原创 夏晓旭 华西医院耳鼻喉科
阅读最新文献,紧跟前沿进展,这是一名研究者必须具备的习惯和要求。我们华西医院耳鼻咽喉头颈外科的硕士、博士研究生和博士后们自2019年以来,每周开展一次文献泛读和文献精读分享会,至今已累计开展了200多次。2023年9月13日开始,本科室陆续将其进行整理,同步推出在线前沿速递和文献解读板块。通过这种学习和分享的方式,使汇报者和大家都能对近期权威期刊发表的高质量研究有所了解,同时也是学习其他优秀研究者思路、方法和理论的良好手段。希望通过这种形式,把科内的分享扩大到所有的读者,一起学习,共同进步!
华西医院耳鼻咽喉头颈外科

【Cancer Cell】2025年1-2月刊论文导读
期刊介绍:
Cancer Cell创刊于2002年,由CELL PRESS出版商出版,收稿方向涵盖医学-肿瘤学全领域,在行业领域中学术影响力很大,属于TOP期刊,国际一流期刊。审议手稿的主要标准是研究是否在回答与自然发生的癌症有关的重要问题方面取得重大进展。影响因子指数48.8。2025年1-3月一共发表50篇,包括Commentary 4篇,Preview 15篇,Review 3篇,Article 23篇,Report 3篇,Correction 2篇。

Jan 13, 2025Volume 43Issue 1p1-160
2025年1月一共发表13篇,包括Commentary 1篇,Preview 4篇,Review 1篇,Article 7篇。
1.Commensal papillomavirus immunity preserves the homeostasis of highly mutated normal skin
共生乳头状瘤病毒免疫维持高度突变的正常皮肤稳态
 美国麻省总医院及哈佛医学院
美国麻省总医院及哈佛医学院
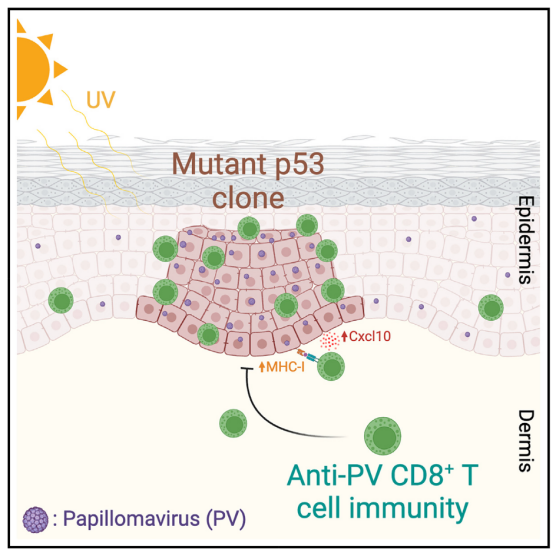
Immunosuppression commonly disrupts the homeostasis of mutated normal skin, leading to widespread skin dysplasia and field cancerization. However, the immune system’s role in maintaining the normal state of mutated tissues remains uncertain. Herein, we demonstrate that T cell immunity to cutaneotropic papillomaviruses promotes the homeostasis of ultraviolet radiation-damaged skin. Mouse papillomavirus (MmuPV1) colonization blocks the expansion of mutant p53 clones in the epidermis in a CD8+ T cell-dependent manner. MmuPV1 activity is increased in p53-deficient keratinocytes, leading to their specific targeting by CD8+ T cells in the skin. Sun-exposed human skin containing mutant p53 clones shows increased epidermal beta-human papillomavirus (β-HPV) activity and CD8+ T cell infiltrates compared with sun-protected skin. The expansion of mutant p53 clones in premalignant skin lesions associates with β-HPV loss. Thus, immunity to commensal HPVs contributes to the homeostasis of mutated normal skin, highlighting the role of virome-immune system interactions in preserving aging human tissues.
机体免疫抑制常常打破突变的正常皮肤稳态,导致广泛的皮肤异型增生和产生癌前病变。然而,免疫系统在维持突变组织正常状态中的具体作用尚不明确。本研究表明,机体针对皮肤共生型HPV的T细胞免疫可维持紫外线损伤的突变皮肤的稳态。小鼠乳头状瘤病毒(MmuPV1)定植可通过CD8⁺ T细胞介导的免疫,抑制表皮中p53突变克隆的扩增。在p53缺失的角化细胞中,MmuPV1的活性增强,使这些细胞更容易被CD8⁺ T细胞特异性清除。并且,相比未受阳光暴露的皮肤,人类日晒皮肤中p53突变克隆的表皮细胞β-HPV活性更高,并伴有更多CD8⁺ T细胞浸润。此外,在癌前皮肤病变中,p53突变克隆的扩增与β-HPV的丧失相关。因此,共生HPV介导的免疫反应有助于维持突变皮肤的稳态,揭示了病毒群与免疫系统相互作用在组织健康维持中的关键作用。
2.EZH2 inhibition enhances T cell immunotherapies by inducing lymphoma immunogenicity and improving T cell function
EZH2抑制可以通过增强淋巴瘤免疫原性和改善T细胞功能提升T细胞免疫疗法的效果

美国康奈尔大学威尔康奈尔医学院血液肿瘤科
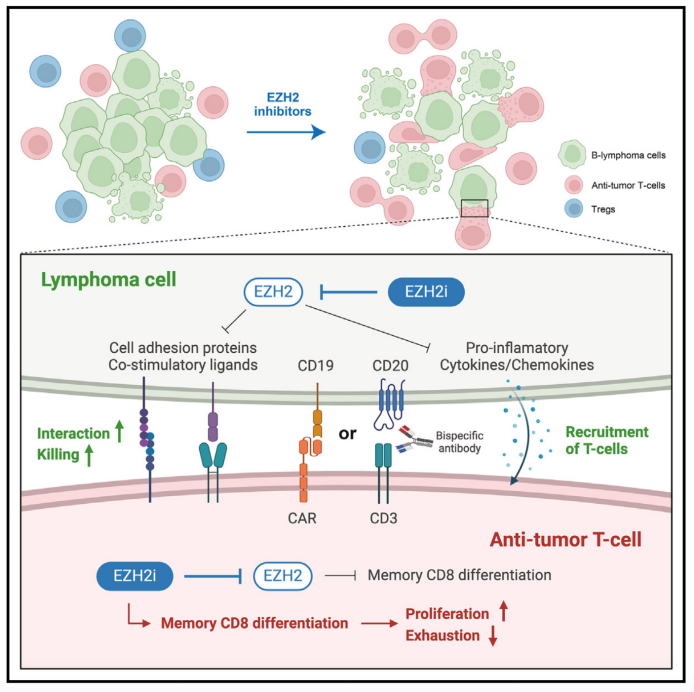
T cell-based immunotherapies have demonstrated effectiveness in treating diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and follicular lymphoma (FL) but predicting response and understanding resistance remains a challenge. To address this, we developed syngeneic models reflecting the genetics, epigenetics, and immunology of human FL and DLBCL. We show that EZH2 inhibitors reprogram these models to re-express T cell engagement genes and render them highly immunogenic. EZH2 inhibitors do not harm tumor-controlling T cells or CAR-T cells. Instead, they reduce regulatory T cells, promote memory chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) CD8 phenotypes, and reduce exhaustion, resulting in a decreased tumor burden. Intravital 2-photon imaging shows increased CAR-T recruitment and interaction within the tumor microenvironment, improving lymphoma cell killing. Therefore, EZH2 inhibition enhances CAR-T cell efficacy through direct effects on CAR-T cells, in addition to rendering lymphoma B cells immunogenic. This approach is currently being evaluated in two clinical trials, NCT05934838 and NCT05994235, to improve immunotherapy outcomes in B cell lymphoma patients.
目前,基于T细胞的免疫疗法已在弥漫性大B细胞淋巴瘤(DLBCL)和滤泡性淋巴瘤(FL)中显示出疗效,但如何预测治疗反应及理解耐药机制仍然是一项挑战。为此,该研究构建了模拟人类FL和DLBCL的遗传、表观遗传及免疫特征的同种异体小鼠模型。研究表明,EZH2抑制剂可重新激活这些淋巴瘤模型中与T细胞相互作用相关的基因表达,提高淋巴瘤细胞免疫原性。同时,EZH2抑制剂不会损害抗肿瘤的T细胞或嵌合抗原受体T细胞(CAR-T),相反,它能减少调节性T细胞,增加记忆型CD8⁺ CAR-T细胞,减少T细胞耗竭,从而降低肿瘤负荷。双光子活体成像进一步显示,EZH2抑制可增加CAR-T细胞在肿瘤微环境中的募集和相互作用,增强淋巴瘤细胞杀伤效果。总的来说,EZH2抑制可通过直接作用于CAR-T细胞,并增强淋巴瘤B细胞的免疫原性,从而提高CAR-T疗法效果。目前,该方法正在两项临床试验(NCT05934838和NCT05994235)中进行评估,以改善B细胞淋巴瘤患者的免疫治疗结局。
3.Neutrophil extracellular traps promote pre-metastatic niche formation in the omentum by expanding innate-like B cells that express IL-10
中性粒细胞胞外捕获网可以通过扩增表达IL-10的先天样B细胞促进大网膜的癌前微环境形成
 美国德克萨斯大学MD安德森癌症中心分子与细胞肿瘤学系
美国德克萨斯大学MD安德森癌症中心分子与细胞肿瘤学系
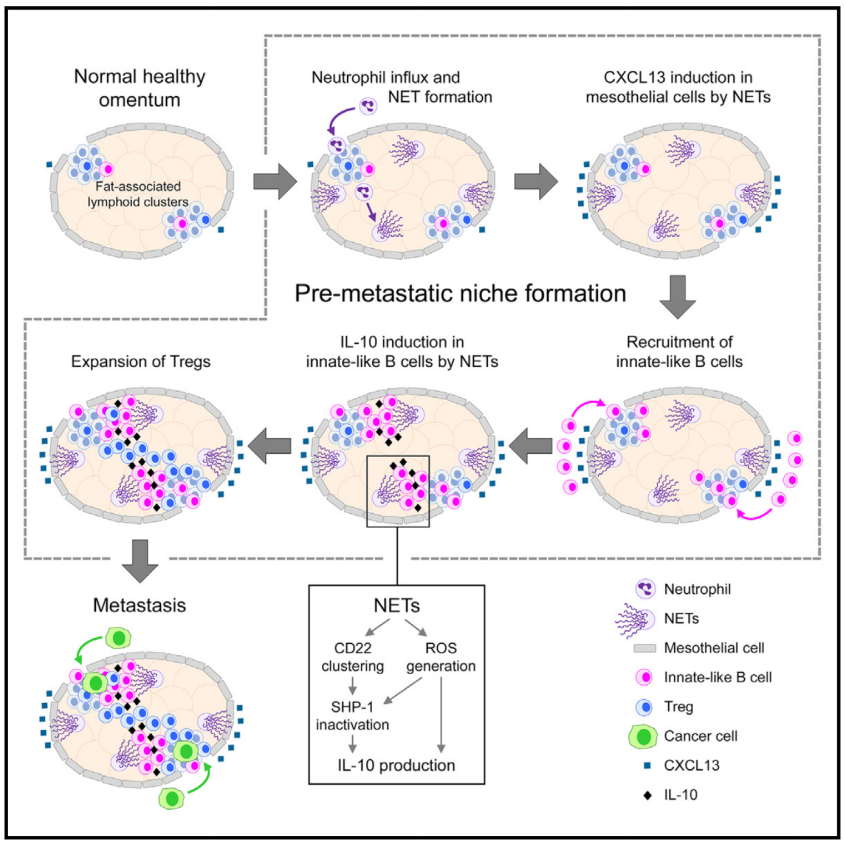
Disseminated cancer cells in the peritoneal fluid often colonize omental fat-associated lymphoid clusters but the mechanisms are unclear. Here, we identify that innate-like B cells accumulate in the omentum of mice and women with early-stage ovarian cancer concomitantly with the extrusion of chromatin fibers by neutrophils called neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). Studies using genetically modified NET-deficient mice, pharmacologic inhibition of NETs, and adoptive B cell transfer show that NETs induce expression of the chemoattractant CXCL13 in the pre-metastatic omentum, stimulating recruitment of peritoneal innate-like B cells that in turn promote expansion of regulatory T cells and omental metastasis through producing interleukin (IL)-10. Ex vivo studies show that NETs elicit IL-10 production in innate-like B cells by inactivating SHP-1, a phosphatase that inhibits B cell activation pathways, and by generating reactive oxygen species. These findings reveal that NETs alter immune cell dynamics in the pre-metastatic omentum, rendering this niche conducive for colonization.
