华西耳鼻喉前沿学术速递——文献导读(第56期)
【Cancer Cell】2024年9-10月刊论文导读
期刊介绍:
Cancer Cell创刊于2002年,由CELL PRESS出版商出版,收稿方向涵盖医学-肿瘤学全领域,在行业领域中学术影响力很大,属于TOP期刊,国际一流期刊。审议手稿的主要标准是研究是否在回答与自然发生的癌症有关的重要问题方面取得重大进展。影响因子指数48.8。2024年9-10月一共发表29篇,包括Commentary 4篇,Preview 7篇,Review 1篇,Perspective 1篇,Article 13篇,Letter 1篇,Report 1篇,Correction 1篇。
Sep 09, 2024 Volume 42Issue 9p1473-1630
在2024年9月,Cancer Cell共发表15篇文章,其中包括Commentary 2篇,Letter 1篇,Preview 3篇,Perspective 1篇,Article 7篇,Correction 1篇。
1.Fibrotic response to anti-CSF-1R therapy potentiates glioblastoma recurrence
抗CSF-1R(Colony Stimulating Factor 1 Receptor,集落刺激因子1受体)
治疗引发的纤维化反应加剧了胶质母细胞瘤的复发
瑞士洛桑大学路德维希癌症研究所
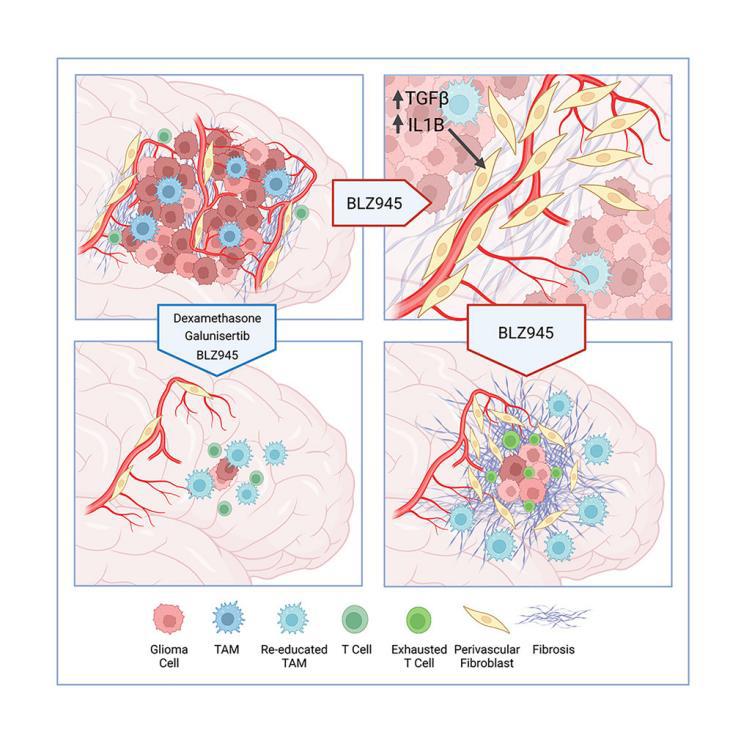
Glioblastoma recurrence is currently inevitable despite extensive standard-of-care treatment. In preclinical studies, an alternative strategy of targeting tumor-associated macrophages and microglia through CSF-1R inhibition was previously found to regress established tumors and significantly increase overall survival. However, recurrences developed in 50% of mice in long-term studies, which were consistently associated with fibrotic scars. This fibrotic response is observed following multiple anti-glioma therapies in different preclinical models herein and in patient recurrence samples. Multi-omics analyses of the post-treatment tumor microenvironment identified fibrotic areas as pro-tumor survival niches that encapsulated surviving glioma cells, promoted dormancy, and inhibited immune surveillance. The fibrotic treatment response was mediated by perivascular-derived fibroblast-like cells via activation by transforming growth factor b (TGF-b) signaling and neuroinflammation. Concordantly, combinatorial inhibition of these pathways inhibited treatment-associated fibrosis, and significantly improved survival in preclinical trials of anti-colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor (CSF-1R) therapy.
胶质母细胞瘤是一种难治性肿瘤,尽管目前在临床上已经广泛采用了标准治疗方案,但胶质母细胞瘤的复发仍然不可避免。在这篇临床前研究中,研究者通过在小鼠模型中抑制CSF-1R来靶向肿瘤相关的巨噬细胞和小胶质细胞,发现这样可以抑制肿瘤的生长并显著延长总体生存期。然而,在长期观察中发现,50%的小鼠出现复发,这些复发与肿瘤微环境中纤维化瘢痕的形成密切相关。并且,这种纤维化在多种抗胶质瘤疗法的不同临床前模型中以及患者的复发样本中均被观察到。多组学分析发现,抗胶质瘤治疗后,肿瘤微环境中形成的纤维化区域会形成“生存壁垒”,包裹着残存的胶质瘤细胞,促进肿瘤存活和休眠,并抑制了机体的免疫监视作用。进一步分析发现,这种纤维化反应是由血管周围来源的成纤维细胞样细胞介导的,其通过转化生长因子β(TGF-β)信号和神经炎症激活纤维化反应。相应地,研究发现,联合抑制这些通路有效抑制了治疗相关的纤维化反应,并在临床前的抗CSF-1R治疗试验中显著提高了生存率。
2.GABAergic neuronal lineage development determines clinically actionable targets in diffuse hemispheric glioma, H3G34-mutant
在GABA能神经元谱系的发育过程中找到了可用于弥漫性半球胶质瘤(H3G34突变型)临床干预的靶点
美国达纳-法伯/波士顿儿童癌症与血液病中心
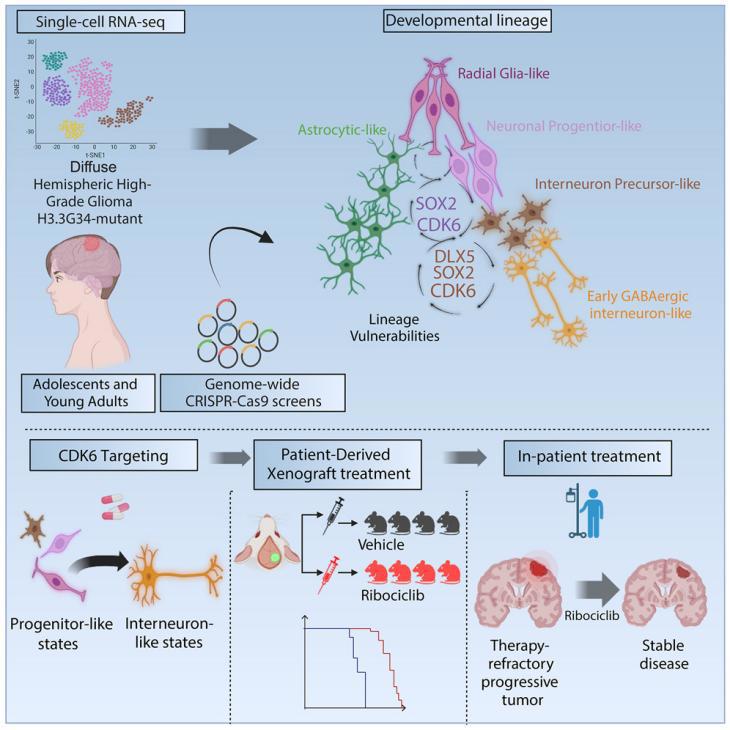
