原创 吴桂儀 华西医院耳鼻喉科
CELL(187卷:25-26期,188卷:1期)导读
2024年9月-11月
期刊介绍:
Cell是Cell Press细胞出版社旗下的旗舰刊,创办于1974年,由爱思唯尔(Elsevier)公司出版发行。这是一本多学科期刊,包括但不限于细胞生物学、分子生物学、神经科学、免疫学、病毒学和微生物学、癌症、人类遗传学、系统生物学、信号传导和疾病机制和疾病治疗。该期刊为双周刊,2024年影响因子为45.5。
Dec 12, 2024;Volume 187, Issue 25;p7045-7350
Cell共发表19篇,其中包括1篇50th Anniversary; 1篇Obituary; 2篇Short Articles; 13篇Articles; 1篇Resources; 1篇Correction。
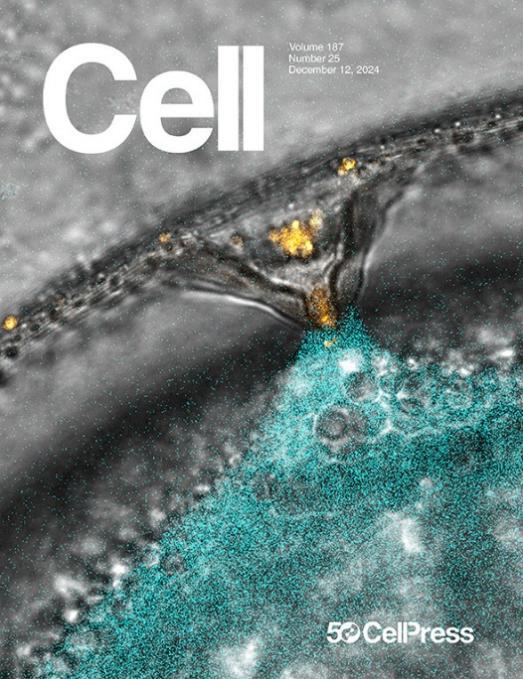
On the cover: Fertilization culminates in the binding and fusion of sperm and egg. In this issue of Cell, Deneke, Blaha et al. uncover a conserved protein complex on vertebrate sperm that recognizes distinct egg ligands in mammals and fish. The cover shows a confocal microscopy movie capturing the moment of fertilization in zebrafish. Sperm is colored in yellow and the egg cytoplasm in turquoise. Image credit: Victoria Deneke, Pauli lab, IMP Vienna; image background was extended with Photoshop Generative Fill.
封面内容:受精过程为精子和卵子的结合与融合。在本期《细胞》杂志中,Deneke、Blaha等人发现了一种存在于脊椎动物精子上的保守蛋白复合物,它能够识别哺乳动物和鱼类中不同的卵子配体。封面显示的是共聚焦显微镜拍摄的斑马鱼受精瞬间-黄色标记的精子正与蓝绿色标记的卵细胞质相遇。图像来源:Victoria Deneke,Pauli实验室,维也纳分子病理学研究所;图像背景使用Photoshop Generative Fill进行了扩展。
1. STK19 positions TFIIH for cell-free transcription-coupled DNA repair
STK19定位TFIIH进行无细胞转录偶联DNA修复

In transcription-coupled nucleotide excision repair (TC-NER), stalled RNA polymerase II (RNA Pol II) binds CSB and CRL4CSA, which cooperate with UVSSA and ELOF1 to recruit TFIIH. To explore the mechanism of TC-NER, we recapitulated this reaction in vitro. When a plasmid containing a site-specific lesion is transcribed in frog egg extract, error-free repair is observed that depends on CSB, CRL4CSA, UVSSA, and ELOF1. Repair also requires STK19, a factor previously implicated in transcription recovery after UV exposure. A 1.9-Å cryo-electron microscopy structure shows that STK19 binds the TC-NER complex through CSA and the RPB1 subunit of RNA Pol II. Furthermore, AlphaFold predicts that STK19 interacts with the XPD subunit of TFIIH, and disrupting this interface impairs cell-free repair. Molecular modeling suggests that STK19 positions TFIIH ahead of RNA Pol II for lesion verification. Our analysis of cell-free TC-NER suggests that STK19 couples RNA Pol II stalling to downstream repair events.
在转录偶联核苷酸切除修复(TC-NER)中,停滞的RNA聚合酶II(RNA Pol II)会结合CSB和CRL4CSA(特异性蛋白),二者与UVSSA和ELOF1协同招募TFIIH。为了探索TC-NER的机制,作者在体外重现了这一反应。当含有特定位点损伤的质粒在青蛙卵提取物中进行转录时,观察到了依赖于CSB、CRL4CSA、UVSSA和ELOF1的无错修复。修复过程还需要STK19,这是一个之前被认为与紫外线照射后转录修复有关的因子。1.9-Å的冷冻电镜结构显示,STK19通过CSA和RNA Pol II的RPB1亚基结合到TC-NER复合物上。此外,AlphaFold预测STK19与TFIIH的XPD亚基相互作用,破坏这一界面会损害无细胞修复。分子建模表明,STK19将TFIIH定位在RNA Pol II之前,以验证病变。本文对无细胞TC-NER的分析揭示了STK19将RNA Pol II的停滞与下游修复事件偶联起来。
2. STK19 facilitates the clearance of lesion-stalled RNAPII during transcription-coupled DNA repair
STK19促进转录耦合DNA修复过程中受损停滞RNAPII的清除

Transcription-coupled DNA repair (TCR) removes bulky DNA lesions impeding RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) transcription. Recent studies have outlined the stepwise assembly of TCR factors CSB, CSA, UVSSA, and transcription factor IIH (TFIIH) around lesion-stalled RNAPII. However, the mechanism and factors required for the transition to downstream repair steps, including RNAPII removal to provide repair proteins access to the DNA lesion, remain unclear. Here, we identify STK19 as a TCR factor facilitating this transition. Loss of STK19 does not impact initial TCR complex assembly or RNAPII ubiquitylation but delays lesion-stalled RNAPII clearance, thereby interfering with the downstream repair reaction. Cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) and mutational analysis reveal that STK19 associates with the TCR complex, positioning itself between RNAPII, UVSSA, and CSA. The structural insights and molecular modeling suggest that STK19 positions the ATPase subunits of TFIIH onto DNA in front of RNAPII. Together, these findings provide new insights into the factors and mechanisms required for TCR.
转录偶联DNA修复(TCR)能够清除阻碍RNA聚合酶II(RNAPII)转录的体积较大的DNA损伤。近期的研究已经概述了TCR因子CSB、CSA、UVSSA和转录因子IIH(TFIIH)围绕因损伤停滞的RNAPII进行逐步组装的过程。然而,目前对于过渡到下游修复步骤(包括移除RNAPII以使修复蛋白能够接触到DNA损伤)的机制和所需因子仍不清楚。本文确定了STK19是一种促进这一过渡的TCR因子。STK19缺失并不影响最初的TCR复合物组装或RNAPII的泛素化,但会延迟因受损停滞的RNAPII的清除,从而干扰下游修复反应。冷冻电镜(cryo-EM)和突变分析发现了STK19与TCR复合物相结合,定位在RNAPII、UVSSA和CSA之间。结构分析和分子建模表明,STK19将TFIIH的ATP酶亚基定位在RNAPII之前的DNA上。总的来说,这些发现为TCR所需的因子和机制提供了新的见解。
3. Selective degradation of multimeric proteins by TRIM21-based molecular glue and PROTAC degraders
基于TRIM21的分子胶和 PROTAC 降解剂对多聚蛋白的选择性降解
Targeted protein degradation (TPD) utilizes molecular glues or proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs) to eliminate disease-causing proteins by promoting their interaction with E3 ubiquitin ligases. Current TPD approaches are limited by reliance on a small number of constitutively active E3 ubiquitin ligases. Here, we report that (S)-ACE-OH, a metabolite of the antipsychotic drug acepromazine, acts as a molecular glue to induce an interaction between the E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM21 and the nucleoporin NUP98, leading to the degradation of nuclear pore proteins and disruption of nucleocytoplasmic trafficking. Functionalization of acepromazine into PROTACs enabled selective degradation of multimeric proteins, such as those within biomolecular condensates, while sparing monomeric proteins. This selectivity is consistent with the requirement of substrate-induced clustering for TRIM21 activation. As aberrant protein assemblies cause diseases such as autoimmunity, neurodegeneration, and cancer, our findings highlight the potential of TRIM21-based multimer-selective degraders as a strategy to tackle the direct causes of these diseases.
靶向蛋白质降解(TPD)利用分子胶或蛋白降解靶向嵌合体(PROTACs)通过促进致病蛋白质与E3泛素连接酶的相互作用来消除致病蛋白。目前的TPD方法受限于对少量组成型活性E3泛素连接酶的依赖。本文报道了抗精神病药物乙酰丙嗪的代谢产物-(S)-ACE-OH充当分子胶诱导E3泛素连接酶TRIM21与核蛋白NUP98之间的相互作用,从而导致核蛋白的降解以及核质转运的破坏。将乙酰丙嗪功能化为PROTACs能够选择性地降解多聚蛋白,例如生物分子凝聚体内的多聚蛋白,而保留单体蛋白。这种选择性与TRIM21激活的要求是一致的。由于异常的蛋白质聚集会导致自身免疫病、神经退行性疾病和癌症等疾病,本文的发现突显了基于TRIM21的多聚体选择性降解剂作为直接靶向疾病根源治疗策略的潜力。
4. Multiscale drug screening for cardiac fibrosis identifies MD2 as a therapeutic target
针对心脏纤维化的多尺度药物筛选将MD2确定为治疗靶点
Cardiac fibrosis impairs cardiac function, but no effective clinical therapies exist. To address this unmet need, we employed a high-throughput screening for antifibrotic compounds using human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived cardiac fibroblasts (CFs). Counter-screening of the initial candidates using iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes and iPSC-derived endothelial cells excluded hits with cardiotoxicity. This screening process identified artesunate as the lead compound. Following profibrotic stimuli, artesunate inhibited proliferation, migration, and contraction in human primary CFs, reduced collagen deposition, and improved contractile function in 3D-engineered heart tissues. Artesunate also attenuated cardiac fibrosis and improved cardiac function in heart failure mouse models. Mechanistically, artesunate targeted myeloid differentiation factor 2 (MD2) and inhibited MD2/Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signaling pathway, alleviating fibrotic gene expression in CFs. Our study leverages multiscale drug screening that integrates a human iPSC platform, tissue engineering, animal models, in silico simulations, and multiomics to identify MD2 as a therapeutic target for cardiac fibrosis.
心脏纤维化会损害心脏功能,但目前尚无有效的临床疗法。为了解决这一需求,研究人员采用高通量筛选技术,通过诱导多能干细胞(iPSC)来源的心脏成纤维细胞(CFs)筛选抗纤维化的化合物。通过使用iPSC来源的心肌细胞和内皮细胞进行反向筛选,排除了具有心脏毒性的候选化合物。该筛选过程确定了青蒿琥酯(artesunate)作为先导化合物。在促纤维化刺激后,青蒿琥酯(artesunate)抑制了人原代CFs的增殖、迁移和收缩,减少了胶原沉积,并改善了三维工程心脏组织的收缩功能。青蒿琥酯(artesunate)还在心力衰竭小鼠模型中减轻了心脏纤维化并改善了心脏功能。从机制上看,青蒿琥酯(artesunate)靶向髓样分化因子2(MD2)并抑制MD2/TLR4信号通路从而减轻CFs中的纤维化基因表达。研究人员利用多尺度药物筛选,整合了人类iPSC平台、组织工程、动物模型、计算机模拟和多组学,确定MD2为心脏纤维化的治疗靶点。
5. Structure-guided discovery of bile acid derivatives for treating liver diseases without causing itch
在结构指导下发现用于治疗肝病且不会引起瘙痒的胆汁酸衍生物