腹腔液中的弥散性癌细胞经常在大网膜脂肪相关淋巴簇定植,但其机制尚不清楚。本研究发现,在早期卵巢癌患者和小鼠模型的大网膜中,先天样B细胞(innate-like B cells)大量积累会伴随中性粒细胞释放染色质纤维(称为中性粒细胞胞外捕获网,NETs)。利用基因修饰的NETs缺陷小鼠、NETs药物抑制及B细胞移植实验,该研究发现NETs可在癌前大网膜中诱导趋化因子CXCL13的表达,促进腹膜先天样B细胞的募集。这些B细胞通过分泌白细胞介素-10促进调节性T细胞(Treg)的扩增,从而促进肿瘤的大网膜转移。另外,体外实验表明,NETs可通过失活SHP-1(抑制B细胞活化的磷酸酶)和产生活性氧(ROS)来诱导先天样B细胞分泌IL-10。本研究揭示了NETs可以改变大网膜中的免疫细胞动态,促进癌细胞定植大网膜的机制。
4.Inhibiting intracellular CD28 in cancer cells enhances antitumor immunity and overcomes anti-PD-1 resistance via targeting PD-L1
抑制癌细胞内CD28可增强抗肿瘤免疫并克服抗PD-1耐药性

中国南开大学生命科学学院免疫学研究所
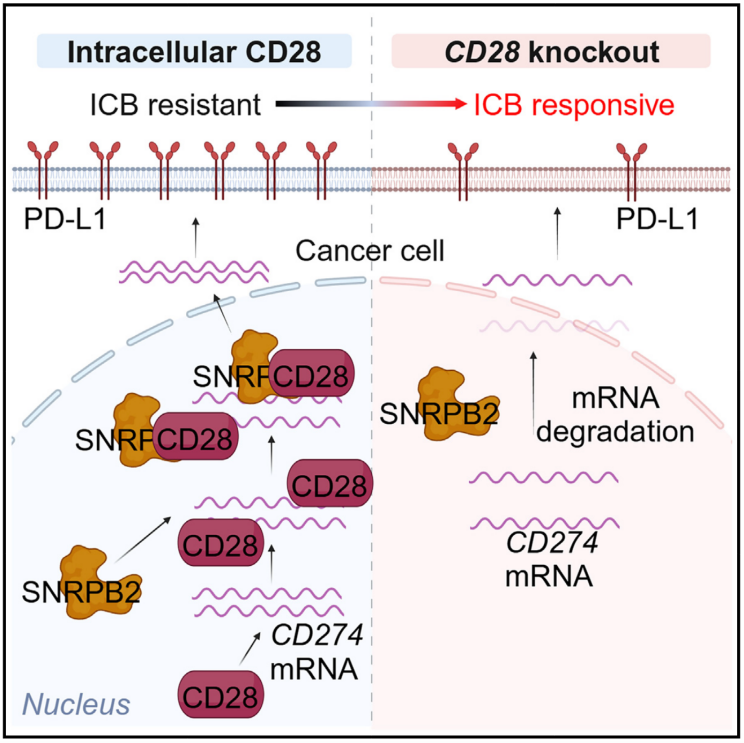
Deciphering mechanisms for cancer immune escape may provide targets for improving immunotherapy efficacy. By in vivo genome-wide CRISPR loss-of-function screening in a mouse model of triple negative breast cancer (TNBC), we uncovered a non-classical function of Cd28 in cancer cells to promote immune escape. Knocking out Cd28 in cancer cells increased infiltration of type I conventional DC (cDC1) and activated tumor-specific CD8+ T cells, and pharmaceutical inducible knockdown of Cd28 inhibited pre-established tumor growth and overcame anti-PD-1 resistance in vivo. Furthermore, high expression of cancer cell CD28 in human TNBC tissues correlated with elevated PD-L1 expression, less CD8+ T cell infiltration, and poor prognosis. Mechanistically, intracellular CD28 directly bound to Cd274 mRNA and recruited spliceosomal factor SNRPB2 to stabilize Cd274 mRNA in nucleus, promoting PD-L1 expression and immune escape. Therefore, disrupting cancer cell CD28-mediated immune escape may provide a potential approach to improve breast cancer immunotherapy.
现有观点认为,揭示癌症免疫逃逸机制有助于改进免疫治疗。因此,该研究通过在三阴性乳腺癌(TNBC)小鼠模型中进行全基因组CRISPR敲除筛选,发现CD28在癌细胞中具有非经典功能,可促进免疫逃逸。敲除癌细胞的CD28可增加I型常规树突细胞(cDC1)的浸润,并激活肿瘤特异性CD8⁺ T细胞。此外,药物诱导的CD28敲低可抑制肿瘤生长,并克服抗PD-1耐药性。通过对人TNBC组织样本的分析显示,高水平的CD28表达与PD-L1高表达、CD8⁺ T细胞浸润减少及不良预后相关。机制研究表明,CD28在癌细胞内直接结合Cd274(PD-L1编码基因)mRNA,并募集剪接因子SNRPB2来稳定Cd274 mRNA,从而促进PD-L1表达并介导免疫逃逸。因此,靶向癌细胞CD28可能成为改善乳腺癌免疫治疗的新策略。
5.Mannose metabolism reshapes T cell differentiation to enhance anti-tumor immunity
甘露糖代谢重塑T细胞分化并增强抗肿瘤免疫

中国苏州系统医学研究所免疫与炎症研究国家重点实验室,中国医学科学院和北京协和医学院
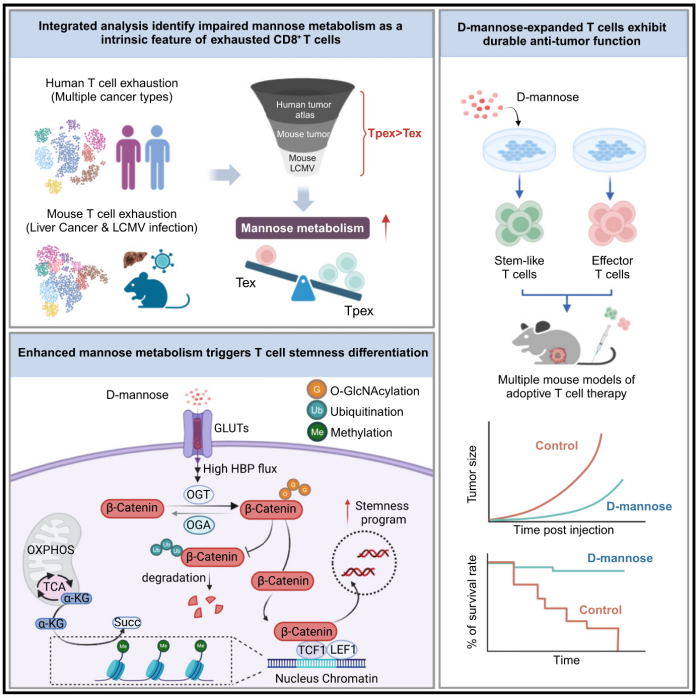
Cellular metabolic status profoundly influences T cell differentiation, persistence, and anti-tumor efficacy. Our single-cell metabolic analyses of T cells reveal that diminished mannose metabolism is a prominent feature of T cell dysfunction. Conversely, experimental augmentation/restoration of mannose metabolism in adoptively transferred T cells via D-mannose supplementation enhances anti-tumor activity and restricts exhaustion differentiation both in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, D-mannose treatment induces intracellular metabolic programming and increases the O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT)-mediated O-GlcNAcylation of β-catenin, which preserves Tcf7 expression and epigenetic stemness, thereby promoting stem-like programs in T cells. Furthermore, in vitro expansion with D-mannose supplementation yields T cell products for adoptive therapy with stemness characteristics, even after extensive long-term expansion, that exhibits enhanced anti-tumor efficacy. These findings reveal cell-intrinsic mannose metabolism as a physiological regulator of CD8+ T cell fate, decoupling proliferation/expansion from differentiation, and underscoring the therapeutic potential of mannose modulation in cancer immunotherapy.
T细胞代谢状态深刻影响T细胞分化、持久性及抗肿瘤功效。该研究通过单细胞代谢分析表明,T细胞功能障碍的一个关键特征是甘露糖代谢的下降。相反,通过D-甘露糖补充剂恢复T细胞甘露糖代谢,可在体内外增强T细胞抗肿瘤活性并抑制T细胞耗竭。机制研究表明,D-甘露糖可诱导细胞内代谢重编程,并增加β-连环蛋白(β-catenin)的O-乙酰氨基葡萄糖转移酶(OGT)介导的糖基化修饰,从而维持Tcf7表达及表观遗传干性(epigenetic stemness),维持T细胞干性状态。此外,D-甘露糖可在体外扩增T细胞,形成干性特征的T细胞群体,即使经历长期扩增后仍具有增强的抗肿瘤功效。本研究揭示了甘露糖代谢作为CD8⁺ T细胞内在调控因子这一事实,并强调了甘露糖代谢调控在癌症免疫治疗中的潜在应用价值。
6.Infiltrating plasma cells maintain glioblastoma stem cells through IgG-Tumor binding
浸润性浆细胞通过IgG-肿瘤结合维持胶质母细胞瘤干细胞的存活

中国江苏省南京市,南京医科大学基础医学学院,江苏省人类功能基因组学重点实验室,细胞生物学系,国家卫生委员会抗体技术重点实验室
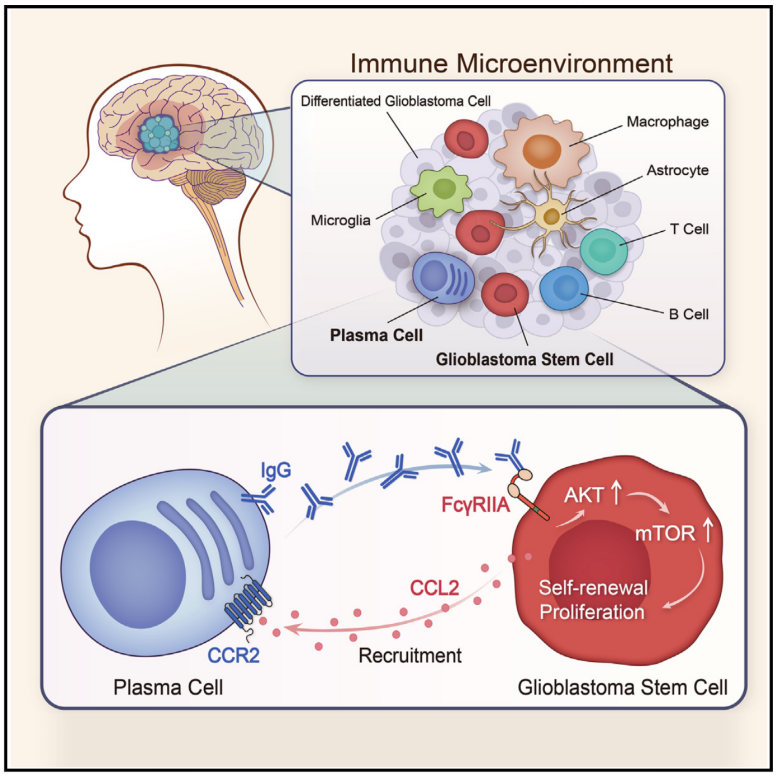
Glioblastoma is a highly aggressive primary brain tumor with glioblastoma stem cells (GSCs) enforcing the intra-tumoral hierarchy. Plasma cells (PCs) are critical effectors of the B-lineage immune system, but their roles in glioblastoma remain largely unexplored. Here, we leverage single-cell RNA and B cell receptor sequencing of tumor-infiltrating B-lineage cells and reveal that PCs are aberrantly enriched in the glioblastoma-infiltrating B-lineage population, experience low level of somatic hypermutation, and are associated with poor prognosis. PCs secrete immunoglobulin G (IgG), which stimulates GSC proliferation via the IgG-FcγRIIA-AKT-mTOR axis. Disruption of IgG-FcγRIIA paracrine communication inhibits GSC proliferation and self-renewal. Glioblastoma-infiltrating PCs are recruited to GSC niches via CCL2-CCR2 chemokine program. GSCs further derive pro-proliferative signals from broadly utilized monoclonal antibody-based immune checkpoint inhibitors via FcγRIIA signaling. Our data generate an atlas of B-lineage cells in glioblastoma with a framework for combinatorial targeting of both tumor cell-intrinsic and microenvironmental dependencies.