Diffuse hemispheric gliomas, H3G34R/V-mutant (DHG-H3G34), are lethal brain tumors lacking targeted therapies. They originate from interneuronal precursors; however, leveraging this origin for therapeutic insights remains unexplored. Here, we delineate a cellular hierarchy along the interneuron lineage development continuum, revealing that DHG-H3G34 mirror spatial patterns of progenitor streams surrounding interneuron nests, as seen during human brain development. Integrating these findings with genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 screens identifies genes upregulated in interneuron lineage progenitors as major dependencies. Among these, CDK6 emerges as a targetable vulnerability: DHG-H3G34 tumor cells show enhanced sensitivity to CDK4/6 inhibitors and a CDK6-specific degrader, promoting a shift toward more mature interneuron-like states, reducing tumor growth, and prolonging xenograft survival. Notably, a patient with progressive DHG-H3G34 treated with a CDK4/6 inhibitor achieved 17 months of stable disease. This study underscores interneuronal progenitor-like states, organized in characteristic niches, as a distinct vulnerability in DHG-H3G34, highlighting CDK6 as a promising clinically actionable target.
弥漫性半球胶质瘤,H3G34R/V突变型(DHG-H3G34),是一种致命的脑肿瘤,目前尚缺乏靶向治疗的方法。尽管该肿瘤源于中间神经元前体细胞,但目前的研究没有从来源细胞获得治疗线索。本研究描绘了中间神经元谱系发育的细胞层级,发现DHG-H3G34发育过程中的细胞排布结构在空间上和人脑发育过程中中间神经元前体细胞流的模式很相似。通过整合这些发现与全基因组CRISPR-Cas9筛选结果,研究发现中间神经元前体细胞中上调的基因是肿瘤发育的主要依赖基因。在这些基因中,CDK6是一个可靶向的弱点:因为DHG-H3G34肿瘤细胞对CDK4/6抑制剂及CDK6特异性降解剂表现出增强的敏感性,促进肿瘤细胞转向更成熟的类似中间神经元的状态,抑制了肿瘤生长,并延长了异种移植模型的生存期。另外,有报道称,一名进展性DHG-H3G34患者在接受CDK4/6抑制剂治疗后,病情稳定了17个月。总的来说,这项研究表明,中间神经元前体细胞是DHG-H3G34的一个独特的弱点,并强调了CDK6可作为潜在的临床靶点。
3.Glioblastoma induces the recruitment and differentiation of dendritic-like “hybrid” neutrophils from skull bone marrow
胶质母细胞瘤诱导头骨骨髓来源的树突状“混合”中性粒细胞的招募和分化

美国加利福尼亚大学旧金山分校(UCSF)神经外科
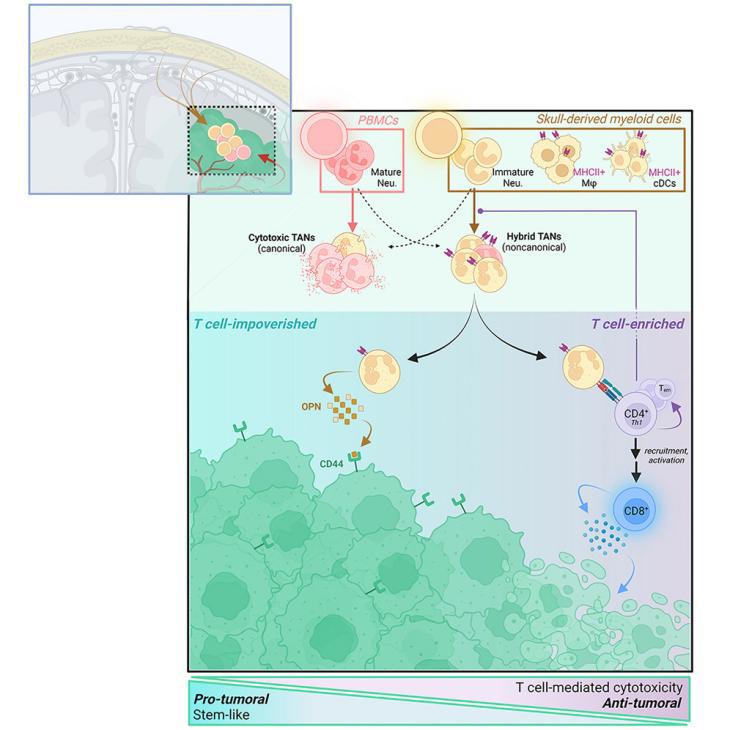
Tumor-associated neutrophil (TAN) effects on glioblastoma (GBM) biology remain under-characterized. We show here that neutrophils with dendritic features—including morphological complexity, expression of antigen presentation genes, and the ability to process exogenous peptide and stimulate major histocompatibility complex (MHC)II-dependent T cell activation—accumulate intratumorally and suppress tumor growth in vivo. Trajectory analysis of patient TAN scRNA-seq identifies this “hybrid” dendritic-neutrophil phenotype as a polarization state that is distinct from canonical cytotoxic TANs, and which differentiates from local precursors. These hybrid-inducible immature neutrophils—which we identified in patient and murine glioblastomas—arise not from circulation, but from local skull marrow. Through labeled skull flap transplantation and targeted ablation, we characterize calvarial marrow as a contributor of antitumoral myeloid antigen-presenting cells (APCs), including TANs, which elicit T cell cytotoxicity and memory. As such, agents augmenting neutrophil egress from skull marrow—such as intracalvarial AMD3100, whose survival-prolonging effect in GBM we report—present therapeutic potential.