Chronic itch is a debilitating symptom profoundly impacting the quality of life in patients with liver diseases like cholestasis. Activation of the human G-protein coupled receptor, MRGPRX4 (hX4), by bile acids (BAs) is implicated in promoting cholestasis itch. However, the detailed underlying mechanisms remain elusive. Here, we identified 3-sulfated BAs that are elevated in cholestatic patients with itch symptoms. We solved the cryo-EM structure of hX4-Gq in a complex with 3-phosphated deoxycholic acid (DCA-3P), a mimic of the endogenous 3-sulfated deoxycholic acid (DCA-3S). This structure revealed an unprecedented ligand-binding pocket in MRGPR family proteins, highlighting the crucial role of the 3-hydroxyl (3-OH) group on BAs in activating hX4. Guided by this structural information, we designed and developed compound 7 (C7), a BA derivative lacking the 3-OH. Notably, C7 effectively alleviates hepatic injury and fibrosis in liver disease models while significantly mitigating the itch side effects.
慢性瘙痒是肝病患者(如胆汁淤积症)中一种严重影响生活质量的症状。胆汁酸(BAs)激活人G蛋白偶联受体MRGPRX4(hX4)与促进胆汁淤积性瘙痒有关。然而,详细的内在机制仍不清楚。在这里,研究人员发现3-硫酸化胆汁酸在有瘙痒症状的胆汁淤积症患者中升高。研究解析了hX4-Gq与3-磷酸脱氧胆酸(DCA-3P)复合物的冷冻电镜结构,3-磷酸脱氧胆酸是内源性3-硫酸脱氧胆酸(DCA-3S)的模拟物。该结构揭示了MRGPR家族蛋白中一个前所未有的配体结合口袋,突出了BAs上的3-羟基(3-OH)基团在激活hX4中的关键作用。基于这一结构信息,研究人员设计并开发了化合物7 (C7),这是一种缺乏3-OH的BA衍生物。值得注意的是,C7可有效缓解肝脏疾病模型的肝损伤和肝纤维化,同时显著减轻瘙痒症状。
6. The CRISPR-associated adenosine deaminase Cad1 converts ATP to ITP to provide antiviral immunity
CRISPR相关腺苷脱氨酶Cad1将ATP转化为ITP,以提供抗病毒免疫力

Type III CRISPR systems provide immunity against genetic invaders through the production of cyclic oligo-adenylate (cAn) molecules that activate effector proteins that contain CRISPR-associated Rossman fold (CARF) domains. Here, we characterized the function and structure of an effector in which the CARF domain is fused to an adenosine deaminase domain, CRISPR-associated adenosine deaminase 1 (Cad1). We show that upon binding of cA4 or cA6 to its CARF domain, Cad1 converts ATP to ITP, both in vivo and in vitro. Cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structural studies on full-length Cad1 reveal an hexameric assembly composed of a trimer of dimers, with bound ATP at inter-domain sites required for activity and ATP/ITP within deaminase active sites. Upon synthesis of cAn during phage infection, Cad1 activation leads to a growth arrest of the host that prevents viral propagation. Our findings reveal that CRISPR-Cas systems employ a wide range of molecular mechanisms beyond nucleic acid degradation to provide adaptive immunity in prokaryotes.
III型CRISPR系统通过产生环状寡腺苷酸(cAn)分子来激活含有CRISPR相关Rossmann折叠(CARF)结构域的效应蛋白,从而提供对遗传入侵者的免疫力。在此研究中,研究人员表描述了一种效应蛋白-CRISPR相关腺苷脱氨酶1(Cad1)的功能和结构,该蛋白的CARF结构域与腺苷脱氨酶结构域融合。研究人员发现,当cA4或cA6与其CARF结构域结合时,Cad1在体内和体外都可以将ATP转化为ITP。对全长Cad1的冷冻电镜(cryo-EM)结构研究表明,Cad1形成一个由二聚体和三聚体组成的六聚体结构,结合的 ATP 位于活性所需的结构域间位点,而ATP/ITP则位于脱氨酶活性位点内。在噬菌体感染期间cAn的合成激活Cad1,导致宿主生长停滞从而阻止病毒传播。这些发现表明,CRISPR-Cas系统利用核酸降解以外的广泛分子机制在原核生物中提供适应性免疫。
7. A potent pan-sarbecovirus neutralizing antibody resilient to epitope diversification
一种能抵抗表位多样化的强效泛沙贝病毒亚属的中和抗体

Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) evolution has resulted in viral escape from clinically authorized monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), creating a need for mAbs that are resilient to epitope diversification. Broadly neutralizing coronavirus mAbs that are sufficiently potent for clinical development and retain activity despite viral evolution remain elusive. We identified a human mAb, designated VIR-7229, which targets the viral receptor-binding motif (RBM) with unprecedented cross-reactivity to all sarbecovirus clades, including non-ACE2-utilizing bat sarbecoviruses, while potently neutralizing SARS-CoV-2 variants since 2019, including the recent EG.5, BA.2.86, and JN.1. VIR-7229 tolerates extraordinary epitope variability, partly attributed to its high binding affinity, receptor molecular mimicry, and interactions with RBM backbone atoms. Consequently, VIR-7229 features a high barrier for selection of escape mutants, which are rare and associated with reduced viral fitness, underscoring its potential to be resilient to future viral evolution. VIR-7229 is a strong candidate to become a next-generation medicine.
严重急性呼吸综合征冠状病毒2型(SARS-CoV-2)的进化导致病毒能逃逸已获临床批准的单克隆抗体(mAbs)的攻击,因此需要能抵抗表位多样化的 mAbs。具有足够临床开发潜力且在病毒进化后仍能保持活性的广谱中和冠状病毒mAbs仍然难以获得。。研究人员发现了一种人源mAb,命名为VIR-7229,其靶向病毒的受体结合基序(RBM),具有对所有沙贝科病毒支系的交叉反应性(包括不利用ACE2的蝙蝠沙贝科病毒),同时还能有效中和2019年以来的SARS-CoV-2变异株(含近期流行的 EG.5、BA.2.86 和 JN.1)。VIR-7229 能够耐受超常的表位变异性,部分原因是其高结合亲和力、受体分子模拟以及与RBM骨架原子的相互作用。因此,VIR-7229在筛选逃逸突变方面具有很高的障碍,逃逸突变体非常罕见,而且会降低病毒的适应性,这表明它具有抵抗未来病毒进化的潜力。VIR-7229有望成为下一代药物的有力候选者。
8. Potent and broad HIV-1 neutralization in fusion peptide-primed SHIV-infected macaques
在融合肽诱导的SHIV感染猕猴体内,HIV – 1的中和作用强力且广泛

An antibody-based HIV-1 vaccine will require the induction of potent cross-reactive HIV-1-neutralizing responses. To demonstrate feasibility toward this goal, we combined vaccination targeting the fusion-peptide site of vulnerability with infection by simian-human immunodeficiency virus (SHIV). In four macaques with vaccine-induced neutralizing responses, SHIV infection boosted plasma neutralization to 45%–77% breadth (geometric mean 50% inhibitory dilution [ID50] ∼100) on a 208-strain panel. Molecular dissection of these responses by antibody isolation and cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure determination revealed 15 of 16 antibody lineages with cross-clade neutralization to be directed toward the fusion-peptide site of vulnerability. In each macaque, isolated antibodies from memory B cells recapitulated the plasma-neutralizing response, with fusion-peptide-binding antibodies reaching breadths of 40%–60% (50% inhibitory concentration [IC50] < 50 μg/mL) and total lineage-concentrations estimates of 50–200 μg/mL. Longitudinal mapping indicated that these responses arose prior to SHIV infection. Collectively, these results provide in vivo molecular examples for one to a few B cell lineages affording potent, broadly neutralizing plasma responses.
一种基于抗体的HIV-1疫苗需要诱导强大的交叉反应性HIV-1中和反应。为了证明这一目标的可行性,研究人员将靶向融合肽易感位点的疫苗接种与猴-人免疫缺陷病毒(SHIV)感染相结合。在四只具有疫苗诱导的中和反应的猕猴中,SHIV感染将血浆中和反应率提高到45%-77%的广度(几何平均50%抑制稀释度[ID50]约为100),在208株病毒株的测试中表现出广泛的中和活性。通过抗体分离和冷冻电镜(cryo-EM)结构测定对这些反应进行分子剖析,发现16个具有交叉中和作用的抗体谱系中,有15个针对易感性的融合肽位点。在每只猕猴中,从记忆B细胞中分离出的抗体都能模拟血浆中和反应,融合肽结合抗体的广度达到40%-60%(50%抑制浓度[IC50]<50μg/mL),总谱系浓度估计为50-200 μg/mL。纵向图谱表明,这些反应在SHIV感染之前就已出现。总之,这些结果提供了一个到几个B细胞系在体内产生强效、广泛中和血浆反应的分子实例。
9. Disruption of cellular plasticity by repeat RNAs in human pancreatic cancer
人类胰腺癌中重复RNA对细胞可塑性造成破坏

Aberrant expression of repeat RNAs in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) mimics viral-like responses with implications on tumor cell state and the response of the surrounding microenvironment. To better understand the relationship of repeat RNAs in human PDAC, we performed spatial molecular imaging at single-cell resolution in 46 primary tumors, revealing correlations of high repeat RNA expression with alterations in epithelial state in PDAC cells and myofibroblast phenotype in cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs). This loss of cellular identity is observed with dosing of extracellular vesicles (EVs) and individual repeat RNAs of PDAC and CAF cell culture models pointing to cell-cell intercommunication of these viral-like elements. Differences in PDAC and CAF responses are driven by distinct innate immune signaling through interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3). The cell-context-specific viral-like responses to repeat RNAs provide a mechanism for modulation of cellular plasticity in diverse cell types in the PDAC microenvironment.
胰腺导管腺癌(PDAC)中的重复RNA的异常表达模拟了病毒样反应,对肿瘤细胞状态和周围微环境的反应产生了影响。为了更好地理解人类PDAC中重复RNA的关系,研究人员在46个原发性肿瘤中进行了单细胞分辨率的空间分子成像,发现了重复RNA的高表达与PDAC细胞上皮状态的改变和癌症相关成纤维细胞(CAFs)中肌成纤维细胞表型的相关性。通过PDAC和CAF细胞培养模型的细胞外囊泡(EVs)和单个重复RNA的剂量实验,观察到细胞特性的丧失,这表明这些病毒样元件通过细胞间通讯发挥作用。PDAC和CAF的差异性应答是由干扰素调节因子3(IRF3)介导的不同先天免疫信号驱动。这些特定细胞环境下的病毒样应答揭示了一种PDAC微环境中不同细胞类型的细胞可塑性调节的机制。
10. IRE1α silences dsRNA to prevent taxane-induced pyroptosis in triple-negative breast cancer
在三阴性乳腺癌中,IRE1 α沉默dsRNA以抑制紫杉烷诱导的细胞焦亡

Chemotherapy is often combined with immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICIs) to enhance immunotherapy responses. Despite the approval of chemo-immunotherapy in multiple human cancers, many immunologically cold tumors remain unresponsive. The mechanisms determining the immunogenicity of chemotherapy are elusive. Here, we identify the ER stress sensor IRE1α as a critical checkpoint that restricts the immunostimulatory effects of taxane chemotherapy and prevents the innate immune recognition of immunologically cold triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). IRE1α RNase silences taxane-induced double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) through regulated IRE1-dependent decay (RIDD) to prevent NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent pyroptosis. Inhibition of IRE1α in Trp53−/− TNBC allows taxane to induce extensive dsRNAs that are sensed by ZBP1, which in turn activates NLRP3-GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis. Consequently, IRE1α RNase inhibitor plus taxane converts PD-L1-negative, ICI-unresponsive TNBC tumors into PD-L1high immunogenic tumors that are hyper-sensitive to ICI. We reveal IRE1α as a cancer cell defense mechanism that prevents taxane-induced danger signal accumulation and pyroptotic cell death.
化疗通常与免疫检查点抑制剂(ICIs)联合使用,以增强免疫治疗的反应。尽管化疗联合免疫疗法已获批准用于多种人类癌症,但许多免疫冷肿瘤仍没有反应。决定化疗免疫原性的机制尚不清楚。研究人员确定了内质网应激传感器IRE1α是限制紫杉烷类化疗免疫刺激作用的关键检查点,并防止免疫反应差的三阴性乳腺癌(TNBC)被先天免疫识别。IRE1α核酸酶通过调控IRE1依赖性降解(RIDD)沉默紫杉烷类药物诱导的双链RNA(dsRNA),从而防止NLRP3炎症小体依赖的细胞焦亡。在Trp53−/−TNBC中抑制IRE1α允许紫杉烷类药物诱导产生大量的dsRNAs,这些dsRNAs被ZBP1感知,进而激活NLRP3-GSDMD介导的细胞焦亡。因此,IRE1α核酸酶抑制剂与紫杉烷类药物联合使用可将PD-L1阴性、ICI无反应的TNBC肿瘤转化为PD-L1高表达的免疫原性肿瘤,这些肿瘤对ICI高度敏感。研究人员揭示了IRE1α作为癌细胞防御机制,它可以防止紫杉烷类药物诱导的危险信号积累和细胞焦亡。
11. Multiparameter imaging reveals clinically relevant cancer cell-stroma interaction dynamics in head and neck cancer
多参数成像揭示了头颈癌中与临床相关的癌细胞-基质相互作用动力学

