulopoiesis at the molecular level and when tumor imprinting occurs during neutrophil development remains underexplored. Here, we combined single-cell, chromatin and functional analyses to unravel the tumor-driven reprogramming of granulopoiesis in the bone marrow, along with intervention studies aimed at reversing this process. We observe that mammary tumors accelerate commitment to the neutrophil lineage at the expense of lymphopoiesis and erythropoiesis without stimulating the development of a novel myeloid lineage. Moreover, tumor-directed immunosuppressive imprinting of neutrophils starts early in hematopoiesis. Treatment with anti-IL-1β normalizes tumor-induced granulopoiesis, reducing neutrophil immunosuppressive phenotype and mitigating metastatic spread. Together, these data provide molecular insights into the aberrant, tumor-driven neutrophil differentiation pathway leading to metastasis-promoting chronic inflammation and how it can be reversed to reduce metastatic spread.
肿瘤诱导的中性粒细胞系统性积聚及其向免疫抑制表型的极化是促进肿瘤转移形成的重要机制。然而,乳腺肿瘤如何在分子水平上重编程粒细胞生成(granulopoiesis),以及肿瘤印记在中性粒细胞发育过程中何时发生,仍知之甚少。本研究结合单细胞转录组、染色质图谱与功能分析,揭示了乳腺肿瘤在骨髓中驱动的粒细胞生成重编程机制,并通过干预实验探讨了其可逆性。该研究发现,乳腺肿瘤加速了中性粒细胞谱系的分化承诺,以牺牲淋巴生成和红系生成为代价,但未诱导出新的髓系分化路径。此外,肿瘤诱导的中性粒细胞免疫抑制表型印记在造血早期阶段即已启动。干预方面,使用抗IL-1β治疗能够恢复肿瘤诱导的异常粒细胞生成过程,减少中性粒细胞的免疫抑制性表型,从而有效抑制转移扩散。综上,本研究提供了乳腺肿瘤如何驱动促进转移的慢性炎症状态的分子机制,并揭示该过程在造血系统中的可塑性,为阻断转移提供了新的治疗策略。
15. Immunosequencing identifies signatures of T cell responses for early detection of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
免疫组库测序识别T细胞应答特征,用于鼻咽癌的早期检测

中山大学肿瘤防治中心及华南肿瘤学国家重点实验室等
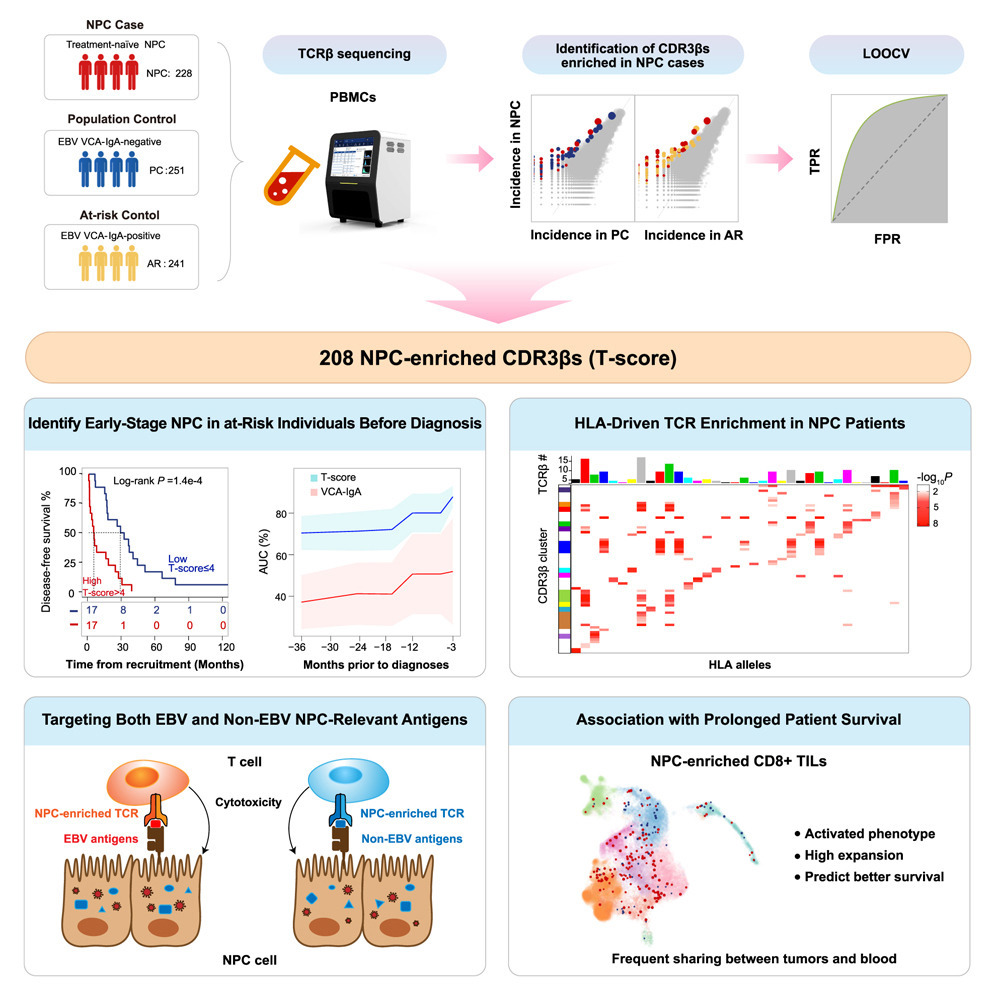
To identify nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC)-relevant T cell receptors (TCRs), we profile the repertoires of peripheral blood TCRβ chains from 228 NPC patients, 241 at-risk controls positive for serum Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) VCA-IgA antibody, and 251 seronegative controls. We develop a TCR-based signature (T-score) based on 208 NPC-enriched CDR3β sequences, which accurately diagnoses NPC in both the original and independent validation cohorts. Notably, a higher T-score, associated with a shorter time interval to NPC diagnosis, effectively identifies early-stage NPC among EBV-seropositive at-risk individuals prior to clinical diagnosis. These NPC-enriched TCRs react against not only EBV-specific antigens but also non-EBV antigens expressed by NPC cells, indicating a broad range of specificities. Moreover, the abundance of NPC-enriched CD8+ T cells in blood correlates with the infiltration of non-exhausted T cell counterparts in tumors and predicts prolonged survival, suggesting that these NPC-enriched T cells have significant potential for disease monitoring and therapeutic applications.