胶质母细胞瘤(GBM)是一种具有高度侵袭性的原发性脑肿瘤,胶质母细胞瘤干细胞(GSCs)在肿瘤内的层级结构中发挥着关键作用。浆细胞是B系免疫系统的重要效应细胞,但其在胶质母细胞瘤中的作用尚未得到充分研究。本研究利用单细胞RNA测序和B细胞受体测序技术分析了肿瘤浸润的B系细胞,发现浆细胞在胶质母细胞瘤浸润的B系群体中异常富集,但体细胞超突变水平较低,并与预后不良相关。浆细胞分泌免疫球蛋白G,可以通过IgG-FcγRIIA-AKT-mTOR通路刺激GSC的增殖。破坏IgG-FcγRIIA的旁分泌通信可以抑制GSC的增殖和自我更新。胶质母细胞瘤浸润的浆细胞通过CCL2-CCR2趋化因子程序被招募到GSC的微环境中,这种免疫细胞的招募进一步促进了GSC的增殖和肿瘤进展。与此同时,GSCs通过广泛使用的单克隆抗体免疫检查点抑制剂,激活FcγRIIA信号通路,进一步获取促增殖信号,增强其在肿瘤微环境中的存活和扩展。该研究的数据生成了胶质母细胞瘤中B系细胞的图谱,为同时靶向肿瘤细胞内在依赖性和微环境依赖性提供了框架。
7.Daily glucocorticoids promote glioblastoma growth and circadian synchrony to the host
每日糖皮质激素促进胶质母细胞瘤生长并同步宿主昼夜节律

美国圣路易斯华盛顿大学生物学系
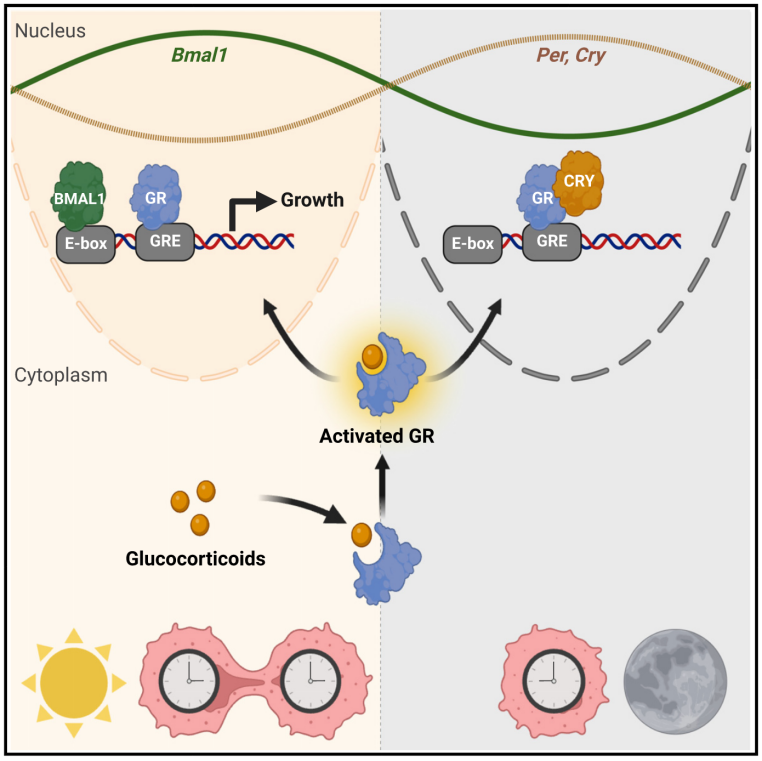
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most common primary malignant brain tumor in adults with a poor prognosis despite aggressive therapy. Here, we hypothesized that daily host signaling regulates tumor growth and synchronizes circadian rhythms in GBM. We find daily glucocorticoids promote or suppress GBM growth through glucocorticoid receptor (GR) signaling depending on time of day and the clock genes, Bmal1 and Cry. Blocking circadian signals, like vasoactive intestinal peptide or glucocorticoids, dramatically slows GBM growth and disease progression. Analysis of human GBM samples from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) shows that high GR expression significantly increases hazard of mortality. Finally, mouse and human GBM models have intrinsic circadian rhythms in clock gene expression in vitro and in vivo that entrain to the host through glucocorticoid signaling, regardless of tumor type or host immune status. We conclude that GBM entrains to the circadian circuit of the brain, modulating its growth through clock-controlled cues, like glucocorticoids.
胶质母细胞瘤(GBM)是成人最常见的原发性恶性脑肿瘤,经过积极治疗的患者预后仍然不好。本研究假设宿主的每日信号(指24小时内的激素变化、代谢变化等等)会调控胶质母细胞瘤生长并同步肿瘤的昼夜节律。结果发现,每日糖皮质激素通过糖皮质激素受体(GR)信号调控胶质母细胞瘤的生长,且此过程依赖于一天中的时钟基因Bmal1和Cry的表达。并且,通过阻断昼夜节律信号,如血管活性肠肽或糖皮质激素,可以显著减缓胶质母细胞瘤的生长和疾病进程。通过对癌症基因组图谱(TCGA)的胶质母细胞瘤样本进行分析,研究发现高表达GR显著增加了患者死亡风险。最后,研究在鼠和人类胶质母细胞瘤的体内外模型中都观察到内在的昼夜节律时钟基因表达,这一节律通过糖皮质激素信号与宿主同步,不受肿瘤类型和宿主免疫状态的影响。总的来说,研究发现,胶质母细胞瘤能通过同步宿主大脑的昼夜节律系统,调节自身生长,并受到糖皮质激素等时钟控制信号的调控。
Feb 10, 2025Volume 43, Issue 2, p161-316
2025年2月一共发表14篇,包括Commentary 1篇,Preview 5篇,Review 1篇,Article 6篇,Report 1篇。
8.Classification of non-TCGA cancer samples to TCGA molecular subtypes using compact feature sets
使用精简特征集将未分型的非TCGA癌症样本分类到TCGA分子亚型
美国俄勒冈健康与科学大学
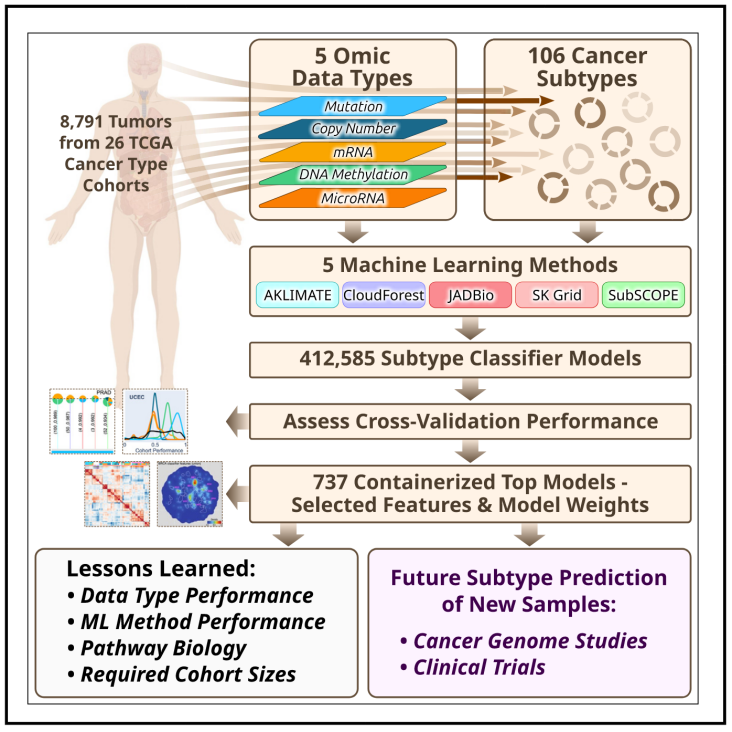
Molecular subtypes, such as defined by The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), delineate a cancer’s underlying biology, bringing hope to inform a patient’s prognosis and treatment plan. However, most approaches used in the discovery of subtypes are not suitable for assigning subtype labels to new cancer specimens from other studies or clinical trials. Here, we address this barrier by applying five different machine learning approaches to multi-omic data from 8,791 TCGA tumor samples comprising 106 subtypes from 26 different cancer cohorts to build models based upon small numbers of features that can classify new samples into previously defined TCGA molecular subtypes—a step toward molecular subtype application in the clinic. We validate select classifiers using external datasets. Predictive performance and classifier-selected features yield insight into the different machine-learning approaches and genomic data platforms. For each cancer and data type we provide containerized versions of the top-performing models as a public resource.
TCGA(The Cancer Genome Atlas)定义的分子亚型能够揭示癌症的生物学特征,并为患者的预后和治疗方案提供指导。然而,大多数分子亚型的检测方法在其他研究或临床试验中的新癌症样本不适用。因此,本研究采用5种不同的机器学习方法,对来自 TCGA 的 8,791 例肿瘤样本(涵盖 26 种癌症队列中的 106 个分子亚型)进行分析,以筛选出少量但关键的分子特征,并构建高效分类模型,从而准确分类新样本并匹配至TCGA已定义的分子亚型。这一方法为分子亚型在临床中的应用迈出了重要一步。该研究还使用外部数据集验证了部分分类模型,并且针对不同类型的癌症和多组学数据,筛选出表现最优的机器学习模型,同时将这些模型打包成容器化(containerized)版本,作为公共资源供研究人员使用。
9.Targeting P4HA1 promotes CD8+ T cell progenitor expansion toward immune memory and systemic anti-tumor immunity
靶向P4HA1能促进CD8+ T细胞祖细胞扩增,增强免疫记忆并激活系统性抗肿瘤免疫

新加坡基因组研究所
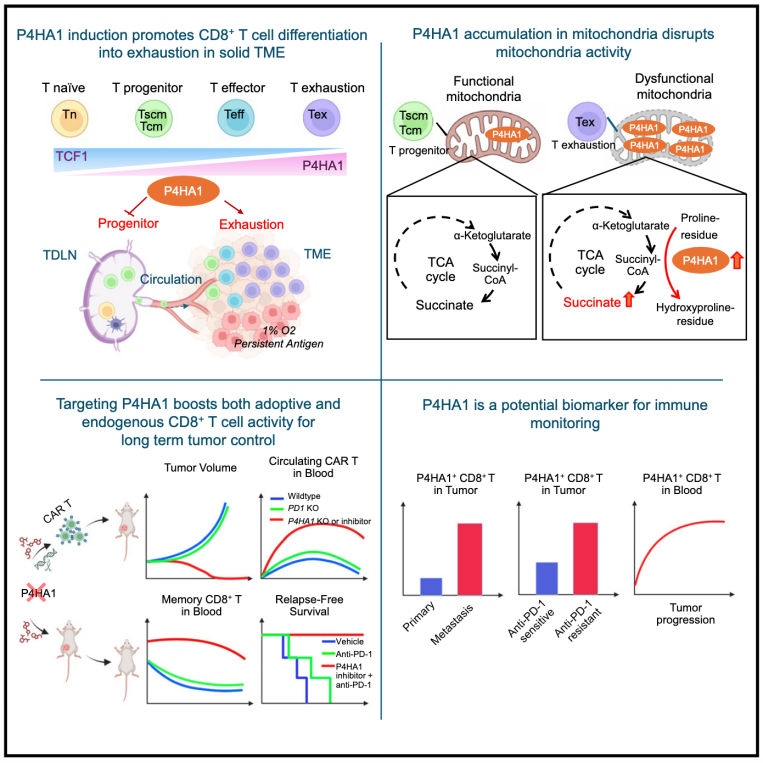
Successful immunotherapy relies on both intratumoral and systemic immunity, which is yet to be achieved for most patients with cancer. Here, we identify P4HA1, encoding prolyl 4-hydroxylase 1, as a crucial regulator of CD8+ T cell differentiation strongly upregulated in tumor-draining lymph nodes (TDLNs) and hypoxic tumor microenvironment. P4HA1 accumulates in mitochondria, disrupting the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle through aberrant α-ketoglutarate and succinate metabolism, promoting mitochondria unfitness and exhaustion while suppressing progenitor expansion. Targeting P4HA1 enhances both adoptive and endogenous TCF1+ CD8+ T progenitor expansion while mitigating the development of exhaustion in the tumor, TDLN, and blood, enabling a notable and durable systemic anti-cancer immunity. We propose that P4HA1 induction in CD8+ T cells in cancer orchestrates an immune-escape program, offering a T cell-directed target for system immunotherapy in solid tumors.