Epithelial tumors are characterized by abundant inter- and intra-tumor heterogeneity, which complicates diagnostics and treatment. The contribution of cancer-stroma interactions to this heterogeneity is poorly understood. Here, we report a paradigm to quantify phenotypic diversity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) with single-cell resolution. By combining cell-state markers with morphological features, we identify phenotypic signatures that correlate with clinical features, including metastasis and recurrence. Integration of tumor and stromal signatures reveals that partial epithelial-mesenchymal transition (pEMT) renders disease outcome highly sensitive to stromal composition, generating a strong prognostic and predictive signature. Spatial transcriptomics and subsequent analyses of cancer spheroid dynamics identify the cancer-associated fibroblast-pEMT axis as a nexus for intercompartmental signaling that reprograms pEMT cells into an invasive phenotype. Taken together, we establish a paradigm to identify clinically relevant tumor phenotypes and discover a cell-state-dependent interplay between stromal and epithelial compartments that drives cancer aggression.
上皮肿瘤的特点是存在丰富的肿瘤间和肿瘤内异质性,这使得诊断和治疗变得复杂。癌细胞与基质相互作用对这种异质性的影响尚不清楚。研究人员报告了一种范例,可以以单细胞分辨率量化头颈鳞状细胞癌(HNSCC)中的表型多样性。通过结合细胞状态标记物和形态特征,研究人员识别出与临床特征(包括转移和复发)相关的表型特征。整合肿瘤和基质特征后发现,部分上皮-间质转化(pEMT)使疾病结局对基质组成高度敏感,从而产生了一个强大的预后和预测特征。空间转录组学和随后对癌症球体动力学的分析确定了癌症相关成纤维细胞-pEMT轴作作为跨室信号传导的枢纽,可以重新编程pEMT细胞成为侵袭性的表型。综上所述,研究人员建立了识别临床相关的肿瘤表型的新范式,并发现了基质和上皮细胞之间依赖细胞状态的相互作用进而驱动了癌症的侵袭。
12. IRGQ-mediated autophagy in MHC class I quality control promotes tumor immune evasion
IRGQ介导的自噬在MHCⅠ类分子质量控制中促进肿瘤免疫逃逸

The autophagy-lysosome system directs the degradation of a wide variety of cargo and is also involved in tumor progression. Here, we show that the immunity-related GTPase family Q protein (IRGQ), an uncharacterized protein to date, acts in the quality control of major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC class I) molecules. IRGQ directs misfolded MHC class I toward lysosomal degradation through its binding mode to GABARAPL2 and LC3B. In the absence of IRGQ, free MHC class I heavy chains do not only accumulate in the cell but are also transported to the cell surface, thereby promoting an immune response. Mice and human patients suffering from hepatocellular carcinoma show improved survival rates with reduced IRGQ levels due to increased reactivity of CD8+ T cells toward IRGQ knockout tumor cells. Thus, we reveal IRGQ as a regulator of MHC class I quality control, mediating tumor immune evasion.
自噬-溶酶体系统负责多种蛋白的降解,并且参与肿瘤进展。研究人员发现了免疫相关的GTP酶家族Q蛋白(IRGQ)(一种至今未被充分表征的蛋白质),在主要组织相容性复合体I类(MHC I类)分子的质量控制中发挥作用。IRGQ通过其与GABARAPL2和LC3B的结合模式,将错误折叠的I类MHC引导至溶酶体降解。在IRGQ缺失的情况下,游离的MHC I类重链不仅在细胞中积累,而且还被转运到细胞表面,促进免疫应答。由于CD8+ T细胞对IRGQ基因敲除的肿瘤细胞的反应性增强,在肝细胞癌小鼠模型中和人类肝细胞癌患者中,在IRGQ水平降低的情况下生存率有所提高。因此,研究人员揭示了IRGQ是MHC I类质量控制的调节因子,并介导肿瘤免疫逃逸。
13. Multiscale organization of neuronal activity unifies scale-dependent theories of brain function
神经元活动的多尺度组织统一了大脑功能的尺度依赖理论
Brain recordings collected at different resolutions support distinct signatures of neural coding, leading to scale-dependent theories of brain function. Here, we show that these disparate signatures emerge from a heavy-tailed, multiscale functional organization of neuronal activity observed across calcium-imaging recordings collected from the whole brains of zebrafish and C. elegans as well as from sensory regions in Drosophila, mice, and macaques. Network simulations demonstrate that this conserved hierarchical structure enhances information processing. Finally, we find that this organization is maintained despite significant cross-scale reconfiguration of cellular coordination during behavior. Our findings suggest that this nonlinear organization of neuronal activity is a universal principle conserved for its ability to adaptively link behavior to neural dynamics across multiple spatiotemporal scales while balancing functional resiliency and information processing efficiency.
在不同分辨率采集的大脑活动记录显示神经编码的不同特征,从而形成了尺度依赖的大脑功能理论。本文中研究人员展示了这些不同的信号源自一种重尾的、多尺度的神经元活动功能组织,它们在斑马鱼和秀丽隐杆线虫的全脑以及果蝇、小鼠和猕猴的感官区域收集的钙成像记录中均观察到。网络模拟表明,这种保守的层级结构增强了信息处理能力。最后,研究人员发现,尽管在行为过程中细胞协调发生了显著的跨尺度重构,但这种组织仍然得以维持。研究结果表明,这种神经活动的非线性组织是一种普遍原则,其进化保守性源于能够自适应性地将行为与多个时空尺度上的神经动态进行联系,同时平衡功能弹性和信息处理效率。
14. Identifying specific functional roles for senescence across cell types
识别衰老在不同细胞类型的特定功能角色

Cellular senescence plays critical roles in aging, regeneration, and disease; yet, the ability to discern its contributions across various cell types to these biological processes remains limited. In this study, we generated an in vivo genetic toolbox consisting of three p16Ink4a-related intersectional genetic systems, enabling pulse-chase tracing (Sn-pTracer), Cre-based tracing and ablation (Sn-cTracer), and gene manipulation combined with tracing (Sn-gTracer) of defined p16Ink4a+ cell types. Using liver injury and repair as an example, we found that macrophages and endothelial cells (ECs) represent distinct senescent cell populations with different fates and functions during liver fibrosis and repair. Notably, clearance of p16Ink4a+ macrophages significantly mitigates hepatocellular damage, whereas eliminating p16Ink4a+ ECs aggravates liver injury. Additionally, targeted reprogramming of p16Ink4a+ ECs through Kdr overexpression markedly reduces liver fibrosis. This study illuminates the functional diversity of p16Ink4a+ cells and offers insights for developing cell-type-specific senolytic therapies in the future.
细胞衰老在衰老、再生和疾病中发挥着关键作用;然而,在各种细胞类型中辨别细胞衰老对这些生物过程的影响仍然困难。本研究中,研究人员构建了一个体内遗传工具箱,由三个p16Ink4a相关的交叉遗传系统组成,能对特定p16Ink4a+细胞类型进行脉冲追踪(Sn-pTracer)、基于Cre的追踪和消融(Sn-cTracer)以及结合基因操作的追踪(Sn-gTracer)。以肝损伤和修复为例,研究人员发现巨噬细胞和内皮细胞(ECs)代表了不同的衰老细胞群体,它们在肝纤维化和修复过程中具有不同的命运和功能。值得注意的是,清除p16Ink4a+巨噬细胞可显著减轻肝细胞损伤,而清除p16Ink4a+ ECs可加重肝损伤。此外,通过Kdr过表达对p16Ink4a+ ECs进行靶向重编程可显著减轻肝纤维化。这项研究阐明了p16Ink4a+细胞的功能多样性,并为未来开发细胞类型特异性的衰老疗法提供了见解。

Dec 26, 2024;Volume 187, Issue 26;p7351-7656
Cell共发表17篇,其中包括16篇Articles; 1篇Editorial Note。
On the cover: Andersson-Rolf et al. describe a human fetal tripotent stem/progenitor cell, capable of long-term expansion in vitro and of generating all three pancreatic cell lineages. Human fetal pancreatic organoids derived from this stem cell recapitulate the epithelial complexity of the native pancreas. The cover image features an artistic representation of how the fetal tripotent pancreatic stem cell (pink, yellow, and white smaller circle) gives rise to the three main cell lineages of the pancreas (pink, yellow, and green fluid lines), which together make up the pancreas organ (yellow, green, and pink larger oval). Image resources: Simona Jole Anna Lafirenze.
封面内容:Andersson-Rolf等人描述了一种人类胎儿三能特性干细胞/祖细胞,这种细胞能够在体外长期扩增,并能生成所有三种胰腺细胞谱系。从这种干细胞衍生的人类胎儿胰腺类器官能够重现原生胰腺的上皮复杂性。封面图像由Simona Jole Anna Lafirenze创作,艺术地展示了胎儿三能特性胰腺干细胞(粉色、黄色和白色的小圆圈)如何产生胰腺的三种主要细胞谱系(粉色、黄色和绿色的流体线),这些细胞谱系共同构成了胰腺器官(黄色、绿色和粉色的大椭圆形)。
1. Spatiotemporal modeling of molecular holograms
分子全息图的时空建模

Quantifying spatiotemporal dynamics during embryogenesis is crucial for understanding congenital diseases. We developed Spateo (https://github.com/aristoteleo/spateo-release), a 3D spatiotemporal modeling framework, and applied it to a 3D mouse embryogenesis atlas at E9.5 and E11.5, capturing eight million cells. Spateo enables scalable, partial, non-rigid alignment, multi-slice refinement, and mesh correction to create molecular holograms of whole embryos. It introduces digitization methods to uncover multi-level biology from subcellular to whole organ, identifying expression gradients along orthogonal axes of emergent 3D structures, e.g., secondary organizers such as midbrain-hindbrain boundary (MHB). Spateo further jointly models intercellular and intracellular interaction to dissect signaling landscapes in 3D structures, including the zona limitans intrathalamica (ZLI). Lastly, Spateo introduces “morphometric vector fields” of cell migration and integrates spatial differential geometry to unveil molecular programs underlying asymmetrical murine heart organogenesis and others, bridging macroscopic changes with molecular dynamics. Thus, Spateo enables the study of organ ecology at a molecular level in 3D space over time.
量化胚胎发生过程中的时空动态对于理解先天性疾病至关重要。研究人员开发了Spateo(https://github.com/aristoteleo/spateo-release),一个3D时空建模框架,并将其应用于E9.5和E11.5的3D小鼠胚胎发生图谱,捕捉了八百万个细胞。Spateo能够进行扩展、局部、非刚性对齐、多切片细化和网格校正,以创建整个胚胎的分子全息图。它引入了数字化方法来揭示从亚细胞到整个器官的多级生物学中,识别沿3D结构的正交轴识别表达梯度,例如中脑-后脑边界(MHB)等次级组织。Spateo进一步联合建模细胞间和细胞内相互作用,以剖析3D结构中的信号图谱,包括丘脑带界膜(ZLI)。最后,Spateo引入了“形态测量矢量场”来描述细胞迁移,并整合空间微分几何学揭示小鼠心脏器官不对称发育等过程中的分子调控程序,将宏观变化与分子动力学联系起来。因此,Spateo能够在3D空间中对分子水平上器官生态随时间的变化进行研究。
2. Decoding transcriptional identity in developing human sensory neurons and organoid modeling
解码发育中人类感觉神经元的转录特征及类器官建模

Dorsal root ganglia (DRGs) play a crucial role in processing sensory information, making it essential to understand their development. Here, we construct a single-cell spatiotemporal transcriptomic atlas of human embryonic DRG. This atlas reveals the diversity of cell types and highlights the extrinsic signaling cascades and intrinsic regulatory hierarchies that guide cell fate decisions, including neuronal/glial lineage restriction, sensory neuron differentiation and specification, and the formation of neuron-satellite glial cell (SGC) units. Additionally, we identify a human-enriched NTRK3+/DCC+ nociceptor subtype, which is involved in multimodal nociceptive processing. Mimicking the programmed activation of signaling pathways in vivo, we successfully establish functional human DRG organoids and underscore the critical roles of transcriptional regulators in the fate commitment of unspecialized sensory neurons (uSNs). Overall, our research elucidates the multilevel signaling pathways and transcription factor (TF) regulatory hierarchies that underpin the diversity of somatosensory neurons, emphasizing the phenotypic distinctions in human nociceptor subtypes.
背根神经节(DRGs)在处理感觉信息方面起着至关重要的作用,因此了解其发育过程至关重要。研究人员构建了人类胚胎DRG的单细胞时空转录组图谱。该图谱揭示了细胞类型的多样性,并强调了指导细胞命运决策的外源性信号转导级联和内在调控层次,包括神经元/神经胶质细胞谱系限制、感觉神经元分化和特化,以及神经元-卫星胶质细胞(SGC)单元的形成。此外,研究人员确定了一种人类富集的NTRK3+/DCC+痛觉感受器亚型,它参与多种模式的痛觉感受加工。通过模拟体内信号通路的程序激活,研究人员成功建立了功能性人类DRG类器官,并强调了转录调节因子在非特化感觉神经元(uSNs)命运中的关键作用。总体而言,研究人员的研究阐明了支撑躯体感觉神经元多样性的多级信号通路和转录因子(TF)调控层级,强调了人类痛觉感受器亚型的表型差异。
3. Long-term in vitro expansion of a human fetal pancreas stem cell that generates all three pancreatic cell lineages
人类胎儿胰腺干细胞的长期体外扩增可生成所有三种胰腺细胞系