为识别与鼻咽癌(NPC)相关的T细胞受体(TCR),本研究对228名NPC患者、241名EB病毒VCA-IgA抗体阳性的高风险人群和251名血清学阴性对照者的外周血TCRβ链谱系进行了分析。研究基于208条NPC富集的CDR3β序列构建出一个TCR特征评分(T-score),该评分在原始队列及独立验证队列中均可准确诊断NPC。值得注意的是,T-score越高,与NPC确诊之间的时间间隔越短,能够在临床确诊前有效识别EBV血清阳性高风险人群中的早期NPC。这些NPC富集的TCR不仅识别EB病毒抗原,还识别NPC细胞表达的非EB病毒抗原,表明其具有广泛的抗原特异性。此外,外周血中NPC富集CD8⁺ T细胞的丰度与肿瘤中未耗竭T细胞的浸润水平正相关,并可预测更长的生存期,提示这些T细胞在疾病监测和治疗中具有重要应用潜力。
16. Spatial and multiomics analysis of human and mouse lung adenocarcinoma precursors reveals TIM-3 as a putative target for precancer interception
人类与小鼠肺腺癌前病变的空间及多组学分析揭示TIM-3为潜在的癌前干预靶点

美国德克萨斯大学MD安德森癌症中心等
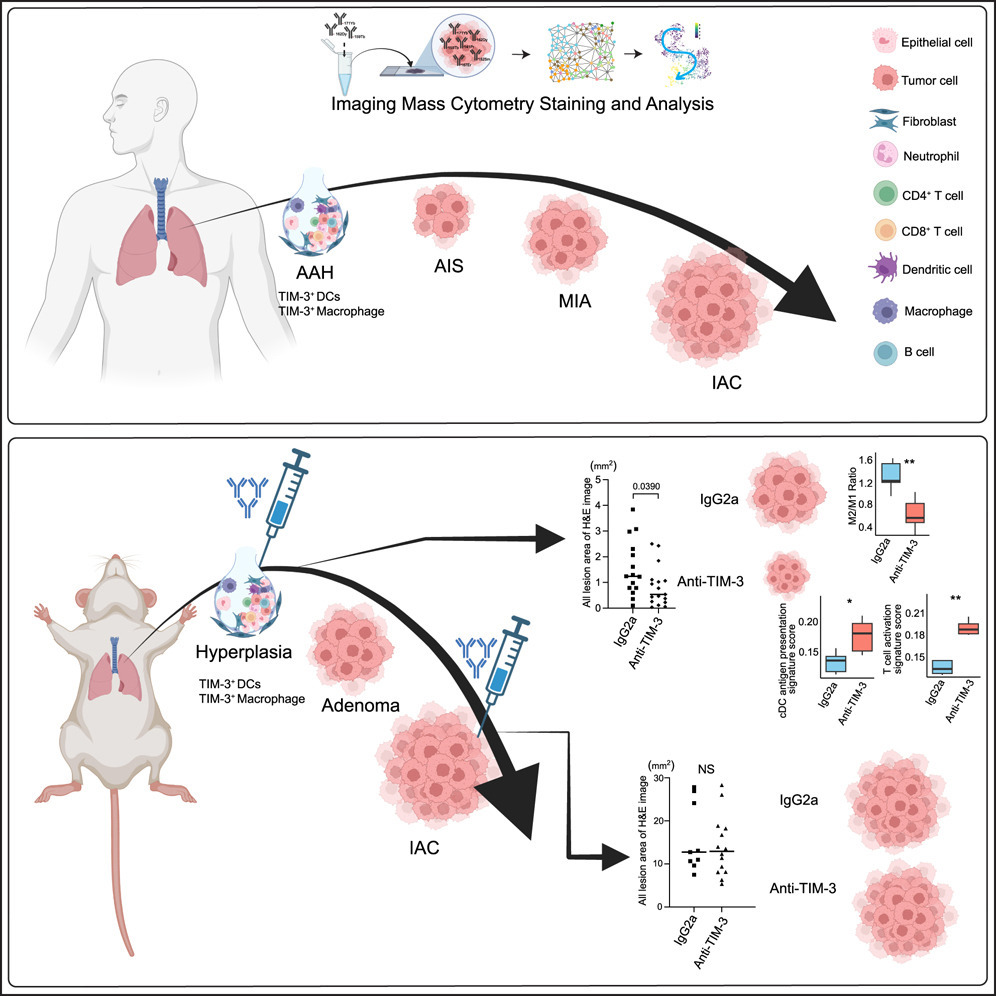
How tumor microenvironment shapes lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) precancer evolution remains poorly understood. Spatial immune profiling of 114 human LUAD and LUAD precursors reveals a progressive increase of adaptive response and a relative decrease of innate immune response as LUAD precursors progress. The immune evasion features align the immune response patterns at various stages. TIM-3-high features are enriched in LUAD precancers, which decrease in later stages. Furthermore, single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) and spatial immune and transcriptomics profiling of LUAD and LUAD precursor specimens from 5 mouse models validate high TIM-3 features in LUAD precancers. In vivo TIM-3 blockade at precancer stage, but not at advanced cancer stage, decreases tumor burden. Anti-TIM-3 treatment is associated with enhanced antigen presentation, T cell activation, and increased M1/M2 macrophage ratio. These results highlight the coordination of innate and adaptive immune response/evasion during LUAD precancer evolution and suggest TIM-3 as a potential target for LUAD precancer interception.
肿瘤微环境如何塑造肺腺癌(LUAD)癌前演化的过程目前仍缺乏深入理解。通过对114例人类LUAD及其前病变的空间免疫图谱分析,研究发现,随着LUAD前病变的进展,适应性免疫反应逐渐增强,而先天免疫反应相对减弱,同时伴随免疫逃逸特征在各阶段呈现一致性模式。研究进一步发现,TIM-3高表达特征在LUAD癌前病变中显著富集,但在癌症晚期逐渐减少。通过5种小鼠模型的单细胞RNA测序及空间免疫与转录组分析,验证了LUAD前病变中TIM-3表达上调的现象。功能实验表明,在癌前阶段阻断TIM-3可显著降低肿瘤负荷,而在晚期癌症阶段无显著疗效。抗TIM-3治疗可增强抗原呈递、T细胞激活,并提高M1/M2巨噬细胞比值。综上,研究揭示了LUAD癌前演化过程中先天与适应性免疫反应/逃逸的协同调控机制,并指出TIM-3是肺腺癌前干预的潜在治疗靶点。
17. KMT2C deficiency drives transdifferentiation of double-negative prostate cancer and confer resistance to AR-targeted therapy
KMT2C缺失驱动双阴性前列腺癌的转分化并赋予其对雄激素受体靶向治疗的耐药性

中国科学院系统营养与健康研究所及生物化学与细胞生物学研究所等
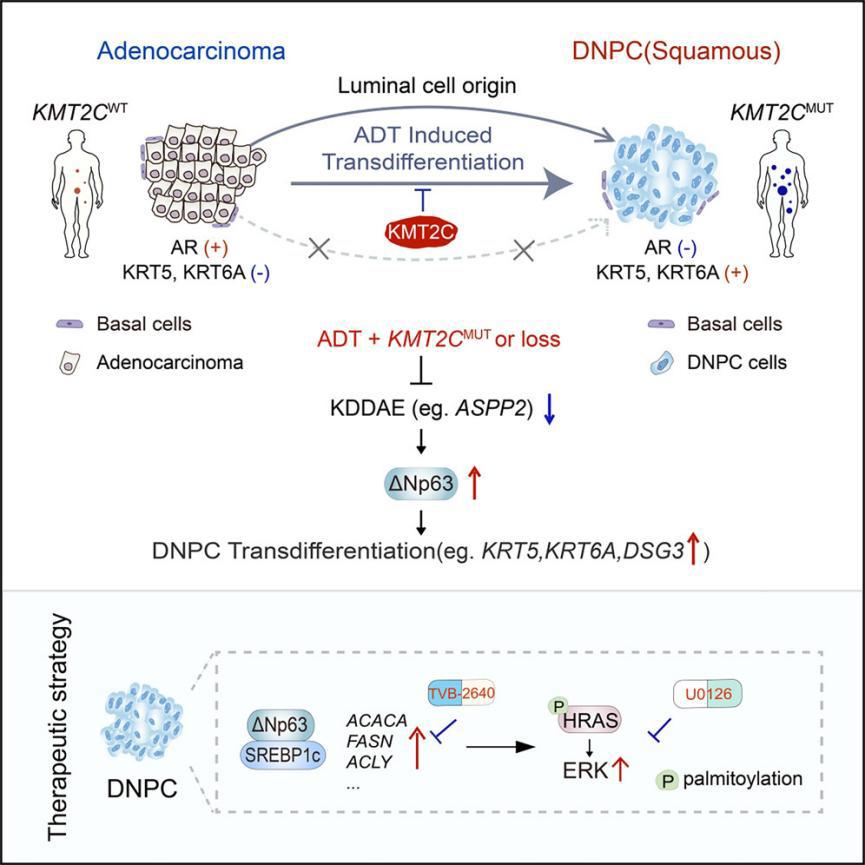
Double-negative prostate cancer (DNPC), characterized by an androgen receptor (AR)- and neuroendocrine-null phenotype, frequently emerges following androgen deprivation therapy (ADT). However, our understanding of the origins and regulatory mechanisms of DNPC remains limited. Here, we discover that tumors with KMT2C mutation or loss are highly susceptible to transitioning into DNPC following ADT. We clarify that DNPC primarily stems from luminal cell transdifferentiation rather than basal cell transformation. Antiandrogen treatment induces KMT2C binding at enhancers of a subset of AR-regulated genes, preserving the adenocarcinoma lineage. KMT2C maintains ASPP2 expression via enhancer-promoter communication post-AR inhibition, while its inactivation reduces ASPP2, triggering ΔNp63-dependent transdifferentiation. This DNPC transition maintains fatty acid (FA) synthesis through ΔNp63-mediated SREBP1c transactivation, fueling DNPC growth via HRAS palmitoylation and MAPK signaling activation. These findings highlight KMT2C as an epigenetic checkpoint against DNPC development and suggest the therapeutic potential of targeting fatty acid synthesis.