目前,肿瘤相关中性粒细胞(TAN)对胶质母细胞瘤(GBM)的生物学影响仍未被充分认识。在此,该研究发现一种具有树突状特征的中性粒细胞(具备形态上的复杂性、有抗原呈递基因的表达、能处理外源性肽并激活MHC-II依赖的T细胞)在肿瘤内部积聚,并在体内抑制肿瘤生长。患者TAN的scRNA-seq的轨迹分析显示,这种“杂合的”树突状-中性粒细胞是一种有别于传统细胞毒性TAN的极化状态,由肿瘤局部的前体细胞分化而来。研究者在患者和小鼠胶质母细胞瘤中发现,这些可诱导的未成熟的“杂合”中性粒细胞并非来自循环血液,而是来源于局部头骨骨髓。通过标记头骨移植和靶向消融实验,研究者确认了头骨骨髓是TANs等抗肿瘤髓系抗原呈递细胞(APCs)的来源,这些细胞能够激活T细胞的细胞毒性和记忆。总的来说,该研究结果揭示了促进中性粒细胞从头骨骨髓中迁出的药物有潜在的治疗前景。(如研究报道的AMD3100有延长GBM患者生存的作用)
4.Effect of neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy with or without PD-1 antibody sintilimab in pMMR locally advanced rectal cancer: A randomized clinical trial
比较新辅助放化疗联合或不联合PD-1抗体信迪利单抗在pMMR局部晚期直肠癌中的疗效:一项随机临床试验

中山大学肿瘤防治中心放射肿瘤科
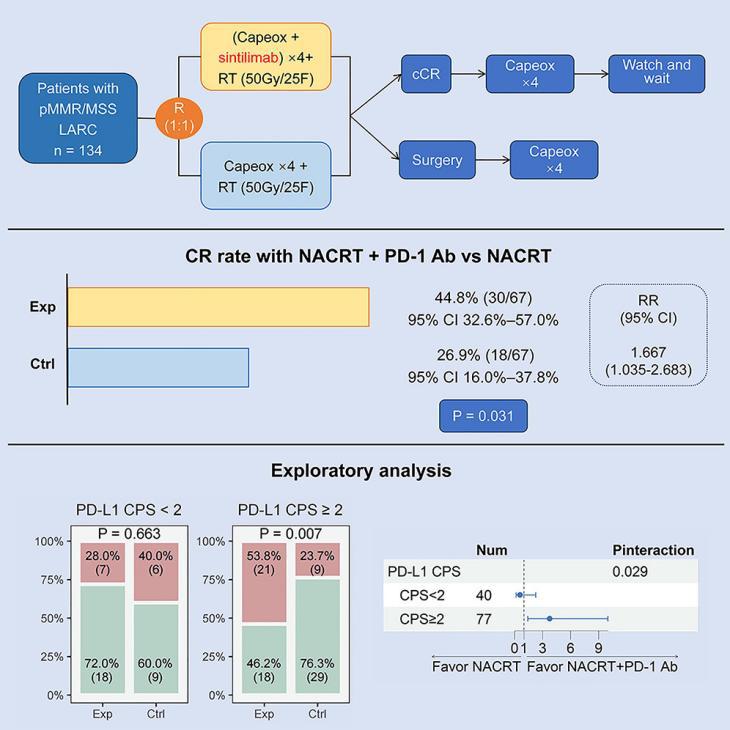
Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (NACRT) was the standard treatment for patients with locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC) with proficient mismatch repair (pMMR) proteins. In this randomized phase 2 trial (ClinicalTrial.gov: NCT04304209), 134 pMMR LARC patients were randomly (1:1) assigned to receive NACRT or NACRT and the programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) antibody sintilimab. As the primary endpoint, the total complete response (CR) rate is 26.9% (18/67, 95% confidence interval [CI] 16.0%–37.8%) and 44.8% (30/67, 95% CI 32.6%–57.0%) in the control and experimental arm, respectively, with significant difference (p = 0.031 for chi-squared test). Response ratio is 1.667 (95% CI 1.035–2.683). Immunohistochemistry shows PD-1 ligand 1 (PD-L1) combined positive score is associated with the synergistic effect. The safety profile is similar between the arms. Adding the PD-1 antibody sintilimab to NACRT significantly increases the CR rate in pMMR LARC, with a manageable safety profile. PD-L1 positivity may help identify patients who might benefit most from the combination therapy.