The mammalian pancreas consists of three epithelial compartments: the acini and ducts of the exocrine pancreas and the endocrine islets of Langerhans. Murine studies indicate that these three compartments derive from a transient, common pancreatic progenitor. Here, we report derivation of 18 human fetal pancreas organoid (hfPO) lines from gestational weeks 8–17 (8–17 GWs) fetal pancreas samples. Four of these lines, derived from 15 to 16 GWs samples, generate acinar-, ductal-, and endocrine-lineage cells while expanding exponentially for >2 years under optimized culture conditions. Single-cell RNA sequencing identifies rare LGR5+ cells in fetal pancreas and in hfPOs as the root of the developmental hierarchy. These LGR5+ cells share multiple markers with adult gastrointestinal tract stem cells. Organoids derived from single LGR5+ organoid-derived cells recapitulate this tripotency in vitro. We describe a human fetal tripotent stem/progenitor cell capable of long-term expansion in vitro and of generating all three pancreatic cell lineages.
哺乳动物的胰腺由三个上皮细胞区域组成:胰腺外分泌区的腺泡和导管,以及内分泌区的胰岛。小鼠研究表明,这三个区域来源于一个短暂的、共同的胰腺祖细胞。研究人员报告了从妊娠8至17周(8-17 GWs)的胎儿胰腺样本中衍生出18个人类胚胎胰腺类器官(hfPO)。其中,来自15至16周样本的四个类器官系在优化的培养条件下能够以指数级扩增2年以上,同时生成腺泡、导管和内分泌细胞。单细胞RNA测序鉴定出在胎儿胰腺和hfPOs中罕见的LGR5+细胞是发育的根源。这些LGR5+细胞与成人胃肠道干细胞共享多个标记物。从单个LGR5+类器官衍生细胞中衍生出的类器官在体外重现了这种三向分化能力。研究人员描述了一种能够在体外长期扩增并生成所有的三种胰腺细胞谱系的人类胚胎三重性干细胞/祖细胞,。
4. Stem cell activity-coupled suppression of endogenous retrovirus governs adult tissue regeneration
干细胞活性与内源性逆转录病毒抑制的结合控制成体组织的再生

Mammalian retrotransposons constitute 40% of the genome. During tissue regeneration, adult stem cells coordinately repress retrotransposons and activate lineage genes, but how this coordination is controlled is poorly understood. Here, we observed that dynamic expression of histone methyltransferase SETDB1 (a retrotransposon repressor) closely mirrors stem cell activities in murine skin. SETDB1 ablation leads to the reactivation of endogenous retroviruses (ERVs, a type of retrotransposon) and the assembly of viral-like particles, resulting in hair loss and stem cell exhaustion that is reversible by antiviral drugs. Mechanistically, at least two molecularly and spatially distinct pathways are responsible: antiviral defense mediated by hair follicle stem cells and progenitors and antiviral-independent response due to replication stress in transient amplifying cells. ERV reactivation is promoted by DNA demethylase ten-eleven translocation (TET)-mediated hydroxymethylation and recapitulated by ablating cell fate transcription factors. Together, we demonstrated ERV silencing is coupled with stem cell activity and essential for adult hair regeneration.
哺乳动物逆转录转座子占基因组的40%。在组织再生过程中,成体干细胞协调抑制逆转录转座子并激活谱系基因,但这种协调的控制机制尚不清楚。研究人员观察到,组蛋白甲基转移酶SETDB1(一种逆转录转座子抑制因子)的动态表达与小鼠皮肤中干细胞的活性密切相关。SETDB1的缺失导致内源性逆转录病毒(ERVs,一种逆转录转座子)的重新激活和病毒样颗粒的组装,结果导致脱发和干细胞耗竭,这一过程可以通过抗病毒药物逆转。从机制上讲,至少有两种在分子和空间上不同的途径负责:由毛囊干细胞和祖细胞介导的抗病毒防御,以及由于瞬时扩增细胞中的复制压力引起的抗病毒独立反应。ERV的重新激活由DNA去甲基化酶TET介导的羟甲基化促进,并通过消除细胞命运转录因子来重激活。总之,研究人员证明了ERV沉默与干细胞活性有关,并对毛发生长至关重要。
5. Structure-guided design of a peripherally restricted chemogenetic system
以结构为导向设计外围受限的化学遗传系统

Designer receptors exclusively activated by designer drugs (DREADDs) are chemogenetic tools for remotely controlling cellular signaling, neural activity, behavior, and physiology. Using a structure-guided approach, we provide a peripherally restricted Gi-DREADD, hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor DREADD (HCAD), whose native receptor is minimally expressed in the brain, and a chemical actuator that does not cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB). This was accomplished by combined mutagenesis, analoging via an ultra-large make-on-demand library, structural determination of the designed DREADD receptor via cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM), and validation of HCAD function. Expression and activation of HCAD in dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons inhibit action potential (AP) firing and reduce both acute and tissue-injury-induced inflammatory pain. The HCAD chemogenetic system expands the possibilities for studying numerous peripheral systems with little adverse effects on the central nervous system (CNS). The structure-guided approach used to generate HCAD also has the potential to accelerate the development of emerging chemogenetic tools for basic and translational sciences.
只由特定药物激活的受体(DREADDs)是一种化学遗传学技术,用于远程控制细胞信号、神经活动、行为和生理。通过结构引导的方法,研究人员提供了一种外周受限的Gi-DREADD,即羟基羧酸受体DREADD(HCAD),其天然受体在大脑中的表达极少,是一种不穿过血脑屏障(BBB)的化学激活剂。这是通过结合突变、利用超大型按需合成库进行模拟、通过冷冻电镜(cryo-EM)确定设计的DREADD受体的结构,以及验证HCAD的功能来实现的。在背根神经节(DRG)神经元中表达和激活HCAD可以抑制动作电位(AP)的激发,并减少急性和组织损伤诱导的炎症性疼痛。HCAD化学遗传系统扩展了研究众多外周系统的可能性并对中枢神经系统(CNS)产生的副作用很小。用于生成HCAD的结构引导方法也有潜力加速新兴化学遗传工具在基础和转化科学中的开发。
6. Organ-specific electrophile responsivity mapping in live C. elegans
活体秀丽隐杆线虫( C. elegans )器官特异性亲电反应性图谱

Proximity labeling technologies are limited to indexing localized protein residents. Such data—although valuable—cannot inform on small-molecule responsivity of local residents. We here bridge this gap by demonstrating in live C. elegans how electrophile-sensing propensity in specific organs can be quantitatively mapped and ranked. Using this method, >70% of tissue-specific responders exhibit electrophile responsivity, independent of tissue-specific abundance. One responder, cyp-33e1—for which both human and worm orthologs are electrophile responsive—marshals stress-dependent gut functions, despite manifesting uniform abundance across all tissues studied. Cyp-33e1’s localized electrophile responsivity operates site specifically, triggering multifaceted responses: electrophile sensing through the catalytic-site cysteine results in partitioning between enzyme inhibition and localized production of a critical metabolite that governs global lipid availability, whereas rapid dual-cysteine site-specific sensing modulates gut homeostasis. Beyond pinpointing chemical actionability within local proteomes, organ-specific electrophile responsivity mapping illuminates otherwise intractable locale-specific metabolite signaling and stress response programs influencing organ-specific decision-making.
邻近标记技术仅限于标记定位蛋白质的分布特征。这些数据虽然很有价值,但无法了解局部蛋白质的小分子反应性。研究人员通过在活体秀丽隐杆线虫中展示如何定量绘制和排列特定器官中的亲电感应倾向来弥补这一不足。使用这种方法,超过70%的组织特异性反应器表现出亲电反应性,与组织特异性丰度无关。其中一个反应者cyp-33e1——人类和蠕虫直系同源物都具有亲电反应性—调控应激依赖的肠道功能,尽管其在所有研究组织中表现出相同的丰度,。Cyp-33e1的局部亲电反应性具有特异性位点,触发多种反应:通过催化位点半胱氨酸的亲电感应导致酶抑制和控制整体脂质可用性的关键代谢物局部产生分离,而快速的双半胱氨酸位点特异性感应调节肠道稳态。除了确定局部蛋白质组内的化学作用外,器官特异性亲电反应图谱还阐明了其他难以处理的局部特异性代谢物信号和影响器官特异性决策的应激反应程序。
7. Multimodal targeting chimeras enable integrated immunotherapy leveraging tumor-immune microenvironment
多模态靶向嵌合体利用肿瘤免疫微环境实现综合免疫治疗

Although immunotherapy has revolutionized cancer treatment, its efficacy is affected by multiple factors, particularly those derived from the complexity and heterogeneity of the tumor-immune microenvironment (TIME). Strategies that simultaneously and synergistically engage multiple immune cells in TIME remain highly desirable but challenging. Herein, we report a multimodal and programmable platform that enables the integration of multiple therapeutic modules into single agents for tumor-targeted co-engagement of multiple immune cells within TIME. We developed the triple orthogonal linker (T-Linker) technology to integrate various therapeutic small molecules and biomolecules as multimodal targeting chimeras (Multi-TACs). The EGFR-CD3-PDL1 Multi-TAC facilitated T-dendritic cell co-engagement to target solid tumors with excellent efficacy, as demonstrated in vitro, in several humanized mouse models and in patient-derived tumor models. Furthermore, Multi-TACs were constructed to coordinate T cells with other immune cell types. The highly modular and programmable feature of our Multi-TACs may find broad applications in immunotherapy and beyond.
虽然免疫疗法已经彻底改变了癌症治疗,但其疗效受到多种因素的影响,特别是肿瘤免疫微环境(TIME)的复杂性和异质性。在TIME中同时协同调动多种免疫细胞的策略仍然非常理想,但却极具挑战性。研究人员报告了一种多模式和可编程平台,它能将多种治疗模块整合到单一药物中,从而实现肿瘤靶向,并协同调动 TIME 内的多种免疫细胞。研究人员开发了三重正交链接器(T-Linker)技术,将各种治疗性小分子和生物大分子整合为多模态靶向嵌合体(Multi-TACs)。EGFR-CD3-PDL1多模态靶向嵌合体可促进T -树突状细胞协同靶向实体瘤,在体外、多种人源化小鼠模型和患者来源的肿瘤模型中均显示出卓越疗效。此外,本研究还构建了T细胞与其他免疫细胞(如自然杀伤细胞、巨噬细胞)协同作用的Multi - TAC。Multi - TAC的高度模块化和可编程特性有望在免疫治疗和其他方面有广泛的应用。
8. Ovarian cancer-derived IL-4 promotes immunotherapy resistance
卵巢癌来源的IL - 4促进免疫治疗抵抗

Ovarian cancer is resistant to immunotherapy, and this is influenced by the immunosuppressed tumor microenvironment (TME) dominated by macrophages. Resistance is also affected by intratumoral heterogeneity, whose development is poorly understood. To identify regulators of ovarian cancer immunity, we employed a spatial functional genomics screen (Perturb-map), focused on receptor/ligands hypothesized to be involved in tumor-macrophage communication. Perturb-map recapitulated tumor heterogeneity and revealed that interleukin-4 (IL-4) promotes resistance to anti-PD-1. We find ovarian cancer cells are the key source of IL-4, which directs the formation of an immunosuppressive TME via macrophage control. IL-4 loss was not compensated by nearby IL-4-expressing clones, revealing short-range regulation of TME composition dictating tumor evolution. Our studies show heterogeneous TMEs can emerge from localized altered expression of cancer-derived cytokines/chemokines that establish immune-rich and immune-excluded neighborhoods, which drive clone selection and immunotherapy resistance. They also demonstrate the potential of targeting IL-4 signaling to enhance ovarian cancer response to immunotherapy.
卵巢癌对免疫治疗具有抵抗性,这受到以巨噬细胞为主的免疫抑制肿瘤微环境(TME)的影响。抗药性还受肿瘤内异质性的影响,而其发展机制尚不清楚。为了识别卵巢癌免疫的调控因子,研究人员采用了空间功能基因组学筛选(Perturb-map),重点关注假设参与肿瘤-巨噬细胞通信的受体/配体。Perturb-map重现了肿瘤异质性,并揭示了白细胞介素-4(IL-4)促进对PD-1抑制剂的抵抗。研究人员发现卵巢癌细胞是IL-4的关键来源,它通过巨噬细胞介导免疫抑制性TME的形成。IL-4的缺失不会被附近表达IL-4的克隆细胞补偿,这揭示了TME组成的短程调节决定了肿瘤的进化。研究表明,局部改变表达的癌症源性细胞因子/趋化因子可产生异质性TMEs,这些因子/趋化因子建立了免疫富集区和免疫排斥区,从而驱动克隆选择和免疫治疗抵抗。这些研究还表明靶向IL-4信号通路增强卵巢癌对免疫治疗反应的潜力。
9. Differential contributions of fetal mononuclear phagocytes to Zika virus neuroinvasion versus neuroprotection during congenital infection
胎儿单核巨噬细胞对在先天性感染过程中寨卡病毒神经侵袭与神经保护的不同贡献

