【Science】2024年10月11日—2024年11月21日刊论文导读
Volume 386|Issue 6718|11 Oct 2024
1.Temporal variability and cell mechanics control robustness in mammalian embryogenesis
2.Epigenetic regulators of clonal hematopoiesis control CD8 T cell stemness during immunotherapy
克隆性造血的表观遗传调控因子在免疫治疗过程中控制CD8 T细胞的干性
3. Helicase-assisted continuous editing for programmable mutagenesis of endogenous genomes
4.Predicting pathogen mutual invasibility and co-circulation
5. Somatic mosaicism in schizophrenia brains reveals prenatal mutational processes
哈佛医学院生物医学信息学系(美国)、麻省理工学院、哈佛大学Broad研究所及西奈山伊坎医学院遗传学和基因组科学系
Volume 386|Issue 6719|18 Oct 2024
1.In vivo dendritic cell reprogramming for cancer immunotherapy
2.Mechanism of bacterial predation via ixotrophy
3.Neurotoxic mixture effects of chemicals extracted from blood of pregnant women
4.Description and functional validation of human enteroendocrine cell sensors
荷兰乌特勒支大学医学中心(UMC Utrecht)荷兰皇家艺术与科学学院(KNAW)下属的Hubrecht研究所和Oncode研究所
Volume 386|Issue 6720|25 Oct 2024
1.The landscape of RNA binding proteins in mammalian spermatogenesis
南京医科大学公共卫生学院、基础医学科学院、附属常州第二人民医院
2.Dietary pro-oxidant therapy by a vitamin K precursor targets PI 3-kinase VPS34 function
通过维生素K前体的饮食促氧化剂疗法靶向PI 3-激酶VPS34功能
3.Multi-omics landscape and molecular basis of radiation tolerance in a tardigrade
4.Hematopoietic aging promotes cancer by fueling IL-1⍺–driven emergency myelopoiesis
5.A human gut Faecalibacterium prausnitzii fatty acid amide hydrolase
6. A ubiquitous mobile genetic element changes the antagonistic weaponry of a human gut symbiont
Volume 386|Issue 6721|1 Nov 2024
1.Group 2 innate lymphoid cells promote inhibitory synapse development and social behavior
加州大学旧金山分校霍华德·休斯医学研究所、精神病学与行为科学系
2.Exploring structural diversity across the protein universe with The Encyclopedia of Domains
3.Brain malformations and seizures by impaired chaperonin function of TRiC
美国圣路易斯华盛顿大学医学院儿科系、斯坦福大学生物系、德国亚琛工业大学医院人类遗传学与基因组医学研究所
5.Two codependent routes lead to high-level MRSA
Volume 386|Issue 6722|8 Nov 2024
1.Continuous evolution of user-defined genes at 1 million times the genomic mutation rate
2.Retrotransposons are co-opted to activate hematopoietic stem cells and erythropoiesis
德国埃森大学医院皮肤科 & 德国癌症联盟,埃森,& 国家肿瘤疾病中心联合德克萨斯大学西南医学中心儿童医学研究所和儿科系
3.The interhemispheric amygdala-accumbens circuit encodes negative valence in mice
4.COVID-19 pandemic interventions reshaped the global dispersal of seasonal influenza viruses
COVID-19大流行干预措施重塑了季节性流感病毒的全球传播
5.Hepatic vagal afferents convey clock-dependent signals to regulate circadian food intake
美国宾夕法尼亚大学佩雷尔曼医学院医学部内分泌学、糖尿病和代谢学分部
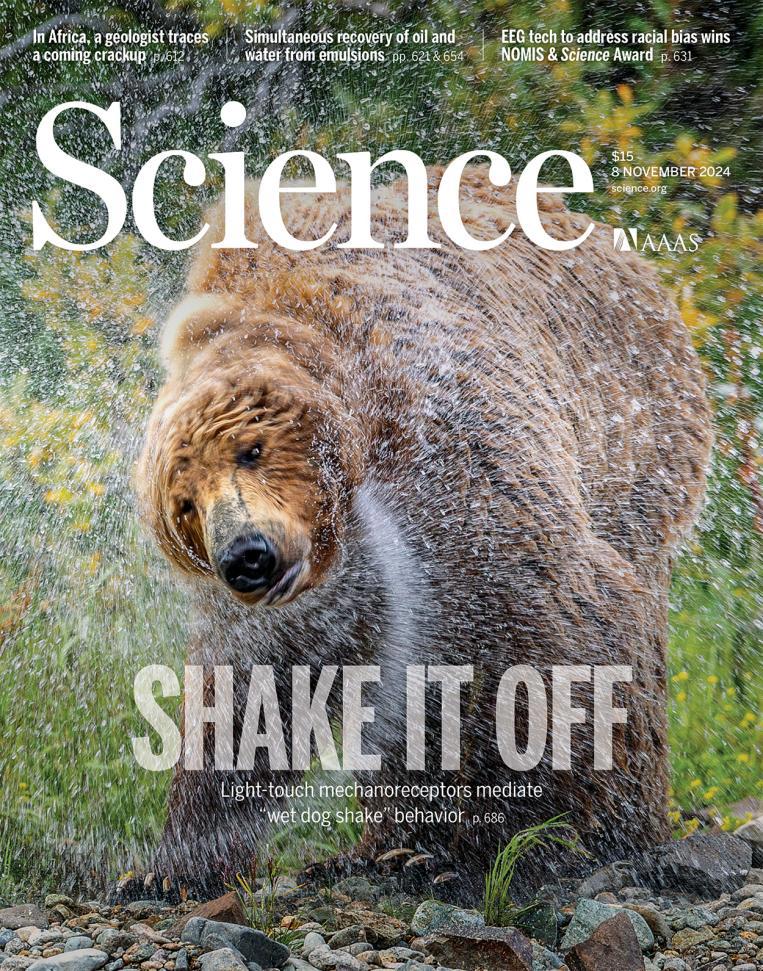
6.C-LTMRs evoke wet dog shakes via the spinoparabrachial pathway
Volume 386|Issue 6723|15 Nov 2024
1.Sequence modeling and design from molecular to genome scale with Evo
美国加利福尼亚大学伯克利分校生物工程系和计算生物学中心联合斯坦福大学化学工程系
2. Ribozyme-activated mRNA trans-ligation enables large gene delivery to treat muscular dystrophies
3.Isolation of psychedelic-responsive neurons underlying anxiolytic behavioral states