双阴性前列腺癌(DNPC)是一种同时缺乏雄激素受体(AR)和神经内分泌特征的肿瘤亚型,常在雄激素剥夺治疗(ADT)后出现。然而,DNPC的起源及其调控机制尚不清楚。本研究发现,携带KMT2C突变或缺失的肿瘤在ADT后极易发生DNPC转分化。研究进一步明确,DNPC主要来源于腺体上皮(luminal)细胞的转分化,而非基底细胞的转化。在抗雄激素治疗条件下,KMT2C可结合于部分AR调控基因的增强子区域,维持腺癌谱系的稳定。KMT2C通过增强子-启动子间的通讯维持ASPP2表达,而其失活会导致ASPP2下调,进而诱发依赖ΔNp63的转分化过程。这一DNPC的转化机制依赖ΔNp63介导的SREBP1c激活,维持脂肪酸(FA)合成,并通过HRAS棕榈酰化及MAPK信号通路激活支持肿瘤持续生长。综上,研究揭示了KMT2C作为限制DNPC发生的表观遗传关卡,并提出脂肪酸合成通路作为潜在治疗靶点,为应对ADT耐药性提供了新的思路。
18. Bone metastases diminish extraosseous response to checkpoint blockade immunotherapy through osteopontin-producing osteoclasts
骨转移通过分泌骨桥蛋白的破骨细胞削弱免疫检查点抑制治疗在骨外病灶中的疗效
中国人民解放军第三军医大学等
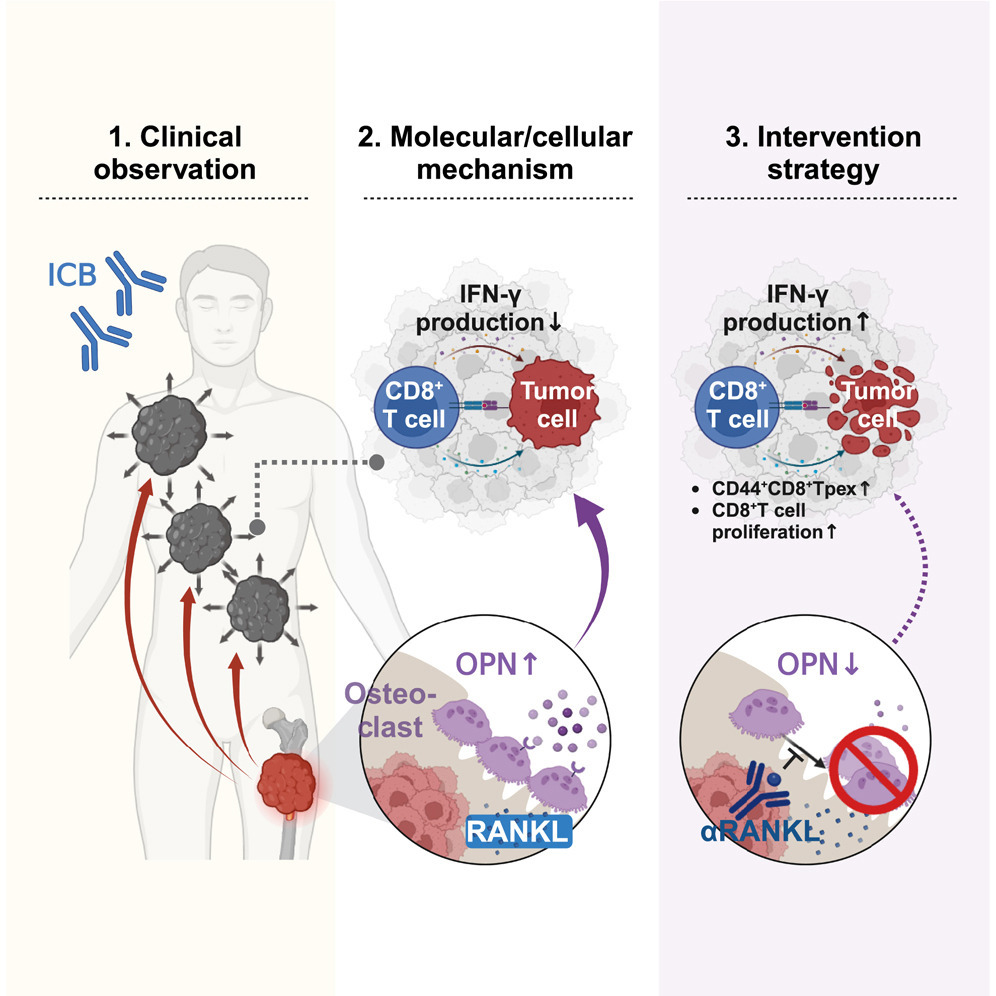
Bone metastatic lesions typically associate with suboptimal responses to immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) therapies. In this study, we observed that across multiple clinical cohorts and a variety of mouse models, the presence of osseous metastases induces ICB resistance in extraosseous tumors. Mechanistically, this long-distance communication is mediated by osseous tumor-conditioned osteoclasts producing osteopontin (OPN). Through circulation, OPN reprograms the extraosseous tumor microenvironment and impairs T cell recruitment and differentiation of CD8+TCF1+ precursor cells, an essential population for ICB efficacy. In mice, ICB responsiveness is restored by αRANKL blockade of osteoclastogenesis, neutralization of OPN in circulation, or tissue-specific depletion of OPN in osteoclasts. Both the mode of action and therapeutic benefit were validated in clinical cohorts with the αRANKL-ICB combinatory regimen. These findings establish bone as a specific immunoregulatory organ exploited by tumor metastasis and suggest osteoclastogenesis as a promising target to improve ICB prognosis in patients with bone metastasis.
骨转移灶通常与免疫检查点抑制(ICB)治疗效果欠佳相关。本研究通过多个临床队列与多种小鼠模型观察到,骨转移的存在可诱导骨外肿瘤对ICB治疗产生抗性。机制研究表明,这种远程免疫抑制效应是由骨转移瘤重塑的破骨细胞分泌骨桥蛋白(osteopontin, OPN)介导的。OPN通过血液循环作用于骨外肿瘤微环境,削弱CD8⁺TCF1⁺前体T细胞的募集与分化,而这一T细胞亚群对ICB疗效至关重要。在小鼠模型中,通过αRANKL抗体阻断破骨细胞生成、循环中OPN中和,或特异性敲除破骨细胞中的OPN,可显著恢复对ICB治疗的敏感性。上述作用机制和治疗获益亦在临床队列中使用αRANKL联合ICB方案得到了验证。本研究将骨确立为一种被肿瘤利用的特异性免疫调节器官,并提出破骨细胞生成过程是改善骨转移患者ICB疗效的潜在干预靶点。
19. Stromal lipid species dictate melanoma metastasis and tropism
基质脂质种类决定黑色素瘤的转移能力与器官趋向性
英国曼彻斯特大学及其癌症研究中心等
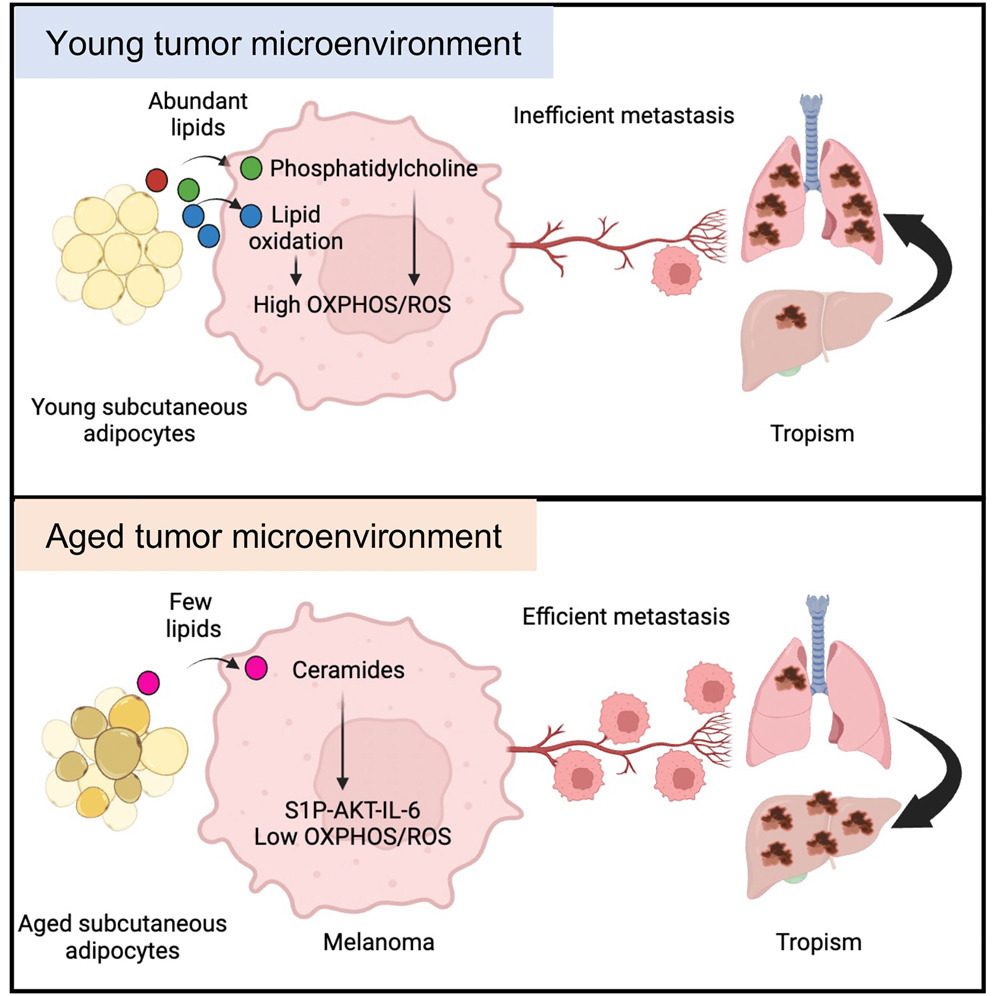