Fetal immune cell functions during congenital infections are poorly understood. Zika virus (ZIKV) can vertically transmit from mother to fetus, causing nervous system infection and congenital ZIKV syndrome (CZS). We identified differential functional roles for fetal monocyte/macrophage cell types and microglia in ZIKV dissemination versus clearance using mouse models. Trafficking of ZIKV-infected primitive macrophages from the yolk sac allowed initial fetal virus inoculation, while recruited monocytes promoted non-productive neuroinflammation. Conversely, brain-resident differentiated microglia were protective, limiting infection and neuronal death. Single-cell RNA sequencing identified transcriptional profiles linked to the protective versus detrimental contributions of mononuclear phagocyte subsets. In human brain organoids, microglia also promoted neuroprotective transcriptional changes and infection clearance. Thus, microglia are protective before birth, contrasting with the disease-enhancing roles of primitive macrophages and monocytes. Differential modulation of myeloid cell phenotypes by genetically divergent ZIKVs underscores the potential of immune cells to regulate diverse outcomes during fetal infections.
胎儿免疫细胞在先天性感染中的功能尚未明确。寨卡病毒(ZIKV)可以通过母婴垂直传播,导致神经系统感染和先天性寨卡病毒综合症(CZS)。研究人员利用小鼠模型,鉴定了胎儿单核细胞/巨噬细胞类型和小胶质细胞在ZIKV传播与清除中的不同功能作用。ZIKV感染的原始巨噬细胞从卵黄囊的迁移,促进了初期的胎儿病毒接种,而招募的单核细胞则会促进非生产性的神经炎症。相反,驻留在大脑中的分化小胶质细胞具有保护作用,限制了感染和神经元死亡。单细胞RNA测序揭示了与单核巨噬细胞亚群的保护性与有害性相关的转录图谱。在人类脑类器官中,小胶质细胞也促进了神经保护性的转录变化和感染清除。因此,小胶质细胞在出生前具有保护作用,与原始巨噬细胞和单核细胞的促进疾病作用形成对比。不同基因型的ZIKV对髓系细胞表型的差异性调节也体现了免疫细胞在胎儿感染过程中调节的不同结果的潜力。
10. Type III interferons induce pyroptosis in gut epithelial cells and impair mucosal repair
Ⅲ型干扰素诱导肠上皮细胞焦亡并破坏黏膜修复
Tissue damage and repair are hallmarks of inflammation. Despite a wealth of information on the mechanisms that govern tissue damage, mechanistic insight into how inflammation affects repair is lacking. Here, we investigated how interferons influence tissue repair after damage to the intestinal mucosa. We found that type III, not type I or type II, interferons delay epithelial cell regeneration by inducing the upregulation of Z-DNA-binding protein 1 (ZBP1). Z-nucleic acids formed following intestinal damage are sensed by ZBP1, leading to caspase-8 activation and the cleavage of gasdermin C (GSDMC). Cleaved GSDMC drives epithelial cell death by pyroptosis and delays repair of the large or small intestine after colitis or irradiation, respectively. The type III interferon/ZBP1/caspase-8/GSDMC axis is also active in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Our findings highlight the capacity of type III interferons to delay gut repair, which has implications for IBD patients or individuals exposed to radiation therapies.
组织损伤和修复是炎症的标志。尽管有大量关于组织损伤机制的信息,但对炎症如何影响修复的机制仍不明确。研究人员调查了干扰素如何影响肠道黏膜受损后的组织修复。研究发现,III型干扰素(而非I型或II型干扰素)通过诱导Z-DNA结合蛋白1(ZBP1)的上调来延迟上皮细胞的再生。肠道损伤后形成的Z核酸被ZBP1感知,导致caspase-8激活和gasderminC(GSDMC)的裂解。裂解的GSDMC通过焦亡驱动上皮细胞死亡,分别延迟了结肠炎或辐照后大肠或小肠的修复。III型干扰素/ZBP1/caspase-8/GSDMC轴在炎症性肠病(IBD)患者中也处于活跃状态。研究结果强调了III型干扰素延迟肠道修复的能力,这对IBD患者或接受放射治疗的患者具有重要意义。
11. Regulatory mechanisms of strigolactone perception in rice
水稻中独脚金内酯感知的调控机制

Strigolactones (SLs) are hormones essential for plant development and environmental responses. SL perception requires the formation of the complex composed of an SL receptor DWARF14 (D14), F-box protein D3, and transcriptional repressor D53, triggering ubiquitination and degradation of D53 to activate signal transduction. However, mechanisms of SL perception and their influence on plant architecture and environmental responses remain elusive and controversial. Here, we report that key residues at interfaces of the AtD14-D3-ASK1 complex are essential for the activation of SL perception, discover that overexpression of the D3-CTH motif negatively regulates SL perception to enhance tillering, and reveal the importance of phosphorylation and N-terminal disordered (NTD) domain in mediating ubiquitination and degradation of D14. Importantly, low nitrogen promotes phosphorylation and stabilization of D14 to repress rice tillering. These findings reveal a panorama of the activation, termination, and regulation of SL perception, which determines the plasticity of plant architecture in complex environments.
独脚金内酯(Strigolactones, SLs)是一类对植物发育和环境响应至关重要的植物激素。SL的感知需要由SL受体DWARF14(D14)、F-box蛋白D3和转录抑制因子D53组成的复合体的形成,从而触发D53的泛素化和降解以激活信号转导。然而,SL感知的机制及其对植物架构和环境响应的影响仍不明确且存在争议。研究人员称,AtD14-D3-ASK1复合体上的关键残基对于SL感知的激活至关重要,发现D3-CTH基序的过表达会负向调节SL感知以增强分蘖,并揭示了磷酸化和N端无序(NTD)结构域在介导D14的泛素化和降解中的重要性。重要的是,低氮环境会促进D14的磷酸化和稳定,从而抑制了水稻的分蘖。这些发现揭示了SL感知的激活、终止和调节的全过程,这决定了植物在复杂环境中的可塑性。
12. Recognition of BACH1 quaternary structure degrons by two F-box proteins under oxidative stress
氧化应激条件下两种F - box蛋白识别BACH1四级结构降解信号

Ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis regulates diverse cellular functions with high substrate specificity, which hinges on the ability of ubiquitin E3 ligases to decode the targets’ degradation signals, i.e., degrons. Here, we show that BACH1, a transcription repressor of antioxidant response genes, features two distinct unconventional degrons encrypted in the quaternary structure of its homodimeric BTB domain. These two degrons are both functionalized by oxidative stress and are deciphered by two complementary E3s. FBXO22 recognizes a degron constructed by the BACH1 BTB domain dimer interface, which is unmasked from transcriptional co-repressors after oxidative stress releases BACH1 from chromatin. When this degron is impaired by oxidation, a second BACH1 degron manifested by its destabilized BTB dimer is probed by a pair of FBXL17 proteins that remodels the substrate into E3-bound monomers for ubiquitination. Our findings highlight the multidimensionality of protein degradation signals and the functional complementarity of different ubiquitin ligases targeting the same substrate.
泛素依赖性蛋白质降解通过高特异性底物识别调控多种细胞功能,这一过程依赖于泛素E3连接酶解码靶标降解信号(即degrons)的能力。研究人员发现,BACH1(一种抗氧化反应基因的转录抑制因子)在其同源二聚体BTB结构域的四级结构中具有两个不同的非常规降解信号(degrons)。这两个降解信号都由氧化应激激活,并被两个互补的E3连接酶识别。FBXO22可识别由BACH1 BTB结构域二聚体构建的降解信号,该信号在氧化应激环境中使BACH1从染色质上释放后,从转录共抑制因子中暴露出来。当这个降解信号因氧化受损时,由其不稳定的BTB二聚体表现出来的第二个BACH1降解信号,被一对FBXL17蛋白探测到,这些蛋白将底物重塑为E3结合的单体以进行泛素化。这些发现突出了蛋白质降解信号的多维性以及针对同一底物的不同泛素连接酶的功能互补性。
13. Dual BACH1 regulation by complementary SCF-type E3 ligases
互补的SCF型E3连接酶对BACH1的双重调控

Broad-complex, tramtrack, and bric-à-brac domain (BTB) and CNC homolog 1 (BACH1) is a key regulator of the cellular oxidative stress response and an oncogene that undergoes tight post-translational control by two distinct F-box ubiquitin ligases, SCFFBXO22 and SCFFBXL17. However, how both ligases recognize BACH1 under oxidative stress is unclear. In our study, we elucidate the mechanism by which FBXO22 recognizes a quaternary degron in a domain-swapped β-sheet of the BACH1 BTB dimer. Cancer-associated mutations and cysteine modifications destabilize the degron and impair FBXO22 binding but simultaneously expose an otherwise shielded degron in the dimer interface, allowing FBXL17 to recognize BACH1 as a monomer. These findings shed light on a ligase switch mechanism that enables post-translational regulation of BACH1 by complementary ligases depending on the stability of its BTB domain. Our results provide mechanistic insights into the oxidative stress response and may spur therapeutic approaches for targeting oxidative stress-related disorders and cancer.
BACH1(Broad-complex, tramtrack, and bric-à-brac domain and CNC homolog 1)是细胞氧化应激反应的关键调节因子,也是一种癌基因,其稳定性受到两种不同的F-box泛素连接酶SCFFBXO22和SCFFBXL17的严格调控。然而,这两种连接酶在氧化应激下如何识别BACH1尚不清楚。研究人员揭示了FBXO22识别BACH1 BTB结构域中一个四聚体降解信号(degron)的机制。癌症相关突变和半胱氨酸修饰会破坏该降解信号的稳定性,导致和FBXO22的结合受损,但同时会暴露一个二聚体界面中原本被屏蔽的降解位点,使FBXL17能够识别BACH1单体。这些发现揭示了一种连接酶转换机制-通过BACH1的BTB结构域的稳定性,互补的泛素连接酶能够实现BACH1的翻译后调控。这些结果为氧化应激反应提供了机制上的见解,并可能促进针对氧化应激相关疾病和癌症的治疗新方法。
14. Transposable element exonization generates a reservoir of evolving and functional protein isoforms
转座子外显化产生不断进化的功能性蛋白质同工酶库

Alternative splicing enhances protein diversity in different ways, including through exonization of transposable elements (TEs). Recent transcriptomic analyses identified thousands of unannotated spliced transcripts with exonizing TEs, but their contribution to the proteome and biological relevance remains unclear. Here, we use transcriptome assembly, ribosome profiling, and proteomics to describe a population of 1,227 unannotated TE exonizing isoforms generated by mRNA splicing and recurrent in human populations. Despite being shorter and lowly expressed, these isoforms are shared between individuals and efficiently translated. Functional analyses show stable expression, specific cellular localization, and, in some cases, modified functions. Exonized TEs are rich in ancient genes, whereas the involved splice sites are recent and can be evolutionarily conserved. In addition, exonized TEs contribute to the secondary structure of the emerging isoforms, supporting their functional relevance. We conclude that TE-spliced isoforms represent a diversity reservoir of functional proteins on which natural selection can act.
可变剪接通过多种方式增加蛋白质多样性,其中包括转座子(TEs)的外显子化。近期的转录组分析发现了数千个未被注释的带有外显子化TEs的剪接转录本,但它们对蛋白质组的贡献和生物学相关性仍不清楚。研究人员利用转录组组装、核糖体分析和蛋白质组学描述了1,227个由mRNA剪接产生的未被注释的TE外显子异构体,并且这些异构体在人类群体中反复出现。尽管这些异构体较短且表达量低,但它们在个体间共享且能高效翻译为蛋白质。功能分析显示这些异构体具有稳定的表达和特定的细胞定位,且在部分情况下具有可变的功能。外显子化的TEs富含古老基因,而涉及的剪接位点则是新的,并且在进化中保守。此外,外显子化的TEs对新出现的异构体的二级结构有贡献,从而支持它们的功能性。研究人员得出结论,TE剪接异构体代表了一个功能蛋白质的多样性库,自然选择可以对其发挥作用。
15. Regulation of human interferon signaling by transposon exonization
转座子外显子化对人类干扰素信号的调控