成功的免疫治疗需要同时激活肿瘤内免疫和全身免疫,但目前大多数癌症患者未能实现这一目标。本研究鉴定了P4HA1(编码脯氨酰4-羟化酶1)在CD8+ T细胞分化中的关键调控作用,该基因在肿瘤引流淋巴结(TDLNs)和缺氧的肿瘤微环境中显著上调。P4HA1通常在线粒体内积累,破坏三羧酸循环,导致α-酮戊二酸和琥珀酸代谢异常,从而诱导线粒体功能障碍和T细胞衰竭,同时抑制T细胞祖细胞的扩增。通过靶向抑制P4HA1,可增强TCF1+ CD8+ T祖细胞(一种耗竭T细胞的前体)的扩增,减轻T细胞在肿瘤、TDLN和外周血液中的衰竭程度,最终激发持久的系统性抗肿瘤免疫。本研究提出,P4HA1在CD8+ T细胞中的表达可驱动癌症相关的免疫逃逸程序,为实体瘤的T细胞定向免疫治疗提供了潜在靶点。
10.Dynamics of molecular heterogeneity in high-risk luminal breast cancer—From intrinsic to adaptive subtyping
高危的激素受体阳性乳腺癌的分子异质性动态变化——从固有亚型到适应性亚型
德国马尔堡大学病理学研究所
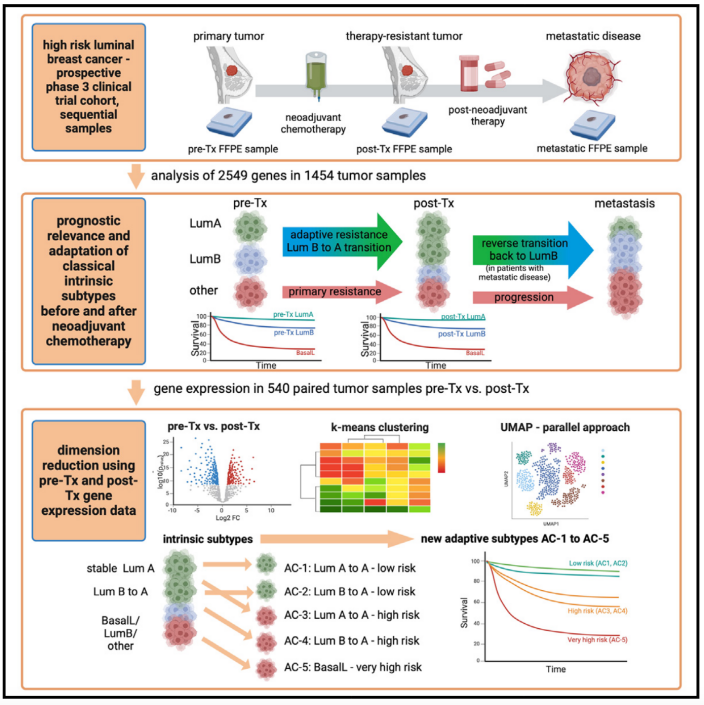
We evaluate therapy-induced molecular heterogeneity in longitudinal samples from high-risk, hormone-receptor positive/HER2-negative breast cancer patients with residual tumor after neoadjuvant chemotherapy from the Penelope-B trial (NCT01864746; EudraCT 2013-001040-62). Intrinsic subtypes are prognostic in pre-therapeutic (Tx) samples (n = 629, p < 0.0001) and post-Tx residual tumors (n = 782, p < 0.0001). After neoadjuvant chemotherapy, a shift of intrinsic subtypes is observed from pre-Tx luminal (Lum) B to post-Tx LumA, with reverse transition back to LumB in metastases. In a combined analysis of 540 paired pre-Tx and post-Tx samples, we identify five adaptive clusters (AC-1–5) based on transcriptomic changes before and after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. These AC-subtypes are prognostic beyond classical intrinsic subtyping, categorizing patients into groups with excellent prognosis (AC-1 and AC-2), poor prognosis (AC-3 and AC-4), and very poor prognosis (AC-5, enriched for basal-like subtype). Our analysis provides a basis for an extended molecular classification of breast cancer patients and improved identification of high-risk patient populations.
本研究分析了Penelope-B试验(NCT01864746;EudraCT 2013-001040-62)中高危的乳腺癌患者,包括激素受体阳性/HER2阴性乳腺癌患者的纵向肿瘤样本,以评估新辅助化疗后肿瘤的分子异质性变化。研究发现,固有分子亚型在新辅助化疗前(n=629,p<0.0001)和治疗后残留肿瘤(n=782,p<0.0001)均具有重要的预后价值。具体而言,在接受新辅助化疗后,肿瘤固有亚型发生转换,表现为从治疗前的Luminal B转变为治疗后的Luminal A,而在肿瘤转移过程中又会逆向转换回Luminal B。此外,在540对配对的治疗前后样本中,该研究基于转录组学变化把乳腺癌分成五种适应性亚型(AC-1至AC-5)。这些适应性亚型的分类相较于传统固有亚型更具预后评估价值,能够将患者分为不同的风险组:AC-1和AC-2预后良好,AC-3和AC-4预后较差,AC-5(富含基底样亚型)预后最差。该研究为乳腺癌的分子分类提供了新的依据,并有助于更精准地识别高风险患者群体。
11.Contrasting cytotoxic and regulatory T cell responses underlying distinct clinical outcomes to anti-PD-1 plus lenvatinib therapy in cancer
抗PD-1联合仑伐替尼治疗癌症的不同临床结局背后的细胞毒性T细胞与调节性T细胞反应对比

中国上海交通大学医学院附属仁济医院
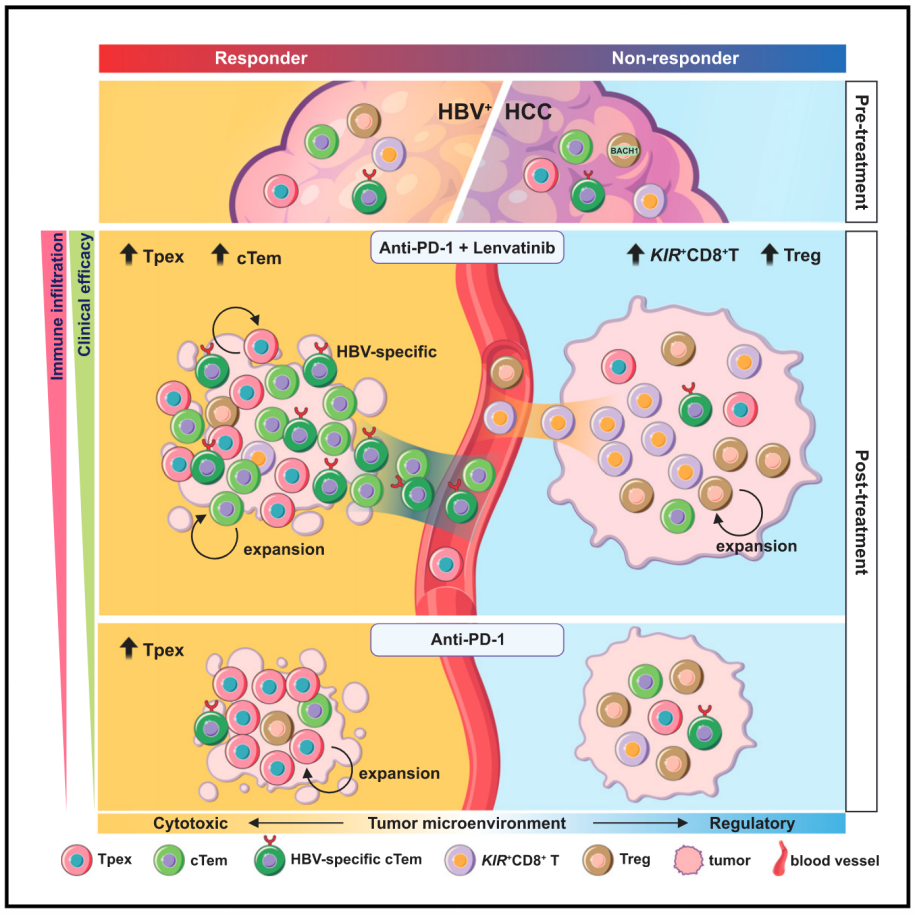
Combination of anti-PD-1 with lenvatinib showed clinical efficacy in multiple cancers, yet the underlying immunological mechanisms are unclear. Here, we compared T cells in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients before and after combination treatment using single-cell transcriptomics and T cell receptor (scTCR) clonotype analyses. We found that tumor-infiltrating GZMK+ CD8+ effector/effector memory T (Teff/Tem) cells, showing a favorable response to combination therapy, comprise progenitor exhausted T (Tpex) cells and also unappreciated circulating Tem (cTem) cells enriched with hepatitis B virus (HBV) specificity. Further integrated analyses revealed that cTem cells are specifically associated with responsiveness to the combination therapy, whereas Tpex cells contribute to responses in both combination therapy and anti-PD-1 monotherapy. Notably, an underexplored KIR+ CD8+ T cell subset in the tumor and FOXP3+ CD4+ regulatory T cells are specifically enriched in non-responders after the combination therapy. Our study thus elucidated T cell subsets associated with clinical benefits and resistance in cancer immunotherapy.
抗PD-1联合仑伐替尼在多种癌症中表现出临床疗效,但其免疫学机制尚不清楚。本研究采用单细胞转录组学和单细胞T细胞受体测序(scTCR)进行T细胞克隆分析,对接受联合治疗的肝细胞癌患者的治疗前后T细胞群体进行了比较。研究发现,肿瘤浸润的GZMK+ CD8+效应/记忆T细胞群体(Teff/Tem)对联合治疗具有良好应答,这一群体包括衰竭前体T细胞(Tpex)和循环效应记忆T细胞(cTem),后者富含针对乙型肝炎病毒(HBV)的特异性T细胞。进一步分析表明,cTem细胞与联合治疗的疗效密切相关,而Tpex细胞不仅参与联合治疗的应答,也在抗PD-1单药治疗中起作用。此外,研究还发现,KIR+ CD8+ T细胞和FOXP3+ CD4+调节性T细胞在治疗无应答者中显著富集。本研究揭示了与癌症免疫治疗疗效相关的T细胞亚群,为优化联合免疫治疗策略提供了新的依据。
12.Adiponectin reduces immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced inflammation without blocking anti-tumor immunity
脂联素可减少免疫检查点抑制剂(ICI)引起的炎症,并且不会削弱抗肿瘤免疫

德国弗莱堡大学医学院
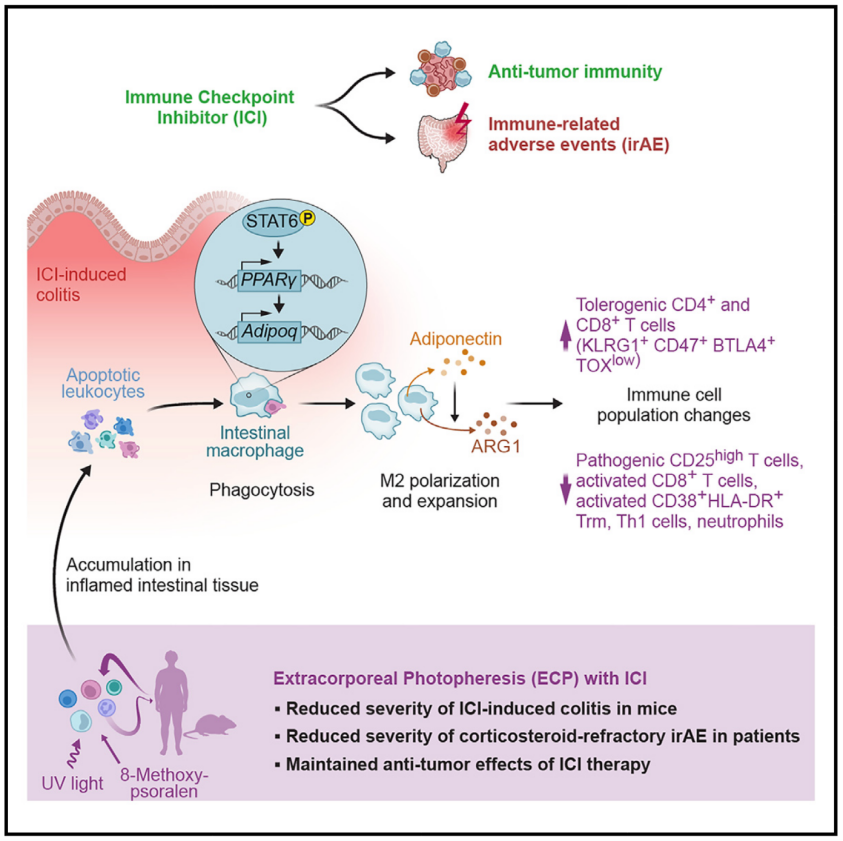
Immune-related adverse events (irAEs) in cancer patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) cause morbidity and necessitate cessation of treatment. Comparing irAE treatments, we find that anti-tumor immunity is preserved in mice after extracorporeal photopheresis (ECP) but reduced with glucocorticosteroids, TNFα blockade, and α4β7-integrin inhibition. Local adiponectin production elicits a tissue-specific effect by reducing pro-inflammatory T cell frequencies in the colon while sparing tumor-specific T cell development. A prospective phase-1b/2 trial (EudraCT-No.2021-002073-26) with 14 patients reveals low ECP-related toxicity. Overall response rate for all irAEs is 92% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 63.97%–99.81%); colitis-specific complete remission rate is 100% (95% CI: 63.06%–100%). Glucocorticosteroid dosages could be reduced for all patients after ECP therapy. The ECP-adiponectin axis reduces intestinal tissue-resident memory T cell activation and CD4+IFN-γ+ T cells in patients with ICI-induced colitis without evidence of loss of anti-tumor immunity. In conclusion, we identify adiponectin as an immunomodulatory molecule that controls ICI-induced irAEs without blocking anti-tumor immunity.