Cancer cells adapt to signals in the tumor microenvironment (TME), but the TME cues that impact metastasis and tropism are still incompletely understood. We show that abundant stromal lipids from young subcutaneous adipocytes, including phosphatidylcholines, are taken up by melanoma cells, where they upregulate melanoma PI3K-AKT signaling, fatty acid oxidation, oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) leading to oxidative stress, resulting in decreased metastatic burden. High OXPHOS melanoma cells predominantly seed the lung and brain; decreasing oxidative stress with antioxidants shifts tropism from the lung to the liver. By contrast, the aged TME provides fewer total lipids but is rich in ceramides, leading to lower OXPHOS and high metastatic burden. Aged TME ceramides taken up by melanoma cells activate the S1P-STAT3-IL-6 signaling axis and promote liver tropism. Inhibiting OXPHOS in the young TME or blocking the IL-6 receptor in the aged TME reduces the age-specific patterns of metastasis imposed by lipid availability.
癌细胞能够对肿瘤微环境(TME)中的信号进行适应性调整,但影响转移潜能和器官趋向性的TME信号仍未被完全揭示。本研究发现,年轻皮下脂肪细胞来源的丰富基质脂质(包括磷脂酰胆碱类)被黑色素瘤细胞摄取后,可激活PI3K-AKT信号通路、脂肪酸氧化与氧化磷酸化(OXPHOS),进而诱导氧化应激,从而抑制转移负担。高OXPHOS活性的黑色素瘤细胞更倾向于转移至肺和脑;使用抗氧化剂降低氧化应激后,器官趋向性从肺转变为肝脏。相对而言,老年TME中的脂质总量较少,但富含神经酰胺(ceramides),其进入黑色素瘤细胞后导致OXPHOS降低,增强转移能力。
更重要的是,老年TME中的神经酰胺激活S1P-STAT3-IL-6信号轴,促使黑色素瘤细胞趋向肝脏转移。在年轻TME中抑制OXPHOS,或在老年TME中阻断IL-6受体,均可显著减少由脂质可利用性驱动的年龄特异性转移模式。综上,研究揭示了TME中不同脂质组成通过代谢与炎症信号重塑黑色素瘤转移路径,并指出OXPHOS与IL-6轴是可干预的潜在靶点。
20. Pan-cancer human brain metastases atlas at single-cell resolution
泛癌种人类脑转移瘤单细胞分辨率图谱

北京大学、中科院、陆军军医大学、中山大学及美国哥伦比亚大学等
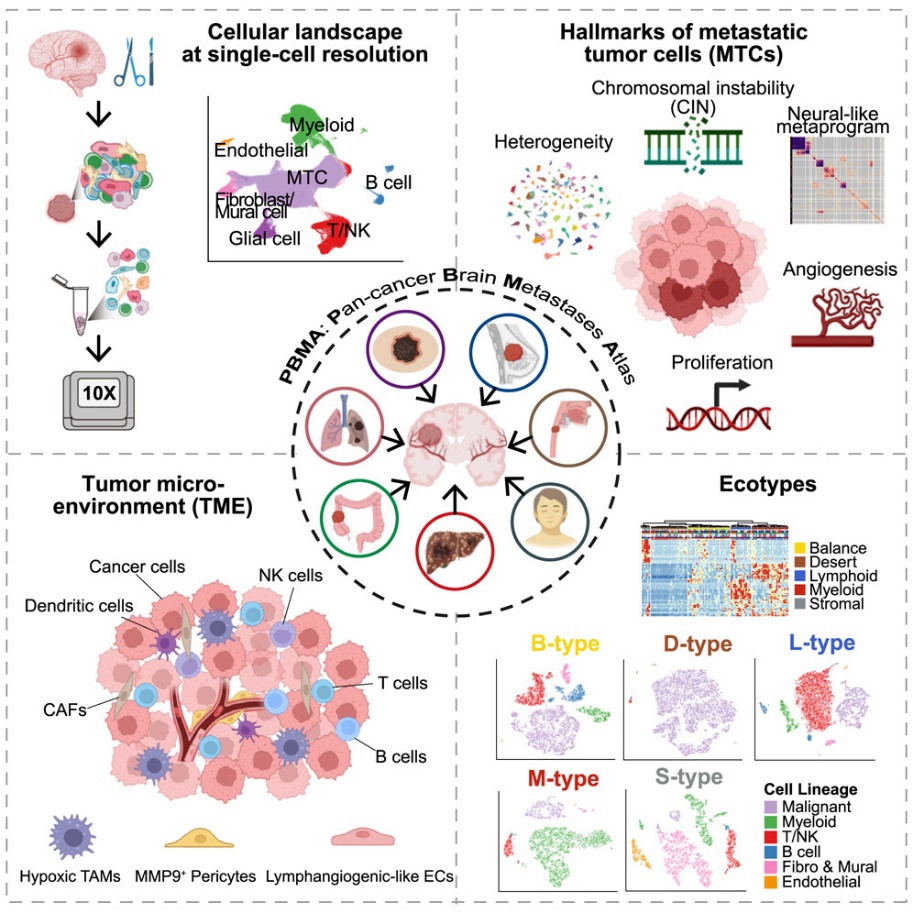
Brain metastases (BrMs) remain a major clinical and therapeutic challenge in patients with metastatic cancers. However, advances in our understanding of BrM have been hampered by the constrained sample size and resolution of BrM profiling studies. Here, we perform integrative single-cell RNA sequencing analysis on 108 BrM samples and 111 primary tumor (PTs) samples to investigate the characteristics and remodeling of cell states and composition across cancer lineages and subsets. Recurring and enriched features of malignant cells are increased chromosomal instability, marked proliferative and angiogenic hallmarks, and adoption of a neural-like BrM-associated metaprogram. Immunosuppressive myeloid and stromal subsets dominate the BrM tumor microenvironment, which are associated with poor prognosis and resistance to immunotherapy. Furthermore, five distinct BrM ecotypes are identified, correlating with specific histopathological patterns and clinical characteristics. This work defines hallmarks of BrM biology across cancer types and suggests that shared dependencies may exist, which may be exploited clinically.