新辅助放化疗(NACRT)是有错配修复功能(pMMR)蛋白的局部晚期直肠癌(LARC)患者的标准治疗方案。在这项随机的II期临床试验中(ClinicalTrial.gov: NCT04304209),134名pMMR LARC患者按1:1随机分组,分别接受NACRT或NACRT联合抗程序性死亡蛋白1抗体(PD-1)信迪利单抗治疗,主要终点为完全缓解(CR)率。结果显示,对照组和实验组的CR率分别为26.9%(18/67, 95% CI 16.0%-37.8%)和44.8%(30/67, 95% CI 32.6%-57.0%),有显著差异(p=0.031)。反应比为1.667(95% CI 1.035-2.683)。免疫组化显示PD-1配体1(PD-L1)结合阳性评分与协同效应相关。两组的安全性相似。总的来说,在NACRT中加入PD-1抗体信迪利单抗显著提高了pMMR LARC患者的CR率,且安全性可控。PD-L1阳性可能有助于识别最可能从联合治疗中获益的患者。
5.Combination anti-PD-1 and anti-CTLA-4 therapy generates waves of clonal responses that include progenitor-exhausted CD8+ T cells
抗PD-1和抗CTLA-4联合治疗引发包含前体耗竭CD8+ T细胞在内的T细胞克隆反应浪潮
美国宾夕法尼亚大学佩雷尔曼医学院血液/肿瘤科
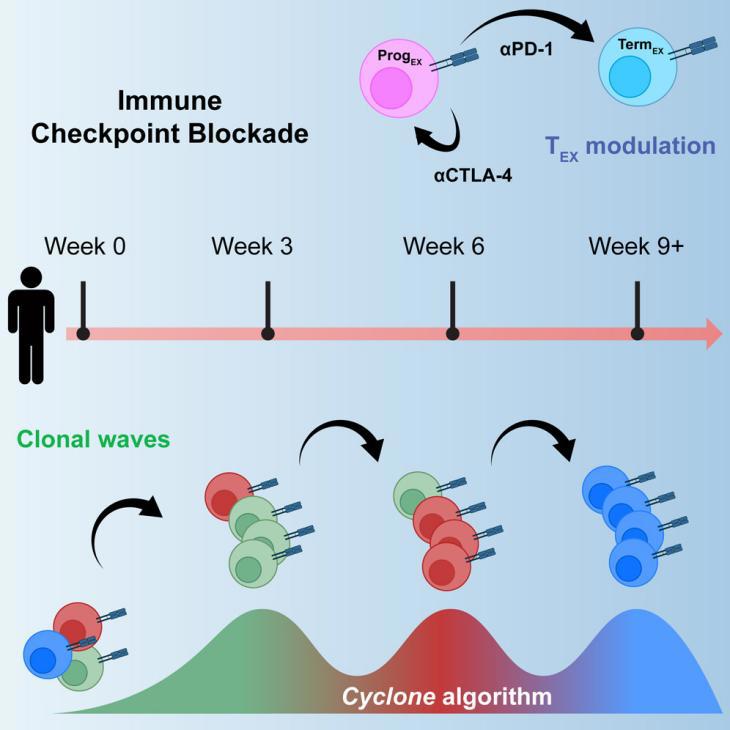
Combination checkpoint blockade with anti-PD-1 and anti-CTLA-4 antibodies has shown promising efficacy in melanoma. However, the underlying mechanism in humans remains unclear. Here, we perform paired single-cell RNA and T cell receptor (TCR) sequencing across time in 36 patients with stage IV melanoma treated with anti-PD-1, anti-CTLA-4, or combination therapy. We develop the algorithm Cyclone to track temporal clonal dynamics and underlying cell states. Checkpoint blockade induces waves of clonal T cell responses that peak at distinct time points. Combination therapy results in greater magnitude of clonal responses at 6 and 9 weeks compared to single-agent therapies, including melanoma-specific CD8+ T cells and exhausted CD8+ T cell (TEX) clones. Focused analyses of TEX identify that anti-CTLA-4 induces robust expansion and proliferation of progenitor TEX, which synergizes with anti-PD-1 to reinvigorate TEX during combination therapy. These next generation immune profiling approaches can guide the selection of drugs, schedule, and dosing for novel combination strategies.
抗PD-1和抗CTLA-4抗体的联合免疫检查点阻断治疗在黑色素瘤中表现出显著疗效,但在人体中的作用机制尚不清楚。该研究对接受抗PD-1、抗CTLA-4或联合治疗的36名IV期黑色素瘤患者进行跨时间的scRNA和TCR测序,并开发了算法Cyclone来跟踪克隆动态变化及其细胞状态。结果发现,检查点阻断会引发克隆性T细胞的反应浪潮,并在不同时间点达到峰值。与单一治疗相比,联合治疗在第6和第9周产生了更大的克隆反应,包括黑色素瘤特异性CD8+T细胞和衰竭的CD8+T细胞(TEX)克隆。对TEX的深入分析表明,抗CTLA-4能够显著促进TEX前体细胞的扩增和增殖,与抗PD-1联合治疗时能协同恢复TEX的活力。这些新一代的免疫图谱分析方法可以指导新型联合治疗策略的药物选择、时间安排及剂量设定。
6.Circulating tumor DNA-based stratification strategy for chemotherapy plus PD-1 inhibitor in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer
基于循环肿瘤DNA的化疗联合PD-1抑制剂在晚期非小细胞肺癌中的分层策略

中国医学科学院癌症医院/国家癌症中心分子肿瘤学重点实验室
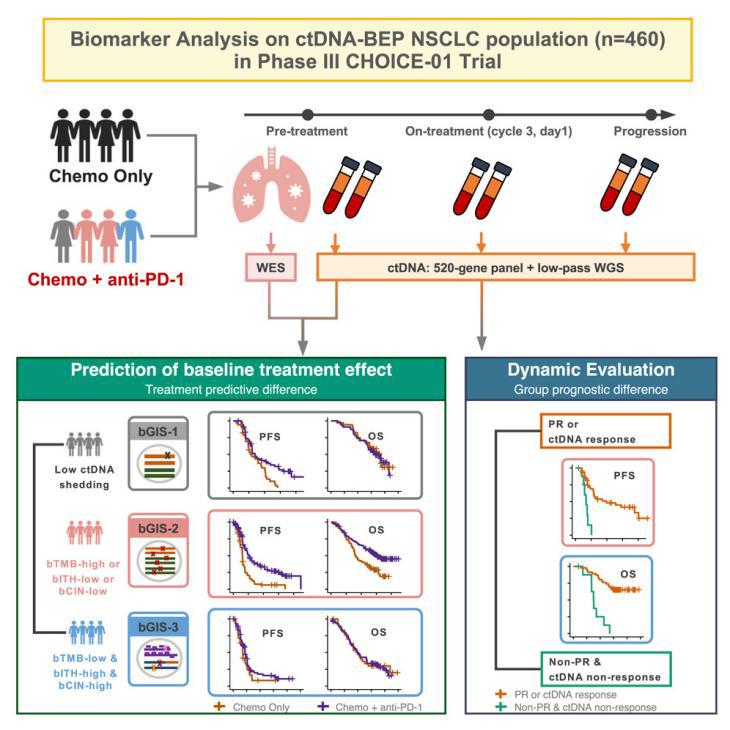