癌症患者接受免疫检查点抑制剂(ICI)治疗后,免疫相关不良事件(irAEs)可能导致严重的副作用,甚至需要终止治疗。本研究比较了不同irAE治疗方法对抗肿瘤免疫的影响,发现体外光动力疗法(ECP)不会削弱抗肿瘤免疫,而糖皮质激素、TNFα抑制剂和α4β7整合素抑制剂则会抑制抗肿瘤免疫。研究进一步发现,局部脂联素可通过降低结肠内促炎T细胞的比例来缓解炎症,同时保留肿瘤特异性T细胞的活性。在一项I/II期临床试验(EudraCT-No.2021-002073-26)中,14名患者接受ECP治疗后,irAEs的总体缓解率达92%(95% CI: 63.97%-99.81%),而ICI诱导的结肠炎的完全缓解率为100%(95% CI: 63.06%-100%),并且所有患者在ECP治疗后均减少了糖皮质激素的使用。本研究主要揭示了,脂联素是一种重要的免疫调节分子,可控制ICI诱导的irAEs,而不会影响抗肿瘤免疫。
13.A constitutive interferon-high immunophenotype defines response to immunotherapy in colorectal cancer
高水平干扰素免疫表型决定结直肠癌对免疫治疗的应答
 英国弗朗西斯·克里克研究所
英国弗朗西斯·克里克研究所
Fewer than 50% of metastatic deficient mismatch repair (dMMR) colorectal cancer (CRC) patients respond to immune checkpoint inhibition (ICI). Identifying and expanding this patient population remains a pressing clinical need. Here, we report that an interferon-high immunophenotype locally enriched in cytotoxic lymphocytes and antigen-presenting macrophages is required for response. This immunophenotype is not exclusive to dMMR CRCs but comprises a subset of MMR proficient (pMMR) CRCs. Single-cell spatial analysis and in vitro cell co-cultures indicate that interferon-producing cytotoxic T cells induce overexpression of antigen presentation in adjacent macrophages and tumor cells, including MHC class II invariant chain CD74. dMMR CRCs expressing high levels of CD74 respond to ICI and a subset of CD74 high pMMR CRC patients show better progression free survival when treated with ICI. Therefore, CD74 abundance can identify the constitutive interferon-high immunophenotype determining clinical benefit in CRC, independently of tumor mutational burden or MMR status.
尽管错配修复缺陷(dMMR)的转移性结直肠癌(CRC)患者对免疫检查点抑制剂有较高应答率,但仍有超过50%的患者无应答。本研究发现,免疫细胞高水平干扰素的免疫表型能够促进细胞毒性淋巴细胞和抗原呈递巨噬细胞在局部肿瘤微环境中的富集,并且这一表型不仅限于dMMR CRC,还存在于部分错配修复正常(pMMR)的CRC患者中。单细胞空间分析和细胞共培养实验表明,IFN-γ+的细胞毒性T细胞可诱导邻近巨噬细胞和肿瘤细胞的抗原呈递能力增强,尤其是MHC II分子CD74的表达。研究还发现,在dMMR CRC中,高CD74表达的患者对ICI治疗更敏感,而在pMMR CRC中,CD74高表达的患者也表现出更好的无进展生存期(PFS)。因此,CD74表达水平可作为CRC患者对ICI治疗应答的潜在生物标志物,并且与肿瘤突变负荷或错配修复(MMR)状态无关。
 Mar 10, 2025 Volume 43Issue 3p317-574
Mar 10, 2025 Volume 43Issue 3p317-574
2025年3月一共发表14篇,包括Commentary 2篇,Preview 6篇,Review 1篇,Article 10篇,Report 2篇,Correction 2篇。
14.Low-dose irradiation of the gut improves the efficacy of PD-L1 blockade in metastatic cancer patients
肠道低剂量辐射可提高PD-L1阻断疗法在转移性癌症患者中的疗效
法国古斯塔夫·鲁西癌症中心
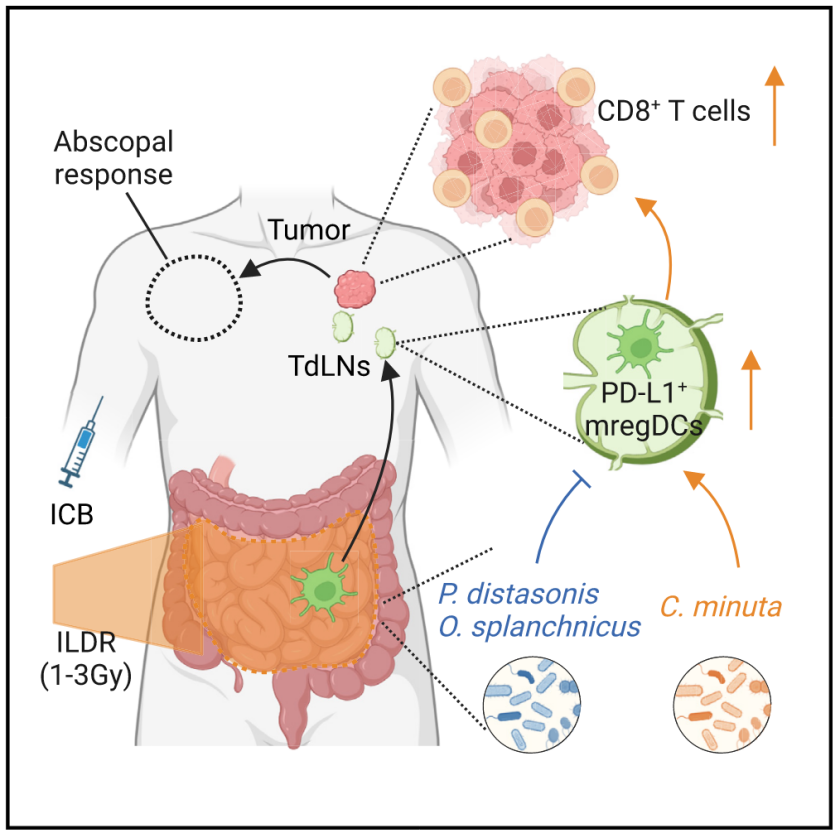
The mechanisms governing the abscopal effects of local radiotherapy in cancer patients remain an open conundrum. Here, we show that off-target intestinal low-dose irradiation (ILDR) increases the clinical benefits of immune checkpoint inhibitors or chemotherapy in eight retrospective cohorts of cancer patients and in tumor-bearing mice. The abscopal effects of ILDR depend on dosimetry (≥1 and ≤3 Gy) and on the metabolic and immune host-microbiota interaction at baseline allowing CD8+ T cell activation without exhaustion. Various strains of Christensenella minuta selectively boost the anti-cancer efficacy of ILDR and PD-L1 blockade, allowing emigration of intestinal PD-L1-expressing dendritic cells to tumor-draining lymph nodes. An interventional phase 2 study provides the proof-of-concept that ILDR can circumvent resistance to first- or second-line immunotherapy in cancer patients. Prospective clinical trials are warranted to define optimal dosimetry and indications for ILDR to maximize its therapeutic potential.
局部放射治疗在癌症患者中产生旁观效应的机制仍然是一个未解之谜。本研究八个回顾性癌症患者队列及肿瘤小鼠模型中发现,离靶的肠道低剂量照射(ILDR)能够提高免疫检查点抑制剂或化疗的临床疗效。ILDR 的旁观效应取决于放射剂量(≥1 Gy且 ≤3 Gy),以及基线状态下的宿主-微生物组相互作用对代谢和免疫的影响,这些因素促进了 CD8+ T 细胞的活化而不会导致T细胞衰竭。研究发现,Christensenella minuta(一种厌氧性革兰氏阴性杆菌)的不同菌株会选择性增强 ILDR 与抗PD-L1的抗癌疗效,并促进肠道中表达PD-L1的树突状细胞迁移至肿瘤引流淋巴结。一项 II期干预性研究表明,ILDR 可以克服癌症患者对一线或二线免疫治疗的耐药性。未来需要开展前瞻性临床试验,以优化 ILDR 的剂量和适应症,从而最大化其治疗潜力。
15.Single-cell multi-stage spatial evolutional map of esophageal carcinogenesis
单细胞多阶段空间进化图谱解析食管癌发生发展过程
 华中科技大学同济医学院公共卫生学院环境与健康重点实验室
华中科技大学同济医学院公共卫生学院环境与健康重点实验室
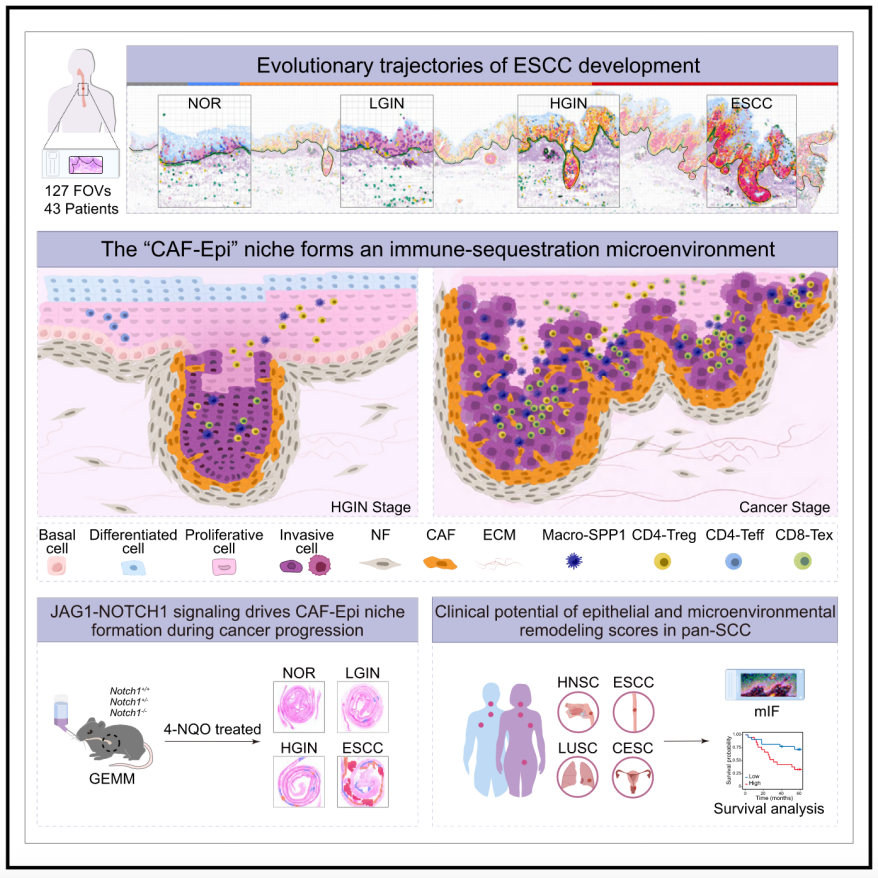
Cancer development involves the co-evolution of cancer cells and their surrounding microenvironment, yet the dynamics of this interaction within the physical architecture remains poorly understood. Here, we present a spatial transcriptomic map at single-cell resolution, encompassing 127 multi-stage fields of view from 43 patients, to chart the evolutionary trajectories of human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). By analyzing 6.4 million cells, we reveal that ESCC progression is driven by a proliferative epithelial cell subpopulation that acquires dedifferentiated and invasive characteristics. At the late precancerous stage, these cells disrupt the epithelial-stromal interface and recruit normal fibroblasts via JAG1-NOTCH1 signaling, transforming them into cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs). This interaction leads to the formation of a “CAF-Epi” (CAF and epithelial cell) niche at the tumor edge that shields the tumor from immune surveillance. The CAF-Epi niche formation is a key indicator of progression in ESCC and other squamous cell carcinomas and patient outcomes.