Innate immune signaling is essential for clearing pathogens and damaged cells and must be tightly regulated to avoid excessive inflammation or autoimmunity. Here, we found that the alternative splicing of exons derived from transposable elements is a key mechanism controlling immune signaling in human cells. By analyzing long-read transcriptome datasets, we identified numerous transposon exonization events predicted to generate functional protein variants of immune genes, including the type I interferon receptor IFNAR2. We demonstrated that the transposon-derived isoform of IFNAR2 is more highly expressed than the canonical isoform in almost all tissues and functions as a decoy receptor that potently inhibits interferon signaling, including in cells infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Our findings uncover a primate-specific axis controlling interferon signaling and show how a transposon exonization event can be co-opted for immune regulation.
先天免疫信号对于清除病原体和受损细胞至关重要,并且必须严格调控以避免过度炎症或自身免疫。研究人员发现,转座子衍生的外显子可变剪接是控制人类细胞免疫信号的关键机制。通过分析长读长转录组数据集,本研究识别了众多转座子的外显化事件,这些事件预测会生成免疫基因的功能性蛋白变体,包括I型干扰素受体IFNAR2。研究人员证明,IFNAR2的转座子衍生异构体在几乎所有组织中的表达量都高于经典异构体,并且在感染严重急性呼吸综合征冠状病毒2(SARS-CoV-2)的细胞中作为一种诱饵受体强力抑制干扰素信号。这些发现揭示了一个灵长类动物特有的控制干扰素信号的轴,并展示了转座子外显子化事件如何被用于免疫调控。
16. Transcriptome-scale RNA-targeting CRISPR screens reveal essential lncRNAs in human cells
转录组水平的RNA靶向CRISPR筛选揭示了人类细胞中必不可少的lncRNA

Mammalian genomes host a diverse array of RNA that includes protein-coding and noncoding transcripts. However, the functional roles of most long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) remain elusive. Using RNA-targeting CRISPR-Cas13 screens, we probed how the loss of ∼6,200 lncRNAs impacts cell fitness across five human cell lines and identified 778 lncRNAs with context-specific or broad essentiality. We confirm their essentiality with individual perturbations and find that the majority of essential lncRNAs operate independently of their nearest protein-coding genes. Using transcriptome profiling in single cells, we discover that the loss of essential lncRNAs impairs cell-cycle progression and drives apoptosis. Many essential lncRNAs demonstrate dynamic expression across tissues during development. Using ∼9,000 primary tumors, we pinpoint those lncRNAs whose expression in tumors correlates with survival, yielding new biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets. This transcriptome-wide survey of functional lncRNAs advances our understanding of noncoding transcripts and demonstrates the potential of transcriptome-scale noncoding screens with Cas13.
哺乳动物基因组中包含多种RNA,包括蛋白质编码和非编码转录本。然而,大多数长链非编码RNA(lncRNAs)的功能作用仍然不明。研究人员利用RNA靶向的CRISPR-Cas13筛选技术,探究了约6200个lncRNAs的缺失对五种人类细胞系(HAP1、HEK293T、K562、MDA-MB-231、THP1)细胞适应性的影响,并鉴定出778个具有特异性或广泛必需性的lncRNAs。通过个体扰动实验确认了它们的必需性,并发现大多数必需的lncRNAs独立于其最近的蛋白质编码基因。利用单细胞转录组分析,研究人员发现必需lncRNAs的缺失会阻碍细胞周期进程并推动细胞凋亡。许多必需的lncRNAs在发育过程中表现出跨组织的动态表达。通过分析约9000个原发性肿瘤,研究人员确定了那些在肿瘤中表达与生存相关的lncRNAs,从而提供了新的生物标志物和潜在的治疗靶点。这项的转录组范围内的功能性lncRNA研究不仅加深了对非编码转录本的了解,并展示了基于 Cas13 进行转录组规模的非编码筛选的潜力。

Jan 09, 2025;Volume 188, Issue 1;p1-272
Cell共发表18篇,其中包括1篇Leading Edge; 15篇Articles; 2篇Resources。
On the cover: In this issue of Cell, Deng et al. provide a comprehensive proteomics atlas for 1,706 human diseases and traits. The integration of machine learning models identifies promising biomarkers for disease discrimination and potential therapeutic targets, paving the way for precision medicine. The cover image portrays a human composed of proteins who is examining their health status (represented by the ECG monitoring interface) with the assistance of artificial intelligence (represented by the chip and binary codes). Image source: Jin-Tai Yu and Wei Cheng.
封面内容:在本期《细胞》杂志中,Deng等人提供了1706种人类疾病和特征的综合蛋白质组学图谱。通过整合机器学习模型,确定了有前景的疾病鉴别生物标志物和潜在的治疗靶点,为精准医疗铺平了道路。封面图像描绘了一个人类正在人工智能(由芯片和二进制代码表示)的辅助下检查自己的健康状况(由心电图监测界面表示)图像来源:Jin-Tai Yu和Wei Cheng。
1. Clade I mpox virus genomic diversity in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, 2018–2024: Predominance of zoonotic transmission
2018-2024年刚果民主共和国CladeⅠ型猴痘病毒基因组多样性:人畜共患病传播占主导地位

Recent reports raise concerns on the changing epidemiology of mpox in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). High-quality genomes were generated for 337 patients from 14/26 provinces to document whether the increase in number of cases is due to zoonotic spillover events or viral evolution, with enrichment of APOBEC3 mutations linked to human adaptation. Our study highlights two patterns of transmission contributing to the source of human cases. All new sequences from the eastern South Kivu province (n = 17; 4.8%) corresponded to the recently described clade Ib, associated with sexual contact and sustained human-to-human transmission. By contrast, all other genomes are clade Ia, which exhibits high genetic diversity with low numbers of APOBEC3 mutations compared with clade Ib, suggesting multiple zoonotic introductions. The presence of multiple clade I variants in urban areas highlights the need for coordinated international response efforts and more studies on the transmission and the reservoir of mpox.
近期报告引发了对刚果民主共和国(DRC)猴痘(mpox)流行病学变化的关注。研究人员为来自14/26个省的337名患者生成了高质量的基因组数据,以确定患者数量增加是由于人畜共患的传播还是病毒的进化,特别是与人类适应相关的APOBEC3突变的富集。研究强调了导致人类病例来源的两种传播模式。来自南基伍省东部的所有新序列(n = 17;4.8%)对应于最近描述的Ib亚群,与性接触和持续的人际传播有关。相比之下,所有其他基因组都属于Ia亚群,其表现出高遗传多样性,并且相比于Ib亚群,APOBEC3突变的数量较少,表明有多个人畜共换的传播事件。在城市地区存在多个I类变异体,表明需要协调的国际力量来应对,并需要更多关于猴痘传播和宿主的研究。
2. Functional genomics of human skeletal development and the patterning of height heritability
人类骨骼发育的功能基因组学和身高遗传模式

Underlying variation in height are regulatory changes to chondrocytes, cartilage cells comprising long-bone growth plates. Currently, we lack knowledge on epigenetic regulation and gene expression of chondrocytes sampled across the human skeleton, and therefore we cannot understand basic regulatory mechanisms controlling height biology. We first rectify this issue by generating extensive epigenetic and transcriptomic maps from chondrocytes sampled from different growth plates across developing human skeletons, discovering novel regulatory networks shaping human bone/joint development. Next, using these maps in tandem with height genome-wide association study (GWAS) signals, we disentangle the regulatory impacts that skeletal element-specific versus global-acting variants have on skeletal growth, revealing the prime importance of regulatory pleiotropy in controlling height variation. Finally, as height is highly heritable, and thus often the test case for complex-trait genetics, we leverage these datasets within a testable omnigenic model framework to discover novel chondrocyte developmental modules and peripheral-acting factors shaping height biology and skeletal growth.
身高变化的基础是构成长骨生长板的软骨细胞的调控变化。目前,对整个人体骨骼中软骨细胞的表观遗传调控和基因表达缺乏了解,导致无法解析控制身高的基本调控机制。研究人员首先通过生成来自发育中人类骨骼不同生长板的软骨细胞的广泛表观遗传和转录组图谱,解决了人类骨骼中软骨细胞的表观遗传调控和基因表达数据缺乏的问题,从而发现了塑造人类骨骼/关节发育的新调控网络。接下来,利用这些图谱与身高全基因组关联研究(GWAS)信号,解析了特异性骨骼变异与全局变异对骨骼生长的调控影响,揭示了调控多效性在控制身高变异中的主导作用。最后,由于身高具有高度遗传性,因此常被用作复杂性状遗传学的测试案例,研究人员利用这些数据集在可验证的的全基因模型框架内,发现了影响身高生物学、骨骼生长的新软骨细胞发育及骨骼生长的外周作用因子。
3. The genomic origin of early maize in eastern North America
北美东部早期玉米的基因组起源

Indigenous maize varieties from eastern North America have played an outsized role in breeding programs, yet their early origins are not fully understood. We generated paleogenomic data to reconstruct how maize first reached this region and how it was selected during the process. Genomic ancestry analyses reveal recurrent movements northward from different parts of Mexico, likely culminating in at least two dispersals from the US Southwest across the Great Plains to the Ozarks and beyond. We find that 1,000-year-old Ozark specimens carry a highly differentiated wx1 gene, which is involved in the synthesis of amylose, highlighting repeated selective pressures on the starch metabolic pathway throughout maize’s domestication. This population shows a close affinity with the lineage that ultimately became the Northern Flints, a major contributor to modern commercial maize.
北美东部本土玉米品种在育种计划中发挥了巨大作用,但其早期起源尚不完全清楚。研究人员生成了古基因组数据,以重建玉米最初是如何到达该地区的,以及在此过程中是如何被选择的。基因组祖先分析揭示了玉米从墨西哥不同地区向北反复迁移的过程,最终可能发生了至少两次从美国西南部穿越大平原到奥萨克山区及更远地区的扩散。研究人员发现,1000年前的奥扎克标本携带一个高度分化的wx1基因,该基因参与直链淀粉的合成,突出了玉米在整个培育过程中淀粉代谢途径的反复选择。这个种群与最终成为Northern Flints品种(现代商业玉米的主要贡献者)的族群密切相关。
4. A Zea genus-specific micropeptide controls kernel dehydration in maize
一种玉米属特异性微肽控制玉米籽粒脱水

Kernel dehydration rate (KDR) is a crucial production trait that affects mechanized harvesting and kernel quality in maize; however, the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. Here, we identified a quantitative trait locus (QTL), qKDR1, as a non-coding sequence that regulates the expression of qKDR1 REGULATED PEPTIDE GENE (RPG). RPG encodes a 31 amino acid micropeptide, microRPG1, which controls KDR by precisely modulating the expression of two genes, ZmETHYLENE-INSENSITIVE3-like 1 and 3, in the ethylene signaling pathway in the kernels after filling. microRPG1 is a Zea genus-specific micropeptide and originated de novo from a non-coding sequence. Knockouts of microRPG1 result in faster KDR in maize. By contrast, overexpression or exogenous application of the micropeptide shows the opposite effect both in maize and Arabidopsis. Our findings reveal the molecular mechanism of microRPG1 in kernel dehydration and provide an important tool for future crop breeding.
籽粒脱水率(KDR)是影响玉米机械化收获和籽粒质量的一个重要生产性状;然而,其潜在机制仍不清楚。本文鉴定了一个数量性状位点(QTL)qKDR1,它是一个非编码序列,可调控qKDR1调节肽基因(RPG)的表达。 RPG 编码一种 31 个氨基酸的微肽microRPG1,它通过精确调节乙烯信号通路中的两个基因 ZmETHYLENE-INSENSITIVE3-like 1和3的表达来控制灌浆后籽粒中的KDR。基因敲除microRPG1 会加快玉米的KDR。相比之下,在玉米和拟南芥中,过表达或外源应用该微肽会产生相反的效果。研究结果揭示了microRPG1在籽粒脱水过程中的分子机制,为未来的作物育种提供了重要工具。
5. The Arabidopsis blue-light photoreceptor CRY2 is active in darkness to inhibit root growth
拟南芥蓝光光受体CRY2在黑暗中具有抑制根生长的活性