Stratification strategies for chemotherapy plus PD-1 inhibitors in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) are critically demanded. We performed high-throughput panel-based deep next-generation sequencing and low-pass whole genome sequencing on prospectively collected circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) specimens from 460 patients in the phase 3 CHOICE-01 study at different time points. We identified predictive markers for chemotherapy plus PD-1 inhibitor, including ctDNA status and genomic features such as blood-based tumor mutational burden, intratumor heterogeneity, and chromosomal instability. Furthermore, we established an integrated ctDNA-based stratification strategy, blood-based genomic immune subtypes (bGIS) scheme, to distinguish patients who benefit from the addition of PD-1 inhibitor to first-line chemotherapy. Moreover, we demonstrated potential applications for the dynamic monitoring of ctDNA. Overall, we proposed a potential therapeutic algorithm based on the ctDNA-based stratification strategy, shedding light on the individualized management of immune-chemotherapies for patients with advanced NSCLC.
目前,晚期非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)急需针对化疗联合PD-1抑制剂的分层策略。在这项CHOICE-01三期研究中,研究者对460名患者的循环肿瘤DNA(ctDNA)进行了不同时间点的高通量深度测序和低通量全基因组测序。研究识别出了可预测化疗联合PD-1抑制剂疗效的标志,包括ctDNA的状态及基因组特征,如肿瘤突变负荷、肿瘤内异质性和染色体不稳定性。此外,研究还建立了基于ctDNA的分层策略,即血液基因组免疫亚型(bGIS)方案,用于识别出能从一线化疗联合PD-1抑制剂中获益的患者。最后,研究展示了ctDNA动态监测的潜在应用。总体而言,该研究提出了一种基于ctDNA分层策略的治疗算法,为晚期NSCLC患者的个体化免疫化疗管理提供了新思路。
7.Distinct clinical outcomes and biological features of specific KRAS mutants in human pancreatic cancer
特定KRAS突变在胰腺癌中的不同临床结果和生物学特征
美国纽约纪念斯隆凯特琳癌症中心肝胰胆外科
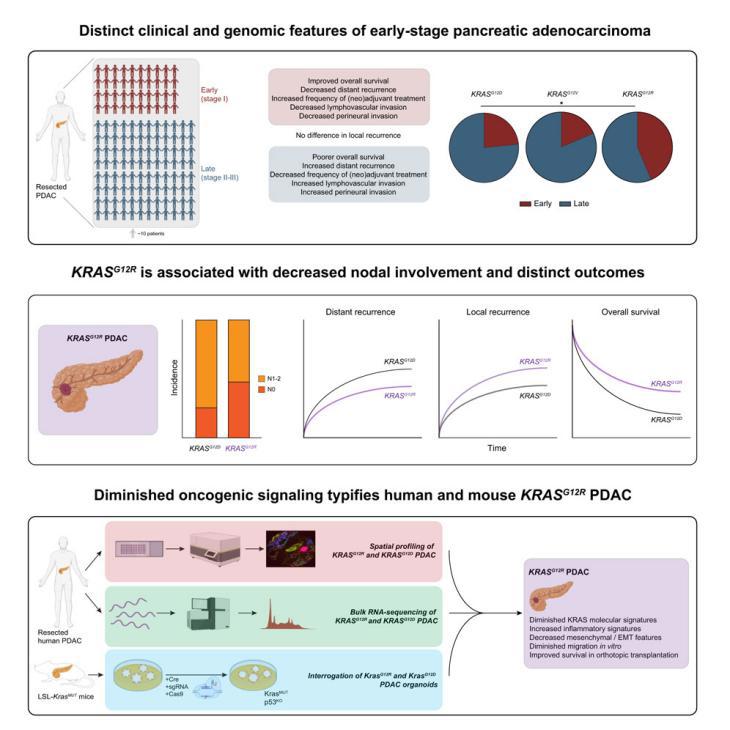
KRAS mutations in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) are suggested to vary in oncogenicity but the implications for human patients have not been explored in depth. We examined 1,360 consecutive PDAC patients undergoing surgical resection and find that KRASG12R mutations are enriched in early-stage (stage I) disease, owing not to smaller tumor size but increased node-negativity. KRASG12R tumors are associated with decreased distant recurrence and improved survival as compared to KRASG12D. To understand the biological underpinnings, we performed spatial profiling of 20 patients and bulk RNA-sequencing of 100 tumors, finding enhanced oncogenic signaling and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in KRASG12D and increased nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) signaling in KRASG12R tumors. Orthogonal studies of mouse KrasG12R PDAC organoids show decreased migration and improved survival in orthotopic models. KRAS alterations in PDAC are thus associated with distinct presentation, clinical outcomes, and biological behavior, highlighting the prognostic value of mutational analysis and the importance of articulating mutation-specific PDAC biology.