脑转移瘤(BrMs)在转移性癌症患者中仍然是重大的临床与治疗难题。然而,现有对脑转移瘤的研究因样本数量有限和分辨率不足而进展缓慢。在本研究对108例脑转移瘤样本和111例原发肿瘤(PT)样本进行了整合性单细胞RNA测序分析,以探究不同癌种及其亚型中细胞状态与组成的特征及其重塑。结果发现,恶性细胞中反复出现且富集的特征包括染色体不稳定性升高、显著的增殖与血管生成特征,以及获得类似神经样的脑转移相关基因表达程序。脑转移瘤的肿瘤微环境中,免疫抑制型的髓系细胞和间质细胞亚群占主导地位,并与不良预后和免疫治疗耐受相关。此外,该研究鉴定出五种不同的脑转移生态亚型(ecotypes),其分别与特定的组织病理学特征和临床表现相关联。本研究定义了跨癌种的脑转移生物学特征,并提示可能存在可被临床利用的共性依赖机制。
21. ZEB2 is a master switch controlling the tumor-associated macrophage program
ZEB2 是调控肿瘤相关巨噬细胞程序的主控开关

以色列魏茨曼科学研究所、耶路撒冷希伯来大学附属哈达萨医学中心等
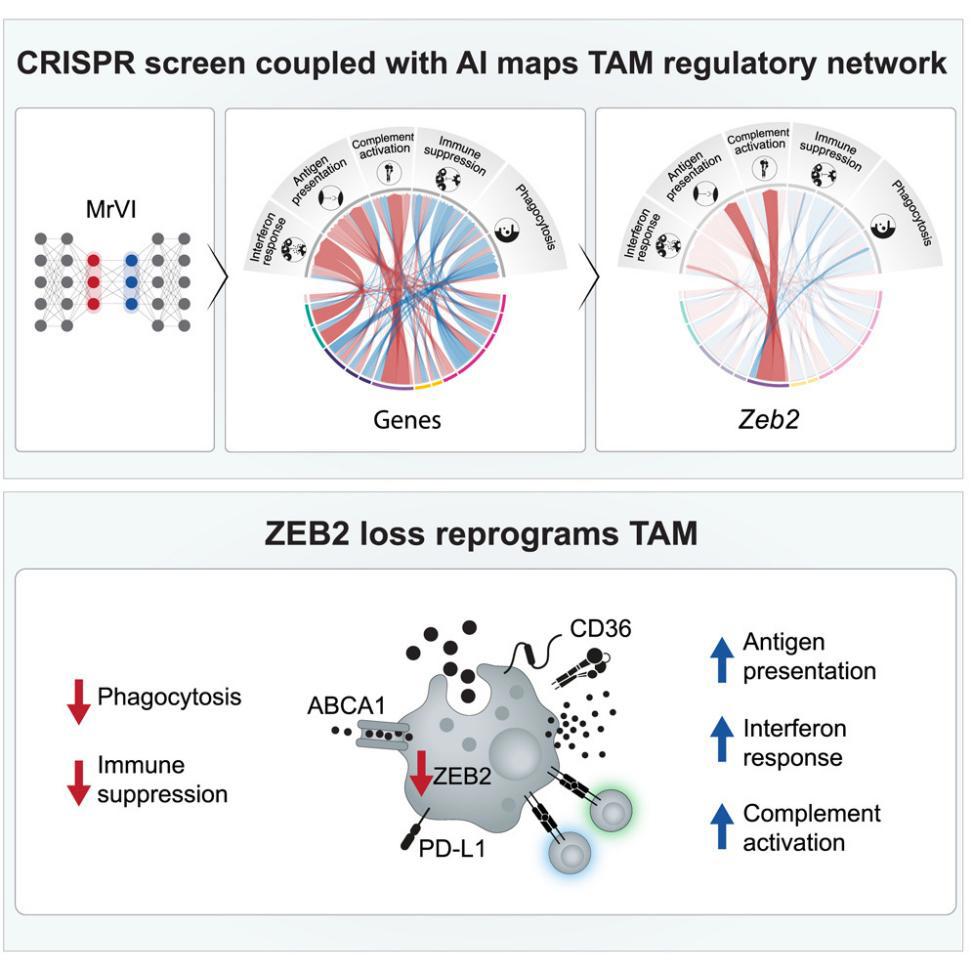
Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are key mediators of tumor immune evasion. However, their regulatory circuits and checkpoints are partially understood. Here, we generated a TAM regulatory network by integrating human tumors single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data with a dedicated CRISPR screen. Using a deep generative model, we constructed a gene perturbation network linking individual candidates with prototypical TAM functions. We identified Zeb2 as the master regulator of TAM programs, orchestrating suppression of type-I interferon response and antigen presentation alongside activation of immune suppression programs. Genetic ablation of ZEB2 reprograms TAM function and identity on the chromatin, RNA, and protein levels. In macrophage-rich human tumors, ZEB2 expression is associated with poor prognosis. Selective Zeb2 in vivo targeting reprograms TAMs and mobilizes systemic T cell responses, achieving robust tumor clearance. Overall, our study generates a detailed roadmap of TAM gene circuits and identifies ZEB2 as a master switch with therapeutic potential.
肿瘤相关巨噬细胞(TAMs)是肿瘤免疫逃逸的关键介导者,但其调控网络与检查点仍未被完全揭示。在本研究通过整合人类肿瘤的单细胞RNA测序(scRNA-seq)数据与专门设计的CRISPR筛选,构建了一个TAM调控网络。借助深度生成模型,建立了一个基因扰动网络,将多个候选基因与TAM的典型功能相互关联。发现 Zeb2 是TAM程序的主调控因子,能够协同抑制I型干扰素反应和抗原呈递功能,并激活免疫抑制通路。ZEB2的基因敲除可在染色质、RNA和蛋白水平上重新编程TAM的功能和特性。在富含巨噬细胞的人类肿瘤中,ZEB2的高表达与不良预后显著相关。在体内选择性靶向Zeb2能够重塑TAM功能,并激活全身性的T细胞免疫反应,从而实现强效的肿瘤清除。总体而言,本研究绘制了TAM基因调控电路的详细图谱,并确立ZEB2作为具有治疗潜力的关键“主控开关”。
22. Spatial determinants of antibody-drug conjugate SHR-A1811 efficacy in neoadjuvant treatment for HER2-positive breast cancer
抗体偶联药物SHR-A1811在HER2阳性乳腺癌新辅助治疗中的空间效应决定因素

复旦大学附属肿瘤医院及其相关学院联合西湖大学、杭州帝普科技公司与上海市预防医学研究院合作完成
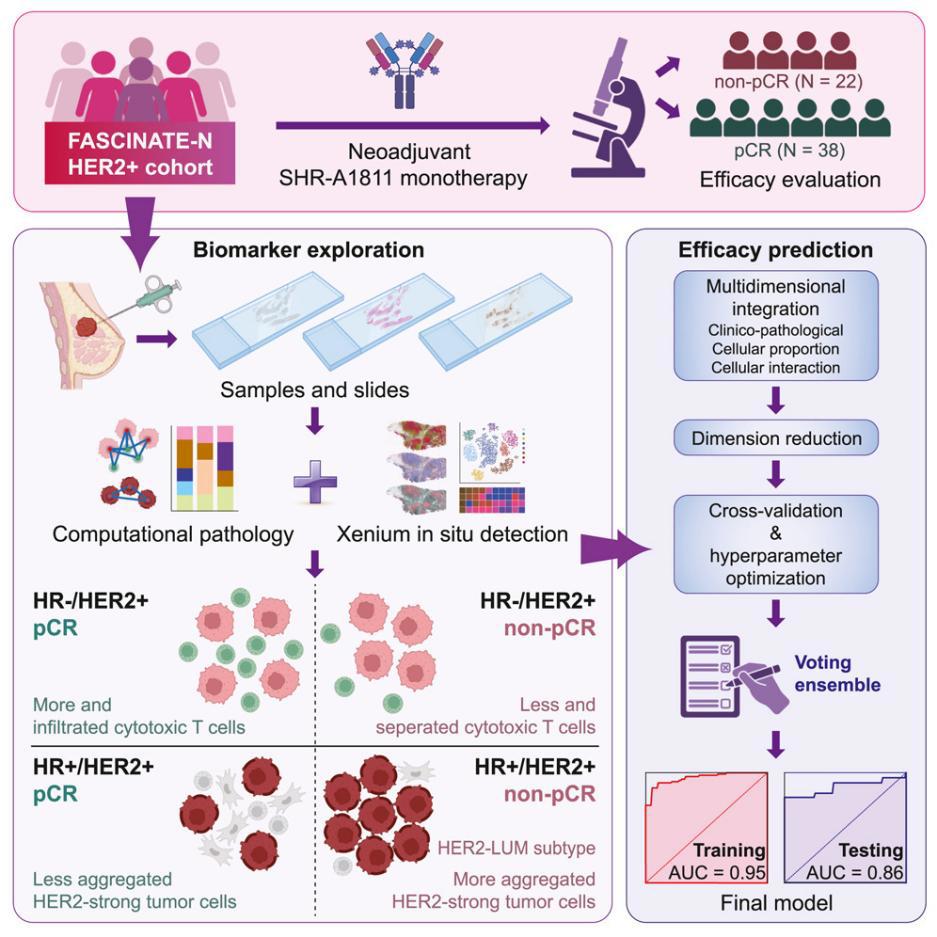
Selecting optimal candidates for next-generation anti-human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) remains challenging. We conduct a prespecified translational study to identify treatment biomarkers in SHR-A1811-treated HER2-positive breast cancer patients from the phase 2 neoadjuvant FASCINATE-N trial using DNA and RNA sequencing, computational pathology, and single-cell in situ spatial imaging. In the hormone receptor (HR)-negative subgroup, a higher proportion and more infiltration of immune cells (i.e., tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes [TILs]), particularly cytotoxic T cells, are associated with better treatment responses. In the HR-positive subgroup, the closeness and aggregation of HER2-strong-positive tumor cells, as opposed to a uniform distribution, are linked to a lower response rate and HER2 luminal-like (HER2-LUM) subtype, which more closely resembles HR+/HER2− breast cancer. In addition, we develop a clinically practical predictive model capable of predicting neoadjuvant treatment responses to SHR-A1811 and other novel ADCs based on clinicopathological characteristics and pathological images.