Cryptochromes (CRYs) are blue-light receptors that regulate diverse aspects of plant growth. However, whether and how non-photoexcited CRYs function in darkness or non-blue-light conditions is unknown. Here, we show that CRY2 affects the Arabidopsis transcriptome even in darkness, revealing a non-canonical function. CRY2 suppresses cell division in the root apical meristem to downregulate root elongation in darkness. Blue-light oligomerizes CRY2 to de-repress root elongation. CRY2 physically interacts with FORKED-LIKE 1 (FL1) and FL3, and these interactions are inhibited by blue light, with only monomeric but not dimeric CRY2 able to interact. FL1 and FL3 associate with the chromatin of cell division genes to facilitate their transcription. This pro-growth activity is inhibited by CRY2’s physical interaction with FLs in darkness. Plants have evolved to perceive both blue-light and dark cues to coordinate activation and repression of competing developmental processes in above- and below-ground organs through economical and dichotomous use of ancient light receptors.
隐花色素(Cryptochromes, CRYs)是植物的蓝光受体,调节植物生长的多个方面。然而,非光激发的CRYs在黑暗或非蓝光条件下是否以及如何发挥作用尚不清楚。研究人员发现,拟南芥的蓝光受体CRY2即使在黑暗中也能影响其转录组,揭示了其非典型功能。CRY2通过抑制根尖分生区细胞分裂来下调黑暗条件下的根部伸长。蓝光则解除该抑制。研究人员进一步发现,CRY2在黑暗中与蛋白FORKED1-LIKE(FL)家族成员FL1和FL3结合,这些结合特异受蓝光抑制,且只有单体而非多聚体的CRY2能够与FL结合。FL1和FL3是位于CRY2遗传学下游的促细胞分裂因子,能够结合细胞分裂基因的染色质并促进基因表达。在黑暗中,CRY2通过结合FL抑制其促进细胞分裂的功能,进而抑制主根伸长。而在蓝光下,CRY2形成多聚体,不再与FL结合,FL的功能被释放,从而促进主根伸长。这一发现揭示了植物如何通过感知蓝光和暗信号来协调地上和地下器官的发育过程,为光信号领域开辟了“光受体在黑暗中的功能”这一全新研究方向。
6. Direct visualization of electric-field-stimulated ion conduction in a potassium channel
钾离子通道中电场刺激离子传导的直接可视化
Understanding protein function would be facilitated by direct, real-time observation of chemical kinetics in the atomic structure. The selectivity filter (SF) of the K+ channel provides an ideal model, catalyzing the dehydration and transport of K+ ions across the cell membrane through a narrow pore. We used a “pump-probe” method called electric-field-stimulated time-resolved X-ray crystallography (EFX) to initiate and observe K+ conduction in the NaK2K channel in both directions on the timescale of the transport process. We observe both known and potentially new features in the high-energy conformations visited along the conduction pathway, including the associated dynamics of protein residues that control selectivity and conduction rate. A single time series of one channel in action shows the orderly appearance of features observed in diverse homologs with diverse methods, arguing for deep conservation of the dynamics underlying the reaction coordinate in this protein family.
直接、实时地观察原子结构中的化学动力学将有助于了解蛋白质的功能。K+通道的选择性过滤器(SF)为此提供了一个理想的模型,它通过狭窄的孔道催化脱水过程和K+离子在细胞膜的运输。研究人员使用一种称为电场刺激时间分辨X射线晶体学(EFX)的“泵浦-探测”方法,在传输过程的时间尺度上启动和观察NaK2K通道中K+的双向传导。研究人员在沿传导途径访问的高能构象中观察到已知和潜在的新特征,包括控制选择性和传导速率的蛋白质残基的相关动力学。一个通道的单一时间序列显示了用不同方法在不同同源物中观察到的特征的有序出现,证明了该蛋白质家族中反应坐标的动力学基础的深度保守型。
7. Configuration of electrical synapses filters sensory information to drive behavioral choices
电突触结构过滤感官信息以驱动行为选择

Synaptic configurations underpin how the nervous system processes sensory information to produce a behavioral response. This is best understood for chemical synapses, and we know far less about how electrical synaptic configurations modulate sensory information processing and context-specific behaviors. We discovered that innexin 1 (INX-1), a gap junction protein that forms electrical synapses, is required to deploy context-specific behavioral strategies underlying thermotaxis behavior in C. elegans. Within this well-defined circuit, INX-1 couples two bilaterally symmetric interneurons to integrate sensory information during migratory behavior across temperature gradients. In inx-1 mutants, uncoupled interneurons display increased excitability and responses to subthreshold sensory stimuli due to increased membrane resistance and reduced membrane capacitance, resulting in abnormal responses that extend run durations and trap the animals in context-irrelevant tracking of isotherms. Thus, a conserved configuration of electrical synapses enables differential processing of sensory information to deploy context-specific behavioral strategies.
突触结构是神经系统处理感官信息以产生行为反应的基础。这一机制在化学突触中得到了最透彻的理解,而人们对于电突触结构如何调节感官信息处理和特定情境下的行为了解较少。研究人员发现,形成电突触的缝隙连接蛋白innexin 1(INX-1)是实现秀丽隐杆线虫热趋性行为的基础。在线虫这一明确的回路中,INX-1将两个双侧对称的中间神经元连接在一起,以整合在跨越温度梯度的迁移行为过程中的感官信息。在INX-1突变体中,未连接的中间神经元由于膜电阻增加和膜电容降低,表现出更强的兴奋性和对亚阈值感觉刺激的反应,进而导致异常反应,延长运行持续时间并使动物陷入与环境无关的等温线追踪中。因此,电突触的保守结构使得感官信息能够差异化处理,从而部署特定环境下的行为策略。
8. The auditory midbrain mediates tactile vibration sensing
听觉中脑介导触觉振动感知

Vibrations are ubiquitous in nature, shaping behavior across the animal kingdom. For mammals, mechanical vibrations acting on the body are detected by mechanoreceptors of the skin and deep tissues and processed by the somatosensory system, while sound waves traveling through air are captured by the cochlea and encoded in the auditory system. Here, we report that mechanical vibrations detected by the body’s Pacinian corpuscle neurons, which are distinguished by their ability to entrain to high-frequency (40–1,000 Hz) environmental vibrations, are prominently encoded by neurons in the lateral cortex of the inferior colliculus (LCIC) of the midbrain. Remarkably, most LCIC neurons receive convergent Pacinian and auditory input and respond more strongly to coincident tactile-auditory stimulation than to either modality alone. Moreover, the LCIC is required for behavioral responses to high-frequency mechanical vibrations. Thus, environmental vibrations captured by Pacinian corpuscles are encoded in the auditory midbrain to mediate behavior.
振动在自然界中无处不在,塑造了动物群体中的行为。对于哺乳动物,作用于身体的机械振动由皮肤和深层组织的机械感受器检测,并由体感系统处理,而通过空气传播的声波则被耳蜗捕获,并在听觉系统中编码。研究人员报告,身体的帕氏神经元小体检测机械振动,这些神经元能够与高频率(40-1,000 Hz)的环境振动保持一致,并且它们主要由中脑下丘外侧皮层(LCIC)的神经元编码。值得注意的是,大多数LCIC神经元接收帕氏神经元和听觉输入,并且对触觉-听觉同时刺激的反应比单一方式要强烈。此外,对高频机械振动的行为反应也需要 LCIC。因此,帕氏神经捕捉到的环境振动被编码到听觉中脑,从而介导行为。
9. Stress disrupts engram ensembles in lateral amygdala to generalize threat memory in mice
压力会破坏小鼠外侧杏仁核中的记忆组合,使威胁记忆泛化

Stress induces aversive memory overgeneralization, a hallmark of many psychiatric disorders. Memories are encoded by a sparse ensemble of neurons active during an event (an engram ensemble). We examined the molecular and circuit processes mediating stress-induced threat memory overgeneralization in mice. Stress, acting via corticosterone, increased the density of engram ensembles supporting a threat memory in lateral amygdala, and this engram ensemble was reactivated by both specific and non-specific retrieval cues (generalized threat memory). Furthermore, we identified a critical role for endocannabinoids, acting retrogradely on parvalbumin-positive (PV+) lateral amygdala interneurons in the formation of a less-sparse engram and memory generalization induced by stress. Glucocorticoid receptor antagonists, endocannabinoid synthesis inhibitors, increasing PV+ neuronal activity, and knocking down cannabinoid receptors in lateral amygdala PV+ neurons restored threat memory specificity and a sparse engram in stressed mice. These findings offer insights into stress-induced memory alterations, providing potential therapeutic avenues for stress-related disorders.
压力会引发厌恶相关记忆的过度泛化,这是许多精神疾病的一个标志。记忆是由在事件期间活跃的稀疏神经元集合(engram集合)编码的。研究人员检查了小鼠中压力诱导的威胁记忆过度泛化的分子和回路过程。发现压力通过皮质酮的作用增加了支持侧杏仁核中威胁记忆的集合密度,并且这种神经元群在特异性和非特异性检索线索(泛化威胁记忆)的作用下被重新激活。此外,研究人员确定了内源性大麻素的关键作用,它们通过逆向作用于小清蛋白阳性(PV+)的外侧杏仁核中间神经元,形成由压力诱导的少稀疏记忆印迹和记忆泛化。糖皮质激素受体拮抗剂、内源性大麻素合成抑制剂、增加PV+神经元活动以及敲低侧杏仁核PV+神经元中的大麻素受体,恢复了受压小鼠的威胁记忆特异性和稀疏记忆印迹。这些发现为压力诱导的记忆改变提供了见解,为压力相关疾病提供了潜在的治疗途径。
10. Glia-like taste cells mediate an intercellular mode of peripheral sweet adaptation
类胶质味觉细胞介导外周甜味适应的细胞间模式

The sense of taste generally shows diminishing sensitivity to prolonged sweet stimuli, referred to as sweet adaptation. Yet, its mechanistic landscape remains incomplete. Here, we report that glia-like type I cells provide a distinct mode of sweet adaptation via intercellular crosstalk with chemosensory type II cells. Using the microfluidic-based intravital tongue imaging system, we found that sweet adaptation is facilitated along the synaptic transduction from type II cells to gustatory afferent nerves, while type I cells display temporally delayed and prolonged activities. We identified that type I cells receive purinergic input from adjacent type II cells via P2RY2 and provide inhibitory feedback to the synaptic transduction of sweet taste. Aligning with our cellular-level findings, purinergic activation of type I cells attenuated sweet licking behavior, and P2RY2 knockout mice showed decelerated adaptation behavior. Our study highlights a veiled intercellular mode of sweet adaptation, potentially contributing to the efficient encoding of prolonged sweetness.
长时间的甜味刺激使味觉对甜味的敏感性减弱,这种现象被称为甜味适应。然而,其机制仍然未完全明确。研究人员报告称,类似胶质的I型细胞通过与化学感觉II型细胞的细胞间相互作用提供了一种独特的甜味适应模式。利用基于微流控的活体舌内成像系统,研究人员发现甜味适应是通过II型细胞到味觉传入神经的突触传递过程得来促进的,而I型细胞则表现出时间延迟和延长的活动。研究人员确定I型细胞通过P2RY2从相邻的II型细胞接收嘌呤能输入,并为甜味的突触传递提供抑制性反馈。与细胞水平的发现一致,I型细胞的嘌呤能激活减少了小鼠的甜味的舔舐行为,而P2RY2基因敲除小鼠表现出的甜味适应行为出现减缓。研究人员的研究强调了一种隐藏的甜味适应的细胞间模式,可能有助于有效编码延长甜味感受。
11. Intermittent fasting triggers interorgan communication to suppress hair follicle regeneration
间歇性禁食触发器官间通讯以抑制毛囊再生

Intermittent fasting has gained global popularity for its potential health benefits, although its impact on somatic stem cells and tissue biology remains elusive. Here, we report that commonly used intermittent fasting regimens inhibit hair follicle regeneration by selectively inducing apoptosis in activated hair follicle stem cells (HFSCs). This effect is independent of calorie reduction, circadian rhythm alterations, or the mTORC1 cellular nutrient-sensing mechanism. Instead, fasting activates crosstalk between adrenal glands and dermal adipocytes in the skin, triggering the rapid release of free fatty acids into the niche, which in turn disrupts the normal metabolism of HFSCs and elevates their cellular reactive oxygen species levels, causing oxidative damage and apoptosis. A randomized clinical trial (NCT05800730) indicates that intermittent fasting inhibits human hair growth. Our study uncovers an inhibitory effect of intermittent fasting on tissue regeneration and identifies interorgan communication that eliminates activated HFSCs and halts tissue regeneration during periods of unstable nutrient supply.
间歇性禁食因其潜在的健康益处而受到全球关注,但其对体细胞干细胞和组织生物学的影响尚不清楚。研究人员发现,常用的间歇性禁食方案通过选择性诱导活化的毛囊干细胞(HFSCs)凋亡来抑制毛囊再生。这种效应独立于卡路里减少、昼夜节律变化或mTORC1细胞营养感应机制。相反,禁食激活了肾上腺和皮肤真皮脂肪细胞之间的细胞通讯,触发游离脂肪酸(FFA)迅速释放到微环境中,扰乱HFSCs的正常代谢并提高其的细胞活性氧(ROS)水平,导致氧化损伤和凋亡。随机临床试验(NCT05800730)表明间歇性禁食抑制人类头发生长。研究人员的研究揭示了间歇性禁食对组织再生的抑制效应,即间歇性禁食会触发器官间通讯,并抑制HFSC的再生活性,从而抑制毛发生长。
12. A β-hydroxybutyrate shunt pathway generates anti-obesity ketone metabolites
β-羟基丁酸分流途径产生抗肥胖的酮体代谢物