KRAS突变在胰腺导管腺癌(PDAC)中的致瘤性有个体间差异,但其对患者的影响尚缺乏深入研究。该研究分析了1,360名接受手术切除的PDAC患者,发现KRAS G12R 突变在早期(I期)疾病中较为集中,并且与肿瘤体积较小无关,但与较高的淋巴结阴性率有关。与KRAS G12D相比,KRAS G12R 与更少的远处复发和更高的生存率相关。为探究其生物学基础,研究对20名患者进行空间组学分析,对100例肿瘤样本进行RNA测序,发现KRAS G12D 肿瘤中的促癌信号和上皮-间质转化(EMT)增强,而KRAS G12R 肿瘤则显示出NF-κB信号增强。另外,在小鼠PDAC类器官中观察到,Kras G12R 肿瘤的迁移能力降低,且在原位模型中具有更好的生存率。由此可见,KRAS突变在PDAC中与特定的临床表现、预后及生物行为相关,突显出突变分析的预后价值及阐明突变特异性PDAC生物学的重要性。

Oct 14, 2024 Volume 42Issue 10p1631-1798
在2024年10月,Cancer Cell共发表14篇文章,其中包括Commentary 2篇,Preview 4篇,Review 1篇,Article 6篇,Report 1篇。
8.Coagulation factor X promotes resistance to androgen-deprivation therapy in prostate cancer
凝血因子X会提高前列腺癌对雄激素剥夺疗法的耐药性
瑞士贝林佐纳肿瘤研究所
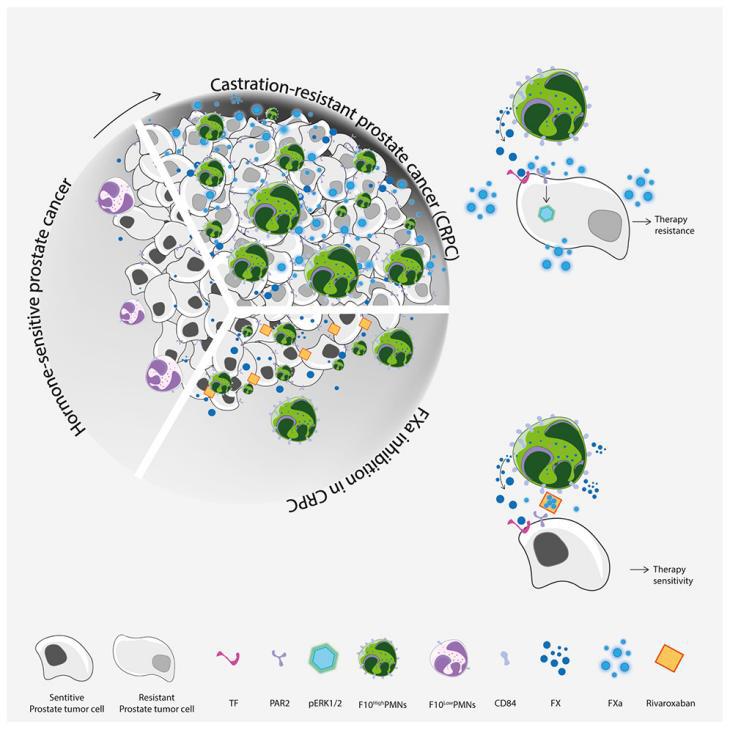
Although hypercoagulability is commonly associated with malignancies, whether coagulation factors directly affect tumor cell proliferation remains unclear. Herein, by performing single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) of the prostate tumor microenvironment (TME) of mouse models of castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC), we report that immunosuppressive neutrophils (PMN-MDSCs) are a key extra-hepatic source of coagulation factor X (FX). FX activation within the TME enhances androgen-independent tumor growth by activating the protease-activated receptor 2 (PAR2) and the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 in tumor cells. Genetic and pharmacological inhibition of factor Xa (FXa) antagonizes the oncogenic activity of PMN-MDSCs, reduces tumor progression, and synergizes with enzalutamide therapy. Intriguingly, F10high PMN-MDSCs express the surface marker CD84 and CD84 ligation enhances F10 expression. Elevated levels of FX, CD84, and PAR2 in prostate tumors associate with worse survival in CRPC patients. This study provides evidence that FXa directly promotes cancer and highlights additional targets for PMN-MDSCs for cancer therapies.
尽管恶性肿瘤常常伴随高凝状态,但凝血因子是否直接影响肿瘤细胞的增殖尚不明确。在该研究中,研究者通过单细胞RNA测序(scRNA-seq)分析小鼠去势抵抗性前列腺癌(CRPC)模型的肿瘤微环境(TME),发现其中的免疫抑制性中性粒细胞(PMN-MDSCs)是肝外凝血因子X(FX)的关键来源。TME中FX通过激活蛋白酶激活受体2(PAR2)和促进肿瘤细胞ERK1/2磷酸化来增强雄激素非依赖性的肿瘤生长。通过基因和药理学抑制FXa能够对抗PMN-MDSCs的致癌活性,减缓肿瘤进展,并与恩杂鲁胺治疗产生协同效果。令人惊讶的是,F10(编码FX的基因)高表达的PMN-MDSCs会表达表面标记物CD84,而CD84配体结合能够增强F10的表达。并且,在CRPC患者中,肿瘤内FX、CD84和PAR2水平升高与较差的生存率相关。总的来说,该研究表明FXa能直接促进癌症发展,揭示了PMN-MDSCs的潜在治疗靶点。
9.Distinct tumor architectures and microenvironments for the initiation of breast cancer metastasis in the brain
乳腺癌脑转移早期脑转移灶的不同肿瘤结构及微环境
美国纽约斯隆凯特琳癌症中心
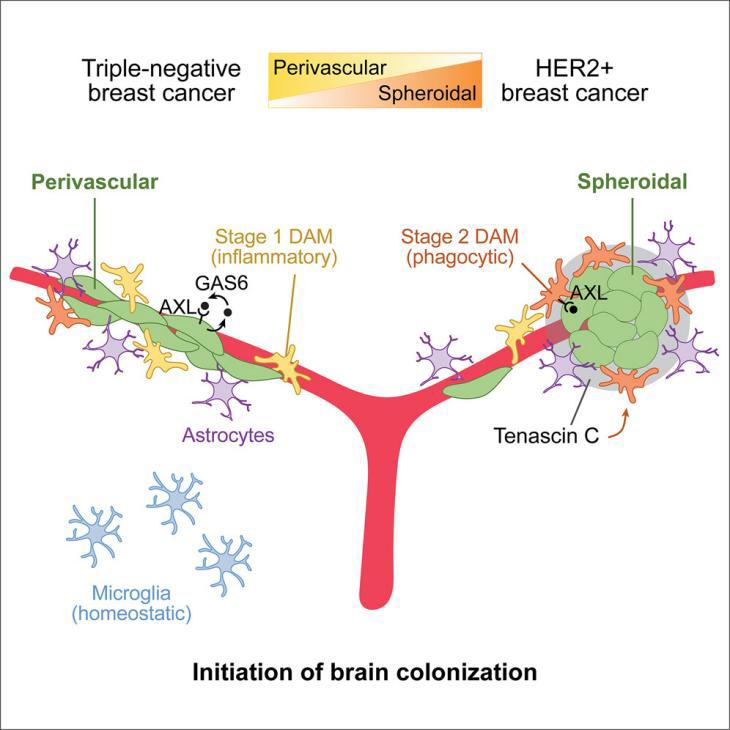