筛选下一代抗HER2抗体偶联药物(ADC)的最优治疗人群仍具挑战性。本研究为一项预设的转化研究,基于FASCINATE-N II期新辅助临床试验中接受SHR-A1811治疗的HER2阳性乳腺癌患者,通过DNA与RNA测序、计算病理学以及单细胞原位空间成像技术,探索潜在的治疗生物标志物。
在激素受体(HR)阴性亚组中,免疫细胞(即肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞 [TILs])的比例更高、浸润程度更深,尤其是细胞毒性T细胞,与更好的治疗反应显著相关。而在HR阳性亚组中,HER2强阳性肿瘤细胞的“聚集性靠近”分布(相较于均匀分布)与较低的治疗响应率相关,并且表现出类似HR+/HER2−乳腺癌的HER2-LUM亚型特征。此外,我们还建立了一个具有临床实用性的预测模型,可基于临床病理特征和病理图像预测SHR-A1811及其他新型ADC的新辅助治疗响应情况。
23. Radiotherapy promotes cuproptosis and synergizes with cuproptosis inducers to overcome tumor radioresistance
放射治疗可诱导铜死亡,并与铜死亡诱导剂协同作用以克服肿瘤放疗耐受性

美国德克萨斯大学MD安德森癌症中心及其生物医学研究生院联合完成
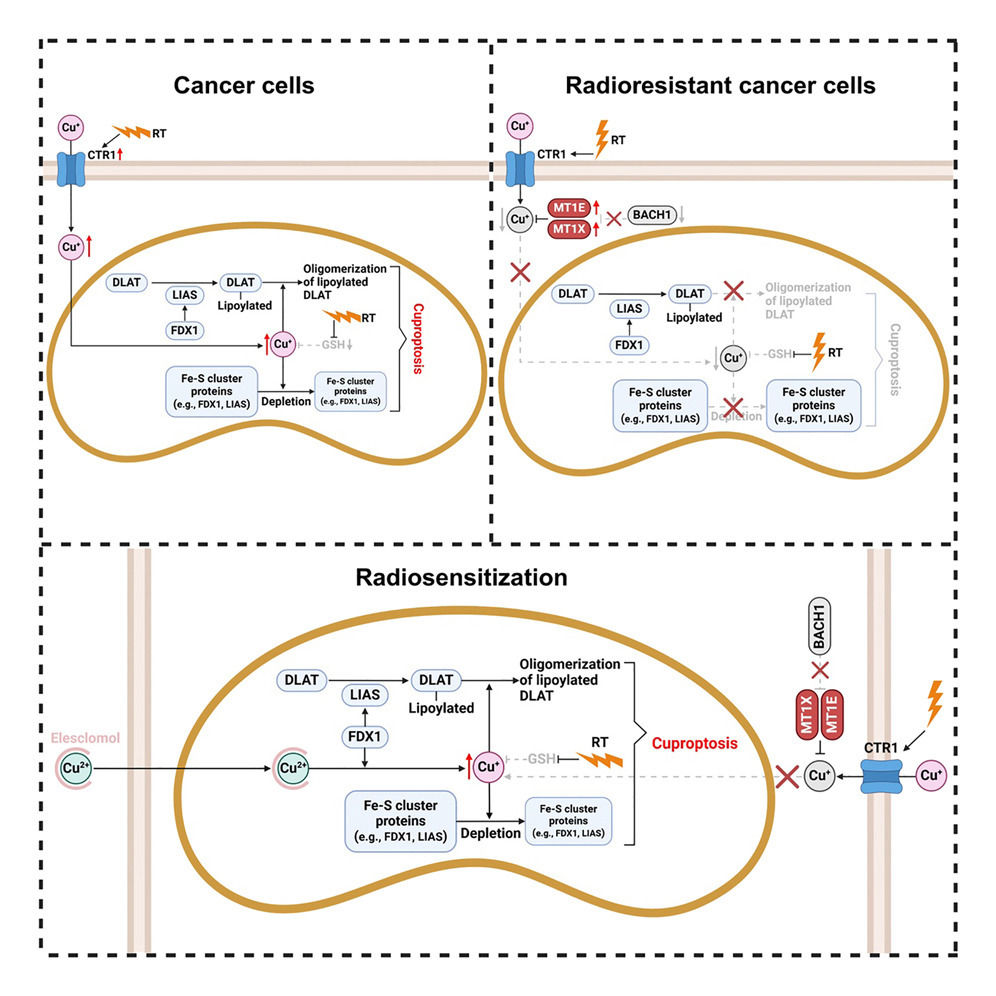
Cuproptosis is a recently identified form of copper-dependent cell death. Here, we reveal that radiotherapy (RT) induces cuproptosis in cancer cells, independent of apoptosis and ferroptosis, and depletes lipoylated proteins and iron-sulfur (Fe-S) cluster proteins—both hallmarks of cuproptosis—in patient tumors. Mechanistically, RT elevates mitochondrial copper levels by upregulating copper transporter 1 (CTR1) and depleting mitochondrial glutathione, a copper chelator, thereby triggering cuproptosis. Integrated analyses of RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) from radioresistant esophageal cancer cells and single-cell RNA-seq from esophageal tumors of patients unresponsive to RT link radioresistance to the downregulation of BTB and CNC homology 1 (BACH1). This downregulation de-represses the expression of copper-sequestering metallothionein (MT) 1E/X, thereby mitigating cuproptosis and contributing to radioresistance. Copper ionophore treatment sensitizes radioresistant cancer cells and cell line- and patient-derived xenografts to RT by potentiating cuproptosis. Our findings unveil a link between RT and cuproptosis and inform a therapeutic strategy to overcome tumor radioresistance by targeting cuproptosis.