癌症的发展涉及癌细胞与其周围微环境的协同进化,但在物理组织架构内,这种相互作用的动态变化仍不清楚。本研究构建了单细胞分辨率的空间转录组图谱,涵盖来自43名患者的 127个不同阶段的组织视野,以描绘人类食管鳞状细胞癌(ESCC)的进化轨迹。通过分析640万个细胞,研究发现 ESCC 进展由一种增殖性的上皮细胞亚群驱动,该亚群逐渐获得去分化和侵袭性特征。在癌前晚期阶段,这些细胞破坏了上皮-基质界面,并通过JAG1-NOTCH1信号通路招募正常成纤维细胞,将其转化为癌症相关成纤维细胞(CAF)。这一相互作用导致肿瘤边缘形成“CAF-Epi”(CAF-上皮细胞)微环境,从而使肿瘤逃避免疫监视。CAF-Epi 微环境的形成是 ESCC 及其他鳞状细胞癌进展的重要标志,并与患者预后密切相关。
16.Multimodal integration of liquid biopsy and radiology for the noninvasive diagnosis of gallbladder cancer and benign disorders
多模态集成液体活检与影像学技术,实现胆囊癌与良性病变的无创诊断
 上海交通大学医学院附属仁济医院,胆胰外科
上海交通大学医学院附属仁济医院,胆胰外科
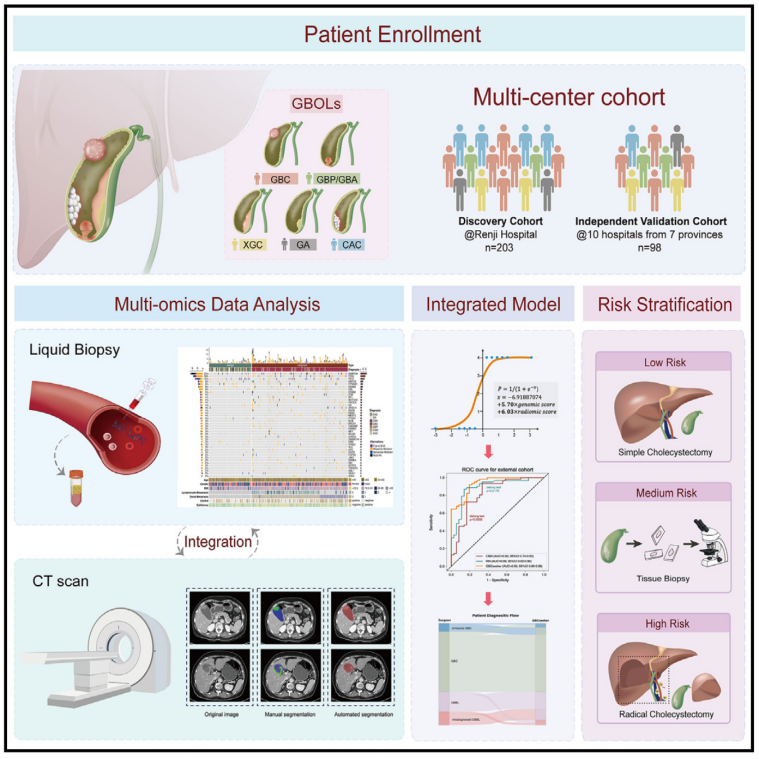
Gallbladder cancer (GBC) frequently mimics gallbladder benign lesions (GBBLs) in radiological images, leading to preoperative misdiagnoses. To address this challenge, we initiated a prospective, multicenter clinical trial (ChicCTR2100049249) and proposed a multimodal, non-invasive diagnostic model to distinguish GBC from GBBLs. A total of 301 patients diagnosed with gallbladder-occupying lesions (GBOLs) from 11 medical centers across 7 provinces in China were enrolled and divided into a discovery cohort and an independent external validation cohort. An artificial intelligence (AI)-based integrated model, GBCseeker, is created using cell-free DNA (cfDNA) genetic signatures, radiomic features, and clinical information. It achieves high accuracy in distinguishing GBC from GBBL patients (93.33% in the discovery cohort and 87.76% in the external validation cohort), reduces surgeons’ diagnostic errors by 56.24%, and reclassifies GBOL patients into three categories to guide surgical options. Overall, our study establishes a tool for the preoperative diagnosis of GBC, facilitating surgical decision-making.
胆囊癌(GBC)在影像学上常与胆囊良性病变(GBBLs)相似,导致术前误诊。为解决这一难题,该研究开展了一项前瞻性、多中心临床试验(ChiCTR2100049249),并提出了一种多模态、无创的诊断模型,用于区分 GBC 和 GBBLs。研究共纳入来自中国7个省份11家医疗中心的301例胆囊占位病变(GBOLs)患者,并将其分为发现队列和独立外部验证队列。研究开发了一种人工智能(AI)驱动的集成模型 GBCseeker,结合游离DNA(cfDNA)的遗传特征、影像组学特征及临床信息,在区分 GBC 和 GBBL 患者方面表现出高准确率(发现队列 93.33%,外部验证队列 87.76%)。此外,该模型可将外科医生的诊断错误率降低 56.24%,并重新分类GBOL患者为三类,以指导手术决策。总体而言,本研究建立了一种用于GBC术前诊断的工具,助力外科治疗决策优化。
17.Microglial reprogramming enhances antitumor immunity and immunotherapy response in melanoma brain metastases
小胶质细胞重编程增强脑转移黑色素瘤的抗肿瘤免疫及免疫治疗反应
 西班牙神经科学研究所
西班牙神经科学研究所
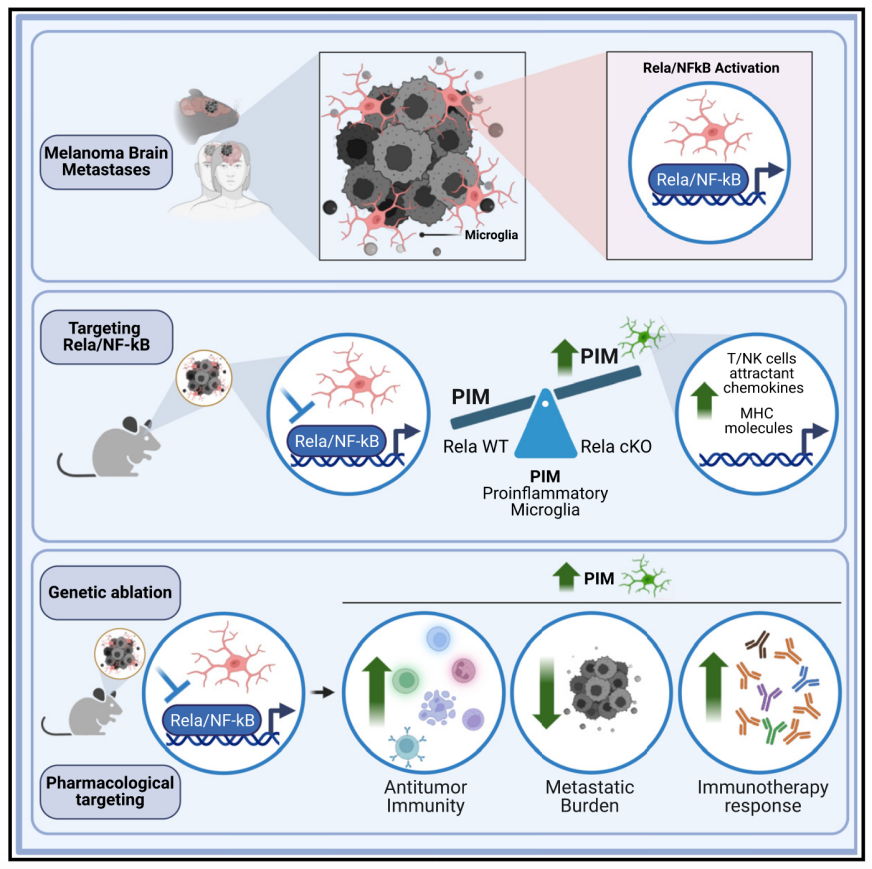
Melanoma is one of the tumor types with the highest risk of brain metastasis. However, the biology of melanoma brain metastasis and the role of the brain immune microenvironment in treatment responses are not yet fully understood. Using preclinical models and single-cell transcriptomics, we have identified a mechanism that enhances antitumor immunity in melanoma brain metastasis. We show that activation of the Rela/Nuclear Factor κB (NF-κB) pathway in microglia promotes melanoma brain metastasis. Targeting this pathway elicits microglia reprogramming toward a proinflammatory phenotype, which enhances antitumor immunity and reduces brain metastatic burden. Furthermore, we found that proinflammatory microglial markers in melanoma brain metastasis are associated with improved responses to immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients and targeting Rela/NF-κB pathway in mice improves responses to these therapies in the brain, suggesting a strategy to enhance antitumor immunity and responses to immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with melanoma brain metastasis.