Brain metastasis, a serious complication of cancer, hinges on the initial survival, microenvironment adaptation, and outgrowth of disseminated cancer cells. To understand the early stages of brain colonization, we investigated two prevalent sources of cerebral relapse, triple-negative (TNBC) and HER2+ (HER2BC) breast cancers. Using mouse models and human tissue samples, we found that these tumor types colonize the brain, with a preference for distinctive tumor architectures, stromal interfaces, and autocrine programs. TNBC models tend to form perivascular sheaths with diffusive contact with astrocytes and microglia. In contrast, HER2BC models tend to form compact spheroids driven by autonomous tenascin C production, segregating stromal cells to the periphery. Single-cell transcriptomics of the tumor microenvironment revealed that these architectures evoke differential Alzheimer’s disease-associated microglia (DAM) responses and engagement of the GAS6 receptor AXL. The spatial features of the two modes of brain colonization have relevance for leveraging the stroma to treat brain metastasis.
癌症脑转移是一种严重的并发症,其发生依赖于癌细胞的初始存活、微环境适应及扩散后增殖。为了解脑部转移早期的机制,该研究分析了三阴性乳腺癌(TNBC)和HER2阳性乳腺癌(HER2BC)这两种常见的脑转移来源。通过小鼠模型和人类组织样本,研究发现这两类肿瘤在脑转移中倾向于形成不同的肿瘤结构、基质界面及自分泌程序。TNBC模型通常形成周围血管鞘,与星形胶质细胞和小胶质细胞接触紧密;而HER2BC模型则倾向于形成紧密的球状结构,通过自分泌腱蛋白C将基质细胞隔离在外围。单细胞转录组分析显示,不同肿瘤结构会激发不同的阿尔茨海默病相关小胶质细胞(DAM)的反应,并激活GAS6受体AXL。总的来说,不同肿瘤脑转移的独特空间特征为利用基质治疗脑转移的治疗思路提供了重要参考。
10.Integrated electrophysiological and genomic profiles of single cells reveal spiking tumor cells in human glioma
单细胞的电生理和基因组特征的综合分析发现了人胶质瘤中的放电肿瘤细胞
 美国休斯顿贝勒医学院
美国休斯顿贝勒医学院
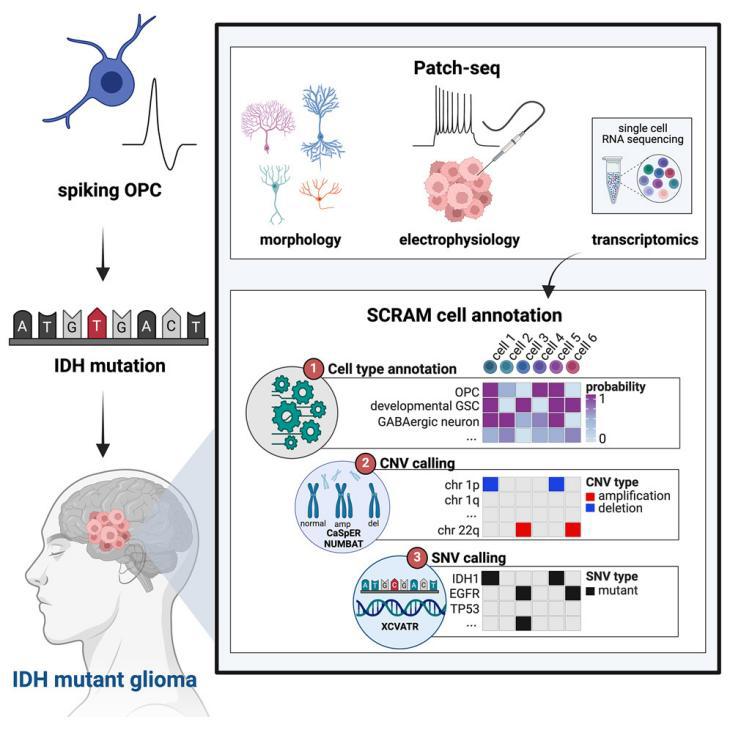
Prior studies have described the complex interplay that exists between glioma cells and neurons; however, the electrophysiological properties endogenous to glioma cells remain obscure. To address this, we employed Patch-sequencing (Patch-seq) on human glioma specimens and found that one-third of patched cells in IDH mutant (IDHmut) tumors demonstrate properties of both neurons and glia. To define these hybrid cells (HCs), which fire single, short action potentials, and discern if they are of tumoral origin, we developed the single cell rule association mining (SCRAM) computational tool to annotate each cell individually. SCRAM revealed that HCs possess select features of GABAergic neurons and oligodendrocyte precursor cells, and include both tumor and non-tumor cells. These studies characterize the combined electrophysiological and molecular properties of human glioma cells and describe a cell type in human glioma with unique electrophysiological and transcriptomic properties that may also exist in the non-tumor brain.