铜死亡(Cuproptosis)是一种新近发现的铜依赖性细胞死亡形式。在本研究中,发现放射治疗(RT)可在肿瘤细胞中诱导铜死亡,这一过程独立于细胞凋亡和铁死亡,并在患者肿瘤中导致铜死亡标志物——脂酰化蛋白和铁硫簇(Fe-S)蛋白的耗竭。机制上,RT通过上调铜转运蛋白CTR1并耗竭线粒体谷胱甘肽(一种铜螯合剂),提高线粒体铜水平,从而诱发铜死亡。通过整合放疗耐受的食管癌细胞系的RNA测序数据及对放疗无应答患者的食管肿瘤单细胞RNA测序分析,发现放疗耐受性与转录因子BACH1的下调密切相关。BACH1的下调解除对铜结合金属硫蛋白(MT)1E/X表达的抑制,从而增强铜离子清除能力、抑制铜死亡并促成耐放疗表型。进一步研究显示,铜离子载体治疗可通过增强铜死亡,使放疗耐受的癌细胞以及细胞系来源和患者来源的异种移植瘤对RT重新敏感。综上,该研究揭示了放疗与铜死亡之间的关键联系,并提出通过靶向铜死亡通路来克服肿瘤放疗耐受性的潜在治疗策略。
24. Cancer cell-derived arginine fuels polyamine biosynthesis in tumor-associated macrophages to promote immune evasion
癌细胞来源的精氨酸为肿瘤相关巨噬细胞提供多胺合成原料,促进免疫逃逸

中山大学中山纪念医院、中国科学院杭州医学研究所、浙江省肿瘤医院、汕头市中心医院、广东医科大学附属东莞儿童医院等多家机构共同完成
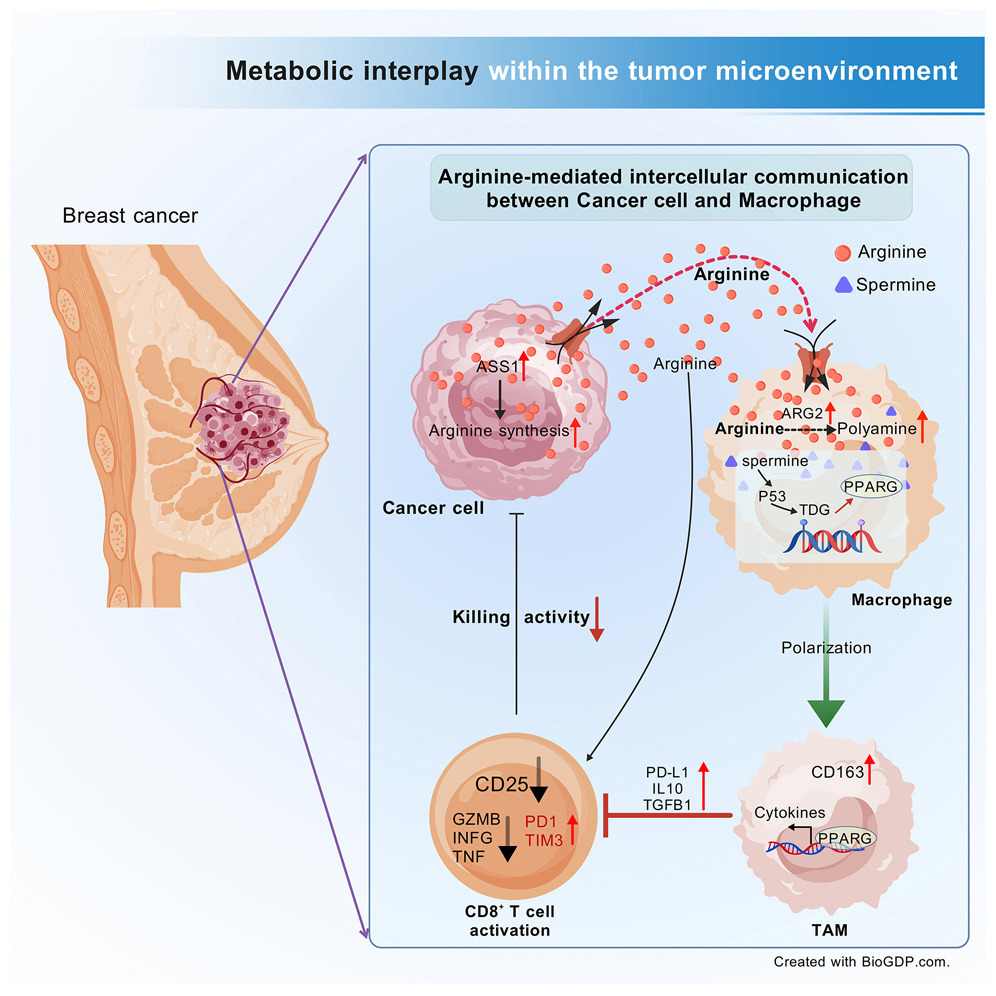
Arginine metabolism reshapes the tumor microenvironment (TME) into a pro-tumor niche through complex metabolic cross-feeding among various cell types. However, the key intercellular metabolic communication that mediates the collective effects of arginine metabolism within the TME remains unclear. Here, we reveal that the metabolic interplay between cancer cells and macrophages plays a dominant role in arginine-driven breast cancer progression. Within the TME, breast cancer cells serve as the primary source of arginine, which induces a pro-tumor polarization of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), thereby suppressing the anti-tumor activity of CD8+ T cells. Notably, this cancer cell-macrophage interaction overrides the arginine-mediated enhancement of CD8+ T cell anti-tumor activity. Mechanistically, polyamines derived from arginine metabolism enhance pro-tumor TAM polarization via thymine DNA glycosylase (TDG)-mediated DNA demethylation, regulated by p53 signaling. Importantly, targeting the arginine-polyamine-TDG axis between cancer cells and macrophages significantly suppresses breast cancer growth, highlighting its therapeutic potential.
精氨酸代谢通过多种细胞类型之间复杂的代谢交互发挥作用,重塑肿瘤微环境(TME),促使其向有利于肿瘤发展的生态位转变。然而,介导TME中精氨酸代谢整体效应的关键细胞间代谢通讯机制仍不清楚。本研究发现,癌细胞与巨噬细胞之间的代谢互作在精氨酸驱动的乳腺癌进展中发挥主导作用。
在TME中,乳腺癌细胞是精氨酸的主要来源,促进肿瘤相关巨噬细胞(TAMs)向促肿瘤表型极化,从而抑制CD8⁺ T细胞的抗肿瘤活性。值得注意的是,这种癌细胞与巨噬细胞之间的代谢互作可削弱精氨酸对CD8⁺ T细胞抗肿瘤效应的增强作用。在机制上,源自精氨酸代谢的多胺通过胸腺嘧啶DNA 糖基化酶(TDG)介导的DNA去甲基化作用,促进TAMs的促肿瘤极化,该过程受p53信号通路调控。重要的是,靶向癌细胞与巨噬细胞之间的“精氨酸-多胺-TDG”代谢轴可显著抑制乳腺癌的生长,显示出良好的治疗潜力。
25. Spatial transcriptomics reveals tryptophan metabolism restricting maturation of intratumoral tertiary lymphoid structures
空间转录组学揭示色氨酸代谢限制肿瘤内三级淋巴结构的成熟

中山大学附属第一医院、深圳华大生命科学研究院(BGI)、中国科学院大学、郑州大学、深圳湾实验室及德国慕尼黑大学联合完成
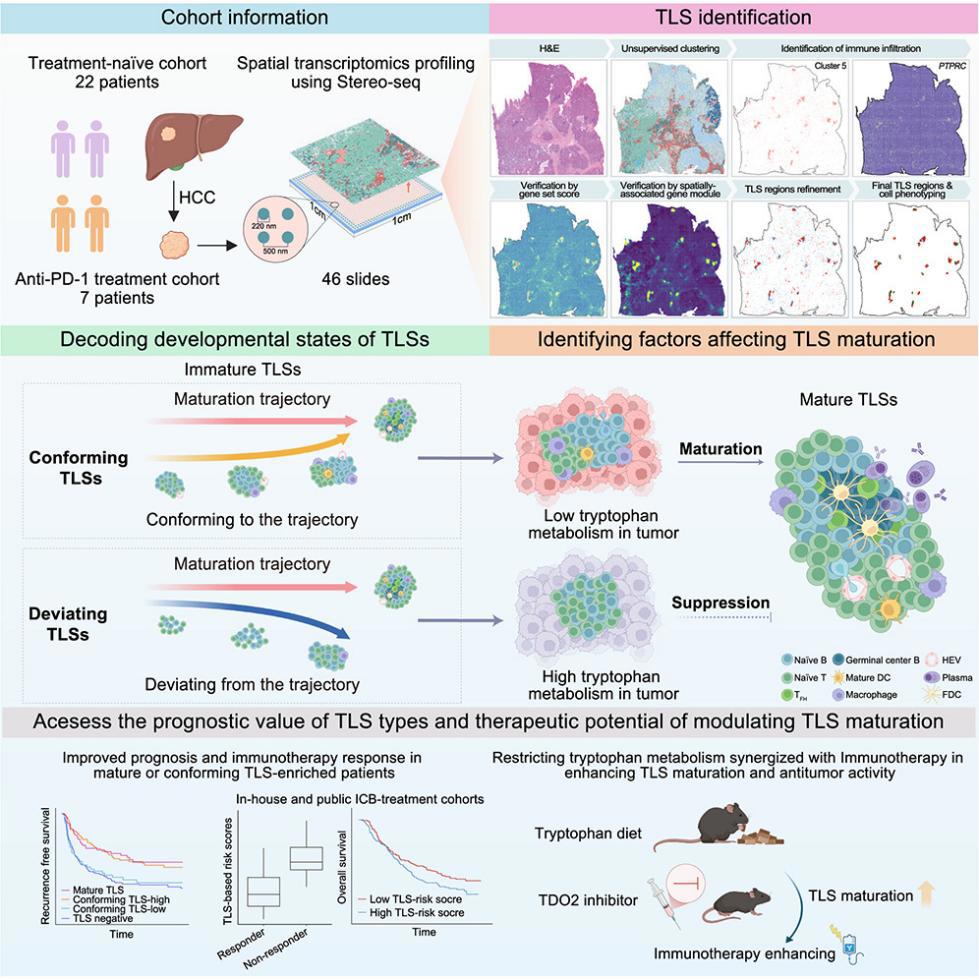
Tertiary lymphoid structures (TLSs) are ectopic lymphoid aggregates found in numerous cancers, often linked to enhanced immunotherapy responses and better clinical outcomes. However, the factors driving TLS maturation are not fully understood. Using near single-cell spatial transcriptomic mapping, we comprehensively profile TLSs under various maturation stages and their microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Based on their developmental trajectories, we classify immature TLSs into two groups: conforming and deviating TLSs. Our findings indicate that conforming TLSs, similar to mature TLSs, possess a niche function for immunotherapy responses, while deviating TLSs do not. We discover that the tryptophan-enriched metabolic microenvironment shaped by malignant cells contributes to the deviation of TLS maturation. Inhibiting tryptophan metabolism promotes intratumoral TLS maturation and enhances tumor control, synergizing with anti-PD-1 treatments. Therefore, promoting TLS maturation represents a potential strategy to improve antitumor responses and immunotherapy outcomes.