黑色素瘤是最易发生脑转移的肿瘤类型之一。然而,脑转移黑色素瘤的生物学特性及脑部免疫微环境在治疗反应中的作用尚未完全阐明。通过临床前模型和单细胞转录组学分析,该研究发现了一种增强脑转移黑色素瘤抗肿瘤免疫的机制。研究表明,小胶质细胞中Rela/NF-κB 信号通路的激活可促进黑色素瘤脑转移,而靶向该通路可诱导小胶质细胞重编程,使其向促炎表型转化,从而增强抗肿瘤免疫并降低脑转移黑色素瘤的负担。此外,研究发现脑转移黑色素瘤患者中,促炎小胶质细胞标志物的表达与免疫检查点抑制剂的治疗反应密切相关。在小鼠模型中,抑制Rela/NF-κB信号通路可增强免疫检查点抑制剂的疗效,为黑色素瘤脑转移的患者提供了一种新的免疫治疗策略。
18.FAK inhibition combined with the RAF-MEK clamp avutometinib overcomes resistance to targeted and immune therapies in BRAF V600E melanoma
FAK抑制联合 RAF-MEK复合抑制剂 avutometinib 能克服 BRAF V600E黑色素瘤对靶向及免疫治疗的耐药性
 意大利比萨大学药学院
意大利比萨大学药学院
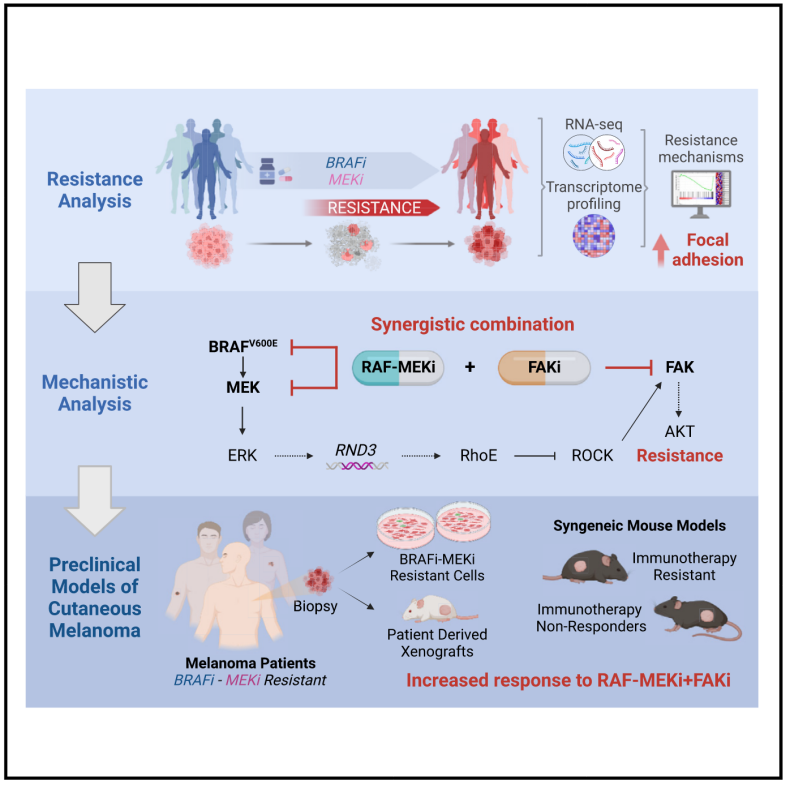
Widespread BRAF mutations result in persistent RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK (MAPK) signaling in melanoma. BRAF (BRAFi) and MEK (MEKi) inhibitors are approved for BRAF V600E melanomas, including those progressing on immunotherapy; however, rapid resistance to these agents highlights the need for novel strategies. Here, transcriptome analysis of BRAF V600E melanomas from patients resistant to BRAFi and MEKi shows activation of focal adhesion signaling. Consistently, BRAFi, MEKi, and the RAF-MEK clamp avutometinib activate focal adhesion kinase (FAK) in melanoma cells. Mechanistically, inhibition of an MAPK-RhoE (RND3) feedback loop results in the adaptive activation of RhoA-FAK-AKT. In turn, FAK inhibitors (FAKi) exert potent pro-apoptotic activity when combined with MAPK pathway inhibition. FAKi plus avutometinib overcomes resistance in multiple models derived from BRAFi plus MEKi-resistant melanoma patients and immunotherapy-resistant syngeneic mouse models. These findings provide a rationale for the development of avutometinib in combination with FAKi for patients with BRAF V600E melanoma progressing on BRAFi plus MEKi or immunotherapy.
文献显示,BRAF突变会导致黑色素瘤中RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK(MAPK)信号通路持续激活。目前BRAF抑制剂(BRAFi)和 MEK抑制剂(MEKi)已获批用于 BRAF V600E黑色素瘤,包括免疫治疗耐药患者,但耐药性问题仍然突出。本研究对耐药患者的 BRAF V600E 黑色素瘤转录组进行分析,发现其存在黏附斑信号的激活。进一步研究表明,BRAFi、MEKi 及RAF-MEK复合抑制剂avutometinib可激活黑色素瘤细胞中的黏附斑激酶(FAK)。机制研究发现,黑色素瘤的MAPK-RhoE(RND3)反馈回路受抑制后,会诱导 RhoA-FAK-AKT 适应性激活。因此,FAK与MAPK通路联合抑制可显著促进细胞凋亡。通过实验验证,将FAKi与 avutometinib(MAPKi)联用,在多个来源于BRAFi + MEKi耐药患者及免疫治疗耐药小鼠模型中均能克服耐药性。这一发现为BRAF V600E黑色素瘤耐药患者的新联合治疗方案提供了科学依据。
19.Distinct cellular mechanisms underlie chemotherapies and PD-L1 blockade combinations in triple-negative breast cancer
三阴性乳腺癌中化疗与 PD-L1 阻断联合治疗的不同细胞机制
 中国医学科学院肿瘤医院/国家癌症中心/国家癌症临床研究中心
中国医学科学院肿瘤医院/国家癌症中心/国家癌症临床研究中心
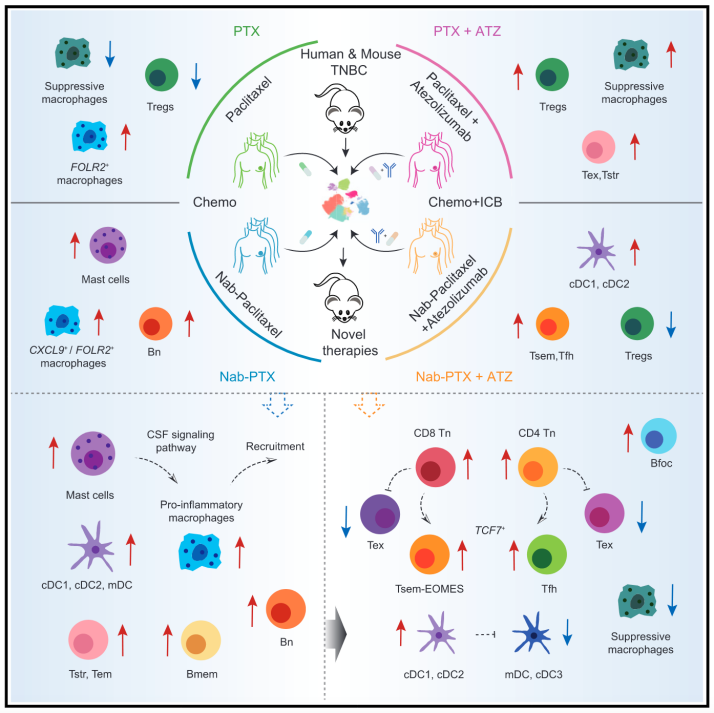
Combining immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) with chemotherapy shows promise for treating triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), though the mechanisms remain incompletely understood. Here, we integrate published and new single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data to investigate the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) in TNBC patients treated with paclitaxel (PTX), nab-paclitaxel (Nab-PTX), and their combinations with the anti-PD-L1 antibody atezolizumab (ATZ). Compared to ATZ plus PTX, ATZ plus Nab-PTX rewires TCF7+ stem-like effector memory CD8+ T cells (Tsem) and CD4+ T follicular helper (Tfh) cells. Nab-paclitaxel, unlike PTX, also reshapes the myeloid compartment, expanding mast cells and pro-inflammatory macrophages. Our analyses in human TNBC and murine models underscore the crucial role of mast cells in orchestrating anti-tumor immune responses, likely by promoting the recruitment and activation of T and B cells. In vivo experiments demonstrate that activating mast cells alongside PD-L1 blockade attenuates TNBC progression, suggesting mast cells as a promising adjunct for enhancing ICB therapy efficacy.
免疫检查点阻断(ICB)联合化疗在三阴性乳腺癌(TNBC)的治疗方面很有前景,但其机制尚不完全清楚。本研究整合了已发表及新测的单细胞RNA数据(scRNA-seq),以解析接受紫杉醇(PTX)或白蛋白结合紫杉醇(Nab-PTX)及其与抗PD-L1抗体阿特珠单抗(ATZ)联合治疗的TNBC患者肿瘤免疫微环境(TIME)。结果显示,与ATZ + PTX组合相比,ATZ + Nab-PTX 可重塑 TCF7+干性效应记忆 CD8+ T细胞(Tsem)和 CD4+滤泡辅助T细胞(Tfh)。此外,Nab-PTX还能重塑髓系细胞群,增加肥大细胞和促炎巨噬细胞,这提示,肥大细胞在抗肿瘤免疫应答中具有关键作用,其活化可增强PD-L1阻断的疗效,为TNBC的免疫治疗提供了新思路。
20.CDK4 selective inhibition improves preclinical anti-tumor efficacy and safety
CDK4选择性抑制提高了抗肿瘤疗效和安全性
 美国辉瑞全球研发中心(圣地亚哥)
美国辉瑞全球研发中心(圣地亚哥)
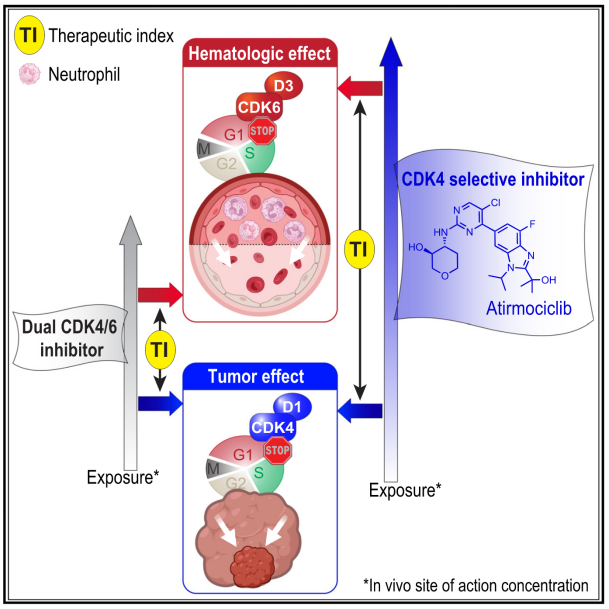
CDK4/6 inhibitors have revolutionized treatment of hormone receptor positive (HR+), HER2 non-amplified (HER2−) breast cancer. Yet, all “dual” CDK4/6 inhibitors show common dose-limiting hematologic toxicities, foremost neutropenia. This poses challenges to provide these agents at concentrations necessary to extinguish cell cycling in tumors. HR+ breast cancer cells are highly dependent on CDK4 but not CDK6. By contrast, CDK4 is dispensable for human bone marrow derived cells, due to the primary and compensatory role of CDK6 in hematopoiesis. This prompted us to develop atirmociclib (PF-07220060), a next-generation CDK4 selective inhibitor. Atirmociclib’s impact on circulating neutrophils was reduced, in proportion with its increase in CDK4 versus CDK6 selectivity. Realized dose intensification led to greater CDK4 inhibition and deeper anti-tumor responses, pointing to CDK4 target coverage as a limiting factor of CDK4/6 inhibitor efficacy. We also highlight combinatorial agents that may counter acquired resistance to CDK4 selective inhibition and widen its clinical application.
目前,CDK4/6抑制剂已经彻底改变了激素受体阳性(HR+)、HER2非扩增(HER2−)乳腺癌的治疗。然而,所有CDK4/6双重抑制剂均表现出剂量限制性血液学毒性,尤其是中性粒细胞减少症。这使得难以提供足够浓度的药物来阻断肿瘤细胞周期。HR+乳腺癌细胞高度依赖CDK4,而不依赖CDK6。而人类骨髓来源的细胞并不依赖CDK4,主要是CDK6在造血过程中起作用。因此,该研究开发了新一代CDK4选择性抑制剂atirmociclib(PF-07220060)。Atirmociclib对循环中性粒细胞的影响减少,这与其对CDK4的选择性抑制成比例。药物剂量的提高能达到更强的CDK4抑制作用和更深的抗肿瘤反应,表明CDK4靶点覆盖率是CDK4/6抑制剂疗效的限制因素。该研究还探讨了可能克服CDK4选择性抑制耐药性的联合治疗策略,以拓宽其临床应用范围。
21.Restoration of LAT activity improves CAR T cell sensitivity and persistence in response to antigen-low acute lymphoblastic leukemia
恢复LAT活性能提高CAR T细胞对低抗原急性淋巴细胞白血病的敏感性和持久性
 美国科罗拉多大学安舒茨医学中心儿科学系
美国科罗拉多大学安舒茨医学中心儿科学系
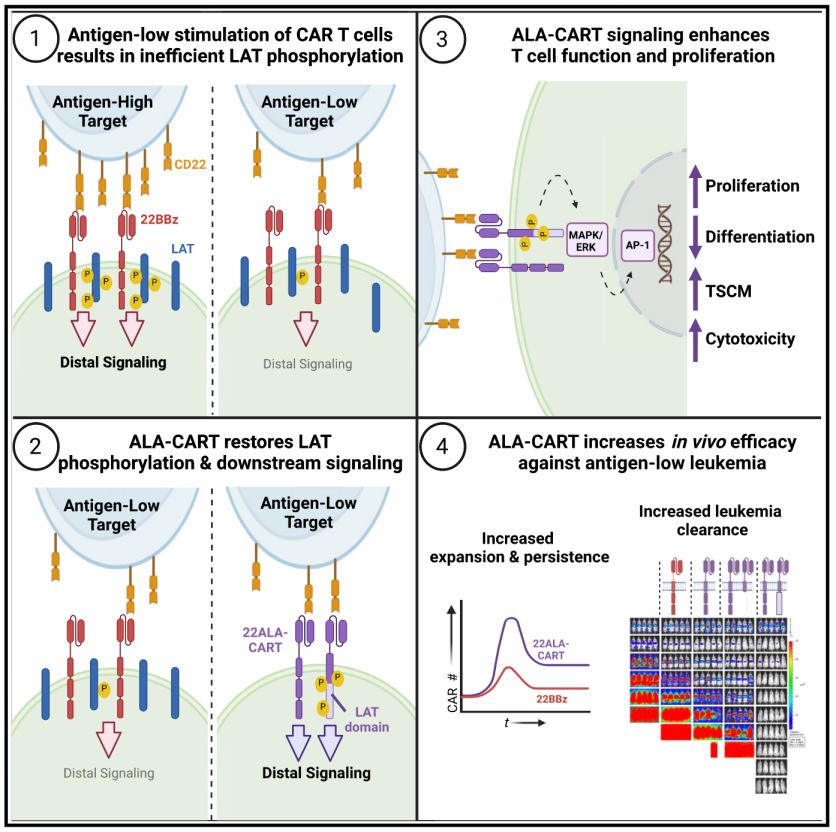
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells induce responses in patients with relapsed/refractory leukemia; however, long-term efficacy is frequently limited by relapse. The inability to target antigen-low cells is an intrinsic vulnerability of second-generation CAR T cells and underlies most relapses following CD22BBz CAR T cell therapy. Here, we interrogate CD22BBz CAR signaling in response to low antigen and find inefficient phosphorylation of the linker for activation of T cells (LAT) limiting downstream signaling. To overcome this, we designed the adjunctive LAT-activating CAR T cell (ALA-CART) platform, pairing a second-generation CAR with a LAT-CAR incorporating the intracellular domain of LAT. ALA-CART cells demonstrate reduced differentiation during manufacturing and increased LAT phosphorylation, MAPK signaling, and AP-1 activity. ALA-CART cells show improved cytotoxicity, proliferation, persistence, and efficacy against antigen-low leukemias that were refractory to clinically active CD22BBz CAR T cells. Restoration of LAT signaling through the ALA-CART platform represents a promising strategy for overcoming multiple mechanisms of CAR T cell failure.