β-Hydroxybutyrate (BHB) is an abundant ketone body. To date, all known pathways of BHB metabolism involve the interconversion of BHB and primary energy intermediates. Here, we identify a previously undescribed BHB secondary metabolic pathway via CNDP2-dependent enzymatic conjugation of BHB and free amino acids. This BHB shunt pathway generates a family of anti-obesity ketone metabolites, the BHB-amino acids. Genetic ablation of CNDP2 in mice eliminates tissue amino acid BHB-ylation activity and reduces BHB-amino acid levels. The most abundant BHB-amino acid, BHB-Phe, is a ketosis-inducible congener of Lac-Phe that activates hypothalamic and brainstem neurons and suppresses feeding. Conversely, CNDP2-KO mice exhibit increased food intake and body weight following exogenous ketone ester supplementation or a ketogenic diet. CNDP2-dependent amino acid BHB-ylation and BHB-amino acid metabolites are also conserved in humans. Therefore, enzymatic amino acid BHB-ylation defines a ketone shunt pathway and bioactive ketone metabolites linked to energy balance.
β-羟基丁酸(β-Hydroxybutyrate, BHB)是一种丰富的酮体。迄今为止,所有已知的BHB代谢途径都涉及BHB与主要能量中间体的相互转化。在本研究中,研究人员发现了一条之前未被描述过的依赖CNDP2酶将BHB与游离氨基酸结合的BHB次级代谢途径。这条BHB旁路途径产生了一类具有抗肥胖作用的酮体代谢物——BHB-氨基酸。在小鼠中,敲除CNDP2基因会导致组织中BHB与氨基酸结合的活性消失,同时BHB-氨基酸水平降低。最为丰富的BHB-氨基酸——BHB-苯丙氨酸(BHB-Phe),是一种酮症诱导的Lac-Phe类似物,能够激活下丘脑和脑干的神经元,并抑制食欲。相反,CNDP2基因敲除的小鼠在补充外源性酮体酯或摄入生酮饮食后,会表现出食欲增加和体重增加的现象。CNDP2依赖的氨基酸BHB-乙酰和BHB-氨基酸代谢物在人体中也有所保留。因此,酶促氨基酸BHB-乙酰化反应定义了一个新的酮体旁路途径以及与能量平衡相关的生物活性酮体代谢物。
13. Decreased lipidated ApoE-receptor interactions confer protection against pathogenicity of ApoE and its lipid cargoes in lysosomes
脂质载脂蛋白E-受体相互作用的减少可防止载脂蛋白E及其脂质载物在溶酶体中致病

While apolipoprotein E (APOE) is the strongest genetic modifier for late-onset Alzheimer’s disease (LOAD), the molecular mechanisms underlying isoform-dependent risk and the relevance of ApoE-associated lipids remain elusive. Here, we report that impaired low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor (LDLR) binding of lipidated ApoE2 (lipApoE2) avoids LDLR recycling defects observed with lipApoE3/E4 and decreases the uptake of cholesteryl esters (CEs), which are lipids linked to neurodegeneration. In human neurons, the addition of ApoE carrying polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs)-CE revealed an allelic series (ApoE4 > ApoE3 > ApoE2) associated with lipofuscinosis, an age-related lysosomal pathology resulting from lipid peroxidation. Lipofuscin increased lysosomal accumulation of tau fibrils and was elevated in the APOE4 mouse brain with exacerbation by tau pathology. Intrahippocampal injection of PUFA-CE-lipApoE4 was sufficient to induce lipofuscinosis in wild-type mice. Finally, the protective Christchurch mutation also reduced LDLR binding and phenocopied ApoE2. Collectively, our data strongly suggest decreased lipApoE-LDLR interactions minimize LOAD risk by reducing the deleterious effects of endolysosomal targeting of ApoE and associated pathogenic lipids.
载脂蛋白E(Apolipoprotein E, APOE)是晚发性阿尔茨海默病(Late-onset Alzheimer's disease, LOAD)最强的遗传修饰因子,但其异构体依赖性风险的分子机制以及与APOE相关脂质的关系仍不清楚。研究人员发现,脂质化ApoE2(lipApoE2)与低密度脂蛋白受体(LDL)受体(LDLR)的结合受损,避免了与脂质化ApoE3/E4相关的LDLR循环缺陷,并减少了胆固醇酯(CEs)的摄取,而胆固醇酯是与神经变性相关的脂质。在人类神经元中,添加携带多不饱和脂肪酸(PUFAs)-CE的ApoE揭示了一系列与脂褐素沉积有关的等位基因(ApoE4> ApoE3 > ApoE2),这是一种由脂质过氧化引起的年龄相关的溶酶体病变。脂褐素增加了溶酶体中tau纤维的积累,并在APOE4小鼠大脑中随着tau病理的加重而升高。在野生型小鼠的海马内注射PUFA-CE-lipApoE4足以诱导脂褐素沉积。最后,具有保护作用的Christchurch突变也减少了LDLR的结合,并表现出与ApoE2相似的表型。这些数据强烈表明,减少脂质化ApoE与LDLR的相互作用可减少ApoE及其相关致病脂质的内溶酶体靶向作用有害影响,从而显著降低了LOAD风险。
14. Proteolethargy is a pathogenic mechanism in chronic disease
蛋白质迁移率降低是慢性病的一种致病机制

The pathogenic mechanisms of many diseases are well understood at the molecular level, but there are prevalent syndromes associated with pathogenic signaling, such as diabetes and chronic inflammation, where our understanding is more limited. Here, we report that pathogenic signaling suppresses the mobility of a spectrum of proteins that play essential roles in cellular functions known to be dysregulated in these chronic diseases. The reduced protein mobility, which we call proteolethargy, was linked to cysteine residues in the affected proteins and signaling-related increases in excess reactive oxygen species. Diverse pathogenic stimuli, including hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, and inflammation, produce similar reduced protein mobility phenotypes. We propose that proteolethargy is an overlooked cellular mechanism that may account for various pathogenic features of diverse chronic diseases.
许多疾病的病理机制在分子水平上已经得到了很好的解释,但对于一些与病理信号相关的常见综合征,如糖尿病和慢性炎症,目前理解仍然有限。研究人员发现,病理信号会抑制一系列蛋白质的流动性,这些蛋白质在细胞功能中发挥着至关重要的作用,而这些细胞功能在这些慢性疾病中被认为是失调的。这种蛋白质流动性的降低,研究人员称之为“蛋白质迁移率降低”(proteolethargy),与受影响蛋白质中的半胱氨酸残基以及信号相关过量活性氧种类的增加有关。高血糖、血脂异常和炎症等多种慢性疾病,会产生类似的蛋白质流动性降低表型。研究人员提出,“蛋白质迁移率降低”是一种被忽视的细胞机制,可能解释了多种慢性疾病的各种病理特征。
15. Fecal microbial load is a major determinant of gut microbiome variation and a confounder for disease associations
粪便微生物符合是肠道微生物群变异的主要决定因素,也是疾病关联的混杂因素之一

The microbiota in individual habitats differ in both relative composition and absolute abundance. While sequencing approaches determine the relative abundances of taxa and genes, they do not provide information on their absolute abundances. Here, we developed a machine-learning approach to predict fecal microbial loads (microbial cells per gram) solely from relative abundance data. Applying our prediction model to a large-scale metagenomic dataset (n = 34,539), we demonstrated that microbial load is the major determinant of gut microbiome variation and is associated with numerous host factors, including age, diet, and medication. We further found that for several diseases, changes in microbial load, rather than the disease condition itself, more strongly explained alterations in patients’ gut microbiome. Adjusting for this effect substantially reduced the statistical significance of the majority of disease-associated species. Our analysis reveals that the fecal microbial load is a major confounder in microbiome studies, highlighting its importance for understanding microbiome variation in health and disease.
不同栖息地中的微生物群在相对组成和绝对丰度上均有所不同。虽然测序方法可以确定群和基因的相对丰度,但无法提供其绝对丰度的信息。研究人员开发了一种机器学习方法,仅从相对丰度数据预测粪便微生物负荷(每克微生物细胞数)。将预测模型应用于大规模宏基因组数据集(n = 34,539),研究人员发现微生物负荷是肠道微生物组变异的主要决定因素,并与多种宿主因素如年龄、饮食和药物相关。本文还发现,对于几种疾病来说,微生物负荷的变化,而不是疾病本身,更有力地解释了患者肠道微生物组的变化。对这一影响进行调整后,大多数疾病相关物种的统计学意义大大降低。分析表明,粪便微生物负荷是微生物组研究中的一个主要混杂因素,强调了其对理解健康和疾病中微生物组变异的重要性。
16. The single-molecule accessibility landscape of newly replicated mammalian chromatin
新复制的哺乳动物染色质的单分子可及性图谱

We present replication-aware single-molecule accessibility mapping (RASAM), a method to nondestructively measure replication status and protein-DNA interactions on chromatin genome-wide. Using RASAM, we uncover a genome-wide state of single-molecule “hyperaccessibility” post-replication that resolves over several hours. Combining RASAM with cellular models for rapid protein degradation, we demonstrate that histone chaperone CAF-1 reduces nascent chromatin accessibility by filling single-molecular “gaps” and generating closely spaced dinucleosomes on replicated DNA. At cis-regulatory elements, we observe unique modes by which nascent chromatin hyperaccessibility resolves: at CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF)-binding sites, CTCF and nucleosomes compete, reducing CTCF occupancy and motif accessibility post-replication; at active transcription start sites, high chromatin accessibility is maintained, implying rapid re-establishment of nucleosome-free regions. Our study introduces a new paradigm for studying replicated chromatin fiber organization. More broadly, we uncover a unique organization of newly replicated chromatin that must be reset by active processes, providing a substrate for epigenetic reprogramming.
研究人员提出了一种名为复制感知单分子可及性图谱(RASAM)的方法,用于无损检测全基因组染色质上的复制状态和蛋白质-DNA相互作用。利用RASAM,研究人员发现新复制的染色质在复制后会出现一种全基因组范围的单分子“高可及性”状态,这种状态会在数小时内逐渐消退。结合RASAM与蛋白质快速降解的细胞模型,研究人员证明了组蛋白伴侣CAF-1通过填补单分子“间隙”并生成紧密排列的二核苷体来降低新生染色质的可及性。在顺式调控元件处,研究人员观察到新生染色质高可及性解决的独特模式:在CCCTC结合因子(CTCF)结合位点,CTCF和核小体相互竞争,导致复制后CTCF占据率和基序可及性降低;在活跃的转录起始位点,高染色质可及性得以维持,暗示着核小体自由区域能够迅速重新建立。本文为研究复制后染色质纤维组织提供了新的范式。更广泛地讲,研究人员揭示了新复制染色质的独特组织结构,这种结构必须通过活性过程重置,为表观遗传重编程提供了基础。
17. Atlas of the plasma proteome in health and disease in 53,026 adults
绘制53026名健康和患病成年人的血浆蛋白质组图谱

Large-scale proteomics studies can refine our understanding of health and disease and enable precision medicine. Here, we provide a detailed atlas of 2,920 plasma proteins linking to diseases (406 prevalent and 660 incident) and 986 health-related traits in 53,026 individuals (median follow-up: 14.8 years) from the UK Biobank, representing the most comprehensive proteome profiles to date. This atlas revealed 168,100 protein-disease associations and 554,488 protein-trait associations. Over 650 proteins were shared among at least 50 diseases, and over 1,000 showed sex and age heterogeneity. Furthermore, proteins demonstrated promising potential in disease discrimination (area under the curve [AUC] > 0.80 in 183 diseases). Finally, integrating protein quantitative trait locus data determined 474 causal proteins, providing 37 drug-repurposing opportunities and 26 promising targets with favorable safety profiles. These results provide an open-access comprehensive proteome-phenome resource (https://proteome-phenome-atlas.com/) to help elucidate the biological mechanisms of diseases and accelerate the development of disease biomarkers, prediction models, and therapeutic targets.
大规模蛋白质组学研究可以完善对健康和疾病的了解,并助力精准医疗的发展。研究人员提供了来自英国生物银行(UK Biobank)的2920种血浆蛋白的详细图谱,这些蛋白与疾病(406种常见疾病和660种新发疾病)和986种健康相关特征相关,涵盖了53026名个体(中位随访时间:14.8年),是迄今为止最全面的蛋白质组学。该图谱揭示了168100种蛋白-疾病关联和554488种蛋白-特征关联。超过650种蛋白至少在50种疾病中共享,超过1000种蛋白表现出性别和年龄的特异性。此外,蛋白在疾病鉴别方面显示出巨大潜力(在183种疾病中曲线下面积[AUC] > 0.80)。最后,整合蛋白定量特征位点数据确定了474种与疾病有因果关系的蛋白,提供了37种药物再利用的机会和26种具有良好安全性的有前景的靶点。这些结果提供了一个开放获取的,全面的蛋白质组-表型资源(https://proteome-phenome-atlas.com/),有助于阐明疾病的生物学机制,并加速疾病生物标志物、预测模型和治疗靶点的开发。

汇报人:吴桂儀
导师:赵宇教授
审核:李朔、任建君