三级淋巴结构(TLSs)是存在于多种癌症中的异位淋巴细胞聚集体,通常与增强的免疫治疗反应和更好的临床结局相关。然而,驱动TLS成熟的因素尚未被完全了解。在本研究中,利用近乎单细胞分辨率的空间转录组图谱,全面描绘了肝细胞癌(HCC)中处于不同成熟阶段的TLS及其微环境。根据其发育轨迹,将未成熟TLS分为两类:顺应型TLS(conforming TLSs)和偏离型TLS(deviating TLSs)。研究结果表明,顺应型TLS类似于成熟TLS,具有促进免疫治疗反应的“利基”功能,而偏离型TLS则不具备该功能。同时发现由恶性细胞塑造的富含色氨酸的代谢微环境促使TLS成熟过程发生偏离。抑制色氨酸代谢可促进肿瘤内TLS的成熟,并增强肿瘤控制,与抗PD-1治疗协同发挥作用。因此,促进TLS成熟是一种有前景的策略,可用于增强抗肿瘤反应并改善免疫治疗效果。
26. A niche driven mechanism determines response and a mutation-independent therapeutic approach for myeloid malignancies
由微环境驱动的机制决定了骨髓系统恶性肿瘤的治疗响应,并揭示一种不依赖突变的治疗策略

哥伦比亚大学医学中心、美国纪念斯隆-凯特琳癌症中心、德克萨斯大学MD安德森癌症中心等联合完成
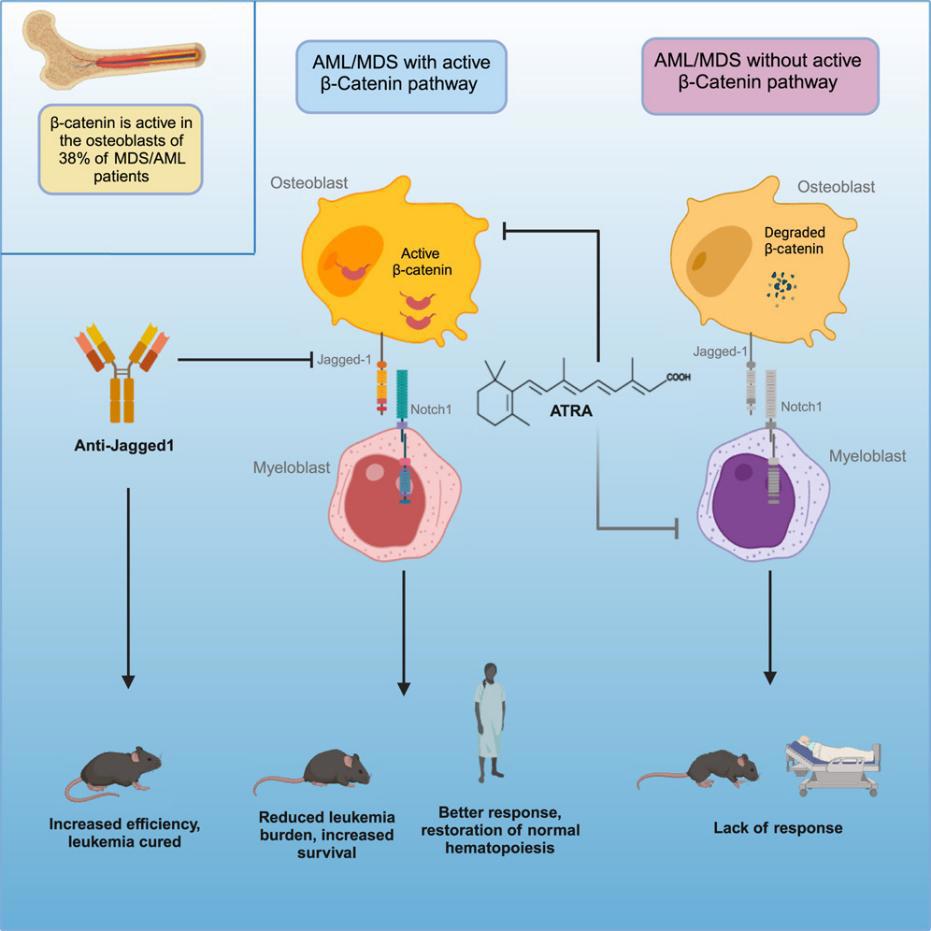
Myeloid cancers such as myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) remain resistant to standard of care (SOC) and targeted therapies. In this study, we demonstrate that responsiveness to therapy is associated with activation of β-catenin-JAG1 in osteoblastic cells of patients treated with all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA). ATRA suppresses β-catenin activity in patients and leukemic mice. Consequently, it inhibits the growth and survival of MDS/AML cells from patients with active β-catenin-JAG1 signaling and promotes their differentiation. This occurs independently of cytogenetics and mutational profile. ATRA also improves disease outcome in mice with no evidence of relapse and a superior safety profile to SOC. A human anti-JAG1 antibody improves efficacy in leukemic mice and patient-derived MDS/AML cells. β-catenin activation provides an explanation for the differential response to ATRA and a mechanistic biomarker for ATRA repurposing in myeloid malignancies, potentially evading relapse and extending across a broad range of cancers.
骨髓增生异常综合征(MDS)和急性髓系白血病(AML)等髓系肿瘤常对标准治疗(SOC)和靶向治疗表现出耐药性。在本研究中,发现治疗反应性与接受全反式维甲酸(ATRA)治疗患者骨生成细胞中β-catenin–JAG1通路的激活状态相关。ATRA可抑制患者和白血病小鼠体内的β-catenin活性,进而抑制具有活跃β-catenin–JAG1信号的MDS/AML细胞的生长与存活,并促进其分化。这一效应与细胞遗传学或突变谱无关。在动物模型中,ATRA改善了疾病结局,无复发证据,并显示出优于标准治疗的安全性。人源抗JAG1抗体在白血病小鼠和患者来源的MDS/AML细胞中也表现出良好疗效。β-catenin的激活不仅解释了ATRA治疗反应的差异性,也可作为ATRA在髓系肿瘤中重新定位治疗用途的机制性生物标志物,具有避免复发并可能扩展至其他癌种的潜力。

汇报人: 孙晓茹
导师:刘世喜 邹剑
审核:李向东、夏轶君、任建君