嵌合抗原受体(CAR)T细胞可在复发/难治性白血病患者中诱导治疗反应,但长期疗效通常受复发的限制。第二代CAR T细胞无法有效靶向低抗原表达的细胞,这是其固有缺陷,也是大多数CD22BBz CAR T细胞治疗后复发的主要原因。因此,该研究分析了CD22BBz CAR在低抗原水平下的信号传导,发现T细胞活化连接蛋白(LAT)的磷酸化效率低,限制了下游信号传导。为此,研究设计了辅助LAT激活的CAR T细胞(ALA-CART)平台,将第二代CAR与包含LAT胞内结构域的LAT-CAR结合。ALA-CART细胞在制造过程中分化减少,LAT磷酸化、MAPK信号传导和AP-1活性增强。实验表明,ALA-CART细胞在对抗低抗原白血病时表现出更强的细胞毒性、增殖能力、持久性和疗效,而这些白血病对CD22BBz CAR T细胞耐受。因此,该研究通过ALA-CART平台恢复LAT信号传导,为克服CAR T细胞治疗失败提供了新的改进策略。
22.Targeting tumor monocyte-intrinsic PD-L1 by rewiring STING signaling and enhancing STING agonist therapy
通过重塑STING信号并增强STING激动剂疗法靶向肿瘤单核细胞内源性PD-L1
 复旦大学华山医院消化科及国家老年医学临床研究中心
复旦大学华山医院消化科及国家老年医学临床研究中心
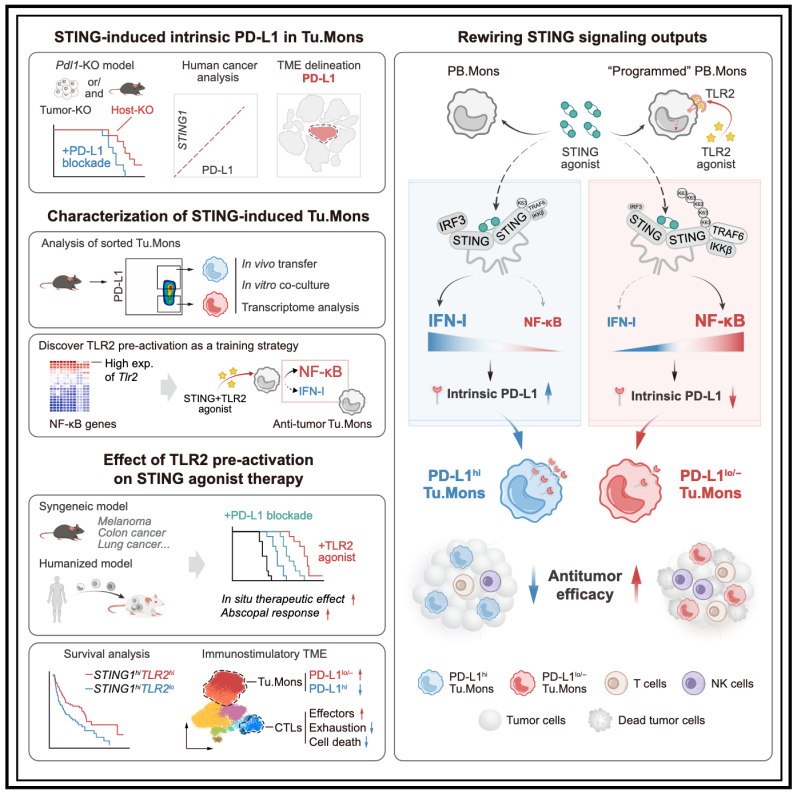
STING is an important DNA sensing machinery in initiating immune response, yet therapies targeting STING have shown poor outcomes in clinical trials. Here, we reveal that STING signaling induces PD-L1hi tumor monocytes (Tu.Mons) that dominate the resistance against STING agonist therapy. Cell-intrinsic PD-L1, induced by the STING-IRF3-IFN-I axis, is identified as the driving factor for protumoral PD-L1hi Tu.Mons. Notably, TLR2-activated Tu.Mons resist STING-induced upregulation of cell-intrinsic PD-L1 and the associated protumoral functions. Mechanistically, TLR2 stimulation remodels STING signaling by facilitating STING and TRAF6 interaction, which suppresses the IRF3-IFN-I response and enhances NF-κB activation. Moreover, we demonstrate that combining STING agonists with TLR2 agonist pretreatment significantly improves antitumor efficacy in murine syngeneic and humanized models. Our findings uncover a protumoral aspect of STING activation mediated by cell-intrinsic PD-L1 and propose a promising strategy to boost antitumor immunity by fine-tuning STING signaling outputs.
STING是一种细胞识别DNA突变损伤的重要感知机制,能启动免疫反应。然而,以STING为靶点的疗法在临床试验中表现不佳。在本研究中,研究者发现STING信号可诱导肿瘤微环境中单核细胞的PD-L1高表达(PD-L1hi Tu.Mons),而这些细胞主导了STING激动剂治疗的耐药性。该研究鉴定了STING-IRF3-IFN-I轴是促进肿瘤单核细胞PD-L1高表达的驱动因素。值得注意的是,TLR2激活的Tu.Mons能够抵抗STING诱导的细胞内源性PD-L1上调及其相关的促肿瘤功能。机制研究表明,TLR2刺激可促进STING与TRAF6的相互作用,从而抑制IRF3-IFN-I信号,增强NF-κB活性。进一步实验表明,在小鼠同种移植瘤和人源化模型中,先给予TLR2激动剂处理后再联合STING激动剂,可显著提高抗肿瘤疗效。本研究揭示了STING激活的促肿瘤作用由细胞内源性PD-L1介导,并提出了一种精细调控STING信号输出来增强抗肿瘤免疫的新策略。
23.Integrative spatial analysis reveals tumor heterogeneity and immune colony niche related to clinical outcomes in small cell lung cancer
整合空间分析揭示小细胞肺癌的肿瘤异质性及与临床结局相关的免疫集落微环境
 复旦大学上海癌症中心胸外科及基因工程国家重点实验室
复旦大学上海癌症中心胸外科及基因工程国家重点实验室
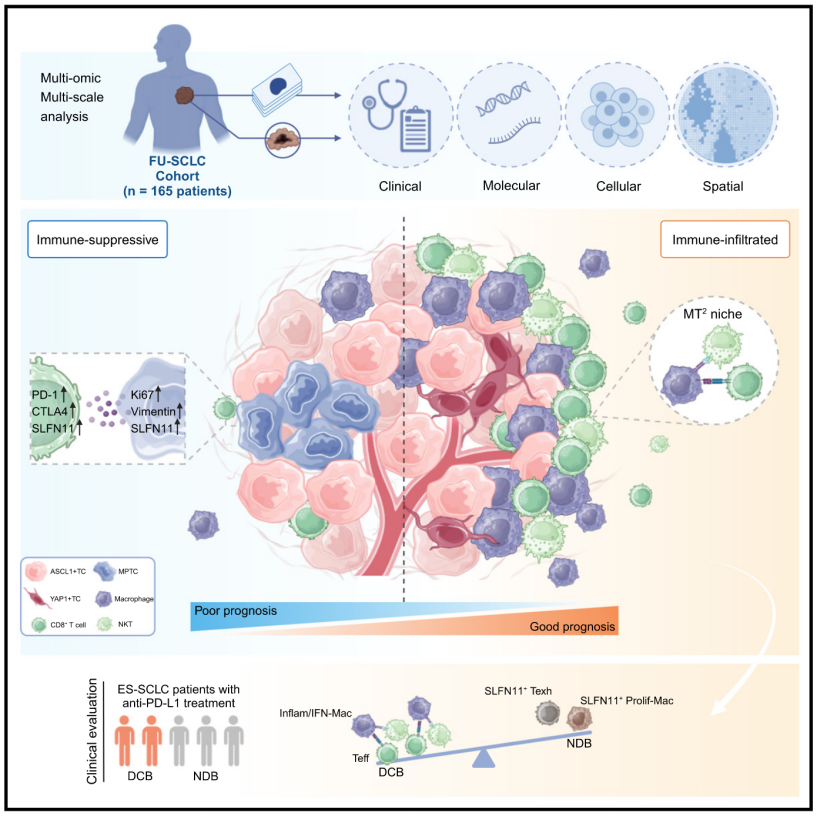
Recent advances have shed light on the molecular heterogeneity of small cell lung cancer (SCLC), yet the spatial organizations and cellular interactions in tumor immune microenvironment remain to be elucidated. Here, we employ co-detection by indexing (CODEX) and multi-omics profiling to delineate the spatial landscape for 165 SCLC patients, generating 267 high-dimensional images encompassing over 9.3 million cells. Integrating CODEX and genomic data reveals a multi-positive tumor cell neighborhood within ASCL1+ (SCLC-A) subtype, characterized by high SLFN11 expression and associated with poor prognosis. We further develop a cell colony detection algorithm (ColonyMap) and reveal a spatially assembled immune niche consisting of antitumoral macrophages, CD8+ T cells and natural killer T cells (MT2) which highly correlates with superior survival and predicts improving immunotherapy response in an independent cohort. This study serves as a valuable resource to study SCLC spatial heterogeneity and offers insights into potential patient stratification and personalized treatments.
近年来,研究已揭示小细胞肺癌(SCLC)的分子异质性,但其肿瘤免疫微环境中的空间组织及细胞相互作用仍需进一步阐明。本研究利用索引共检测(CODEX)技术和多组学分析,绘制了165例SCLC患者的空间图谱,共获得267幅高维图像,涵盖超过930万个细胞。CODEX数据与基因组数据整合分析显示,在ASCL1+(SCLC-A)亚型中,存在一种多阳性肿瘤细胞区域,其特征为高SLFN11表达,并与不良预后相关。此外,研究开发了一种细胞集落检测算法(ColonyMap),揭示了由抗肿瘤巨噬细胞、CD8+ T细胞和自然杀伤T细胞(MT2)组成的空间免疫集落微环境。该免疫集落与更长的生存期高度相关,并能预测独立队列中免疫治疗应答的改善。本研究为研究SCLC的空间异质性提供了重要资源,并为患者分层及个性化治疗提供了新见解。

汇报人:夏晓旭
导师:赵宇,任建君
审核:张子妍、李婧媛、任建君