过去的研究已经描述了胶质瘤细胞与神经元之间的复杂相互作用,但胶质瘤细胞本身的内源性电生理特性尚不清楚。为了解答这一问题,该研究在IDH突变型(IDHmut)胶质瘤样本上采用了Patch-seq方法,发现三分之一的细胞展现出神经元和神经胶质细胞的双重特性。为了定义这些混合特性细胞(HCs)并判断其是否源自肿瘤,该研究开发了单细胞关联挖掘算法SCRAM来逐个标注每个细胞。结果表明,HCs具有部分GABA能神经元和少突胶质前体细胞的特征,并且包含了肿瘤和非肿瘤细胞。总的来说,该研究首次描绘了人胶质瘤细胞的电生理和分子特性,并描述了一种可能存在于非肿瘤脑组织中的独特细胞类型。
11.Fusobacterium nucleatum facilitates anti-PD-1 therapy in microsatellite stable colorectal cancer
核梭形菌能增强微卫星稳定的结直肠癌对抗PD-1治疗的敏感性
 中国广州中山大学附属第一医院肿瘤科
中国广州中山大学附属第一医院肿瘤科
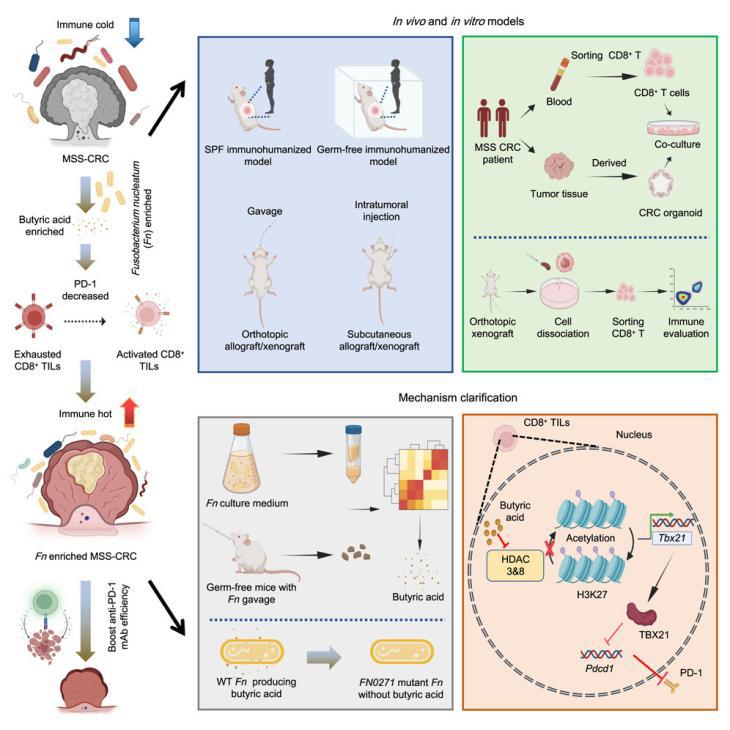
Microsatellite stable (MSS) colorectal cancers (CRCs) are often resistant to anti-programmed death-1 (PD-1) therapy. Here, we show that a CRC pathogen, Fusobacterium nucleatum (Fn), paradoxically sensitizes MSS CRC to anti-PD-1. Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) from patients with Fn-high MSS CRC to germ-free mice bearing MSS CRC confers sensitivity to anti-PD-1 compared to FMT from Fn-low counterparts. Single Fn administration also potentiates anti-PD-1 efficacy in murine allografts and CD34+-humanized mice bearing MSS CRC. Mechanistically, we demonstrate that intratumoral Fn generates abundant butyric acid, which inhibits histone deacetylase (HDAC) 3/8 in CD8+ T cells, inducing Tbx21 promoter H3K27 acetylation and expression. TBX21 transcriptionally represses PD-1, alleviating CD8+ T cell exhaustion and promoting effector function. Supporting this notion, knockout of a butyric acid-producing gene in Fn abolishes its anti-PD-1 boosting effect. In patients with MSS CRC, high intratumoral Fn predicts favorable response to anti-PD-1 therapy, indicating Fn as a potential biomarker of immunotherapy response in MSS CRC.
微卫星稳定(MSS)的结直肠癌(CRC)通常对抗程序性死亡-1(PD-1)治疗耐药。该研究发现,CRC的病原菌核梭形菌(Fn)可使MSS CRC对抗PD-1治疗敏感。研究将Fn高丰度MSS CRC患者的粪便微生物移植(FMT)到MSS CRC无菌小鼠体内,结果发现,与低Fn的对照相比,显著提高了抗PD-1的疗效。单独给予Fn也能增强MSS CRC移植瘤小鼠和CD34+人源化小鼠模型中抗PD-1的效果。机制上,Fn在肿瘤中生成丰富的丁酸,可抑制CD8+T细胞中的组蛋白去乙酰化酶(HDAC)3/8,诱导Tbx21启动子的H3K27乙酰化及其表达。TBX21转录会下调PD-1,缓解CD8+T细胞衰竭并提升其效应功能。此外,敲除Fn的丁酸生成基因会削弱其增强抗PD-1的效果。患者的高丰度Fn提示更好的抗PD-1治疗反应,表明Fn可作为MSS CRC免疫治疗反应的潜在生物标志物。
12.A prospective study of neoadjuvant pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy for resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: The Keystone-001 trial
一项针对帕姆单抗联合化疗治疗可切除食管鳞癌的新辅助治疗的前瞻性研究:Keystone-001试验

中国天津医科大学肿瘤医院微创食管外科、国家癌症临床医学研究中心、癌症预防和治疗重点实验室、天津癌症临床研究中心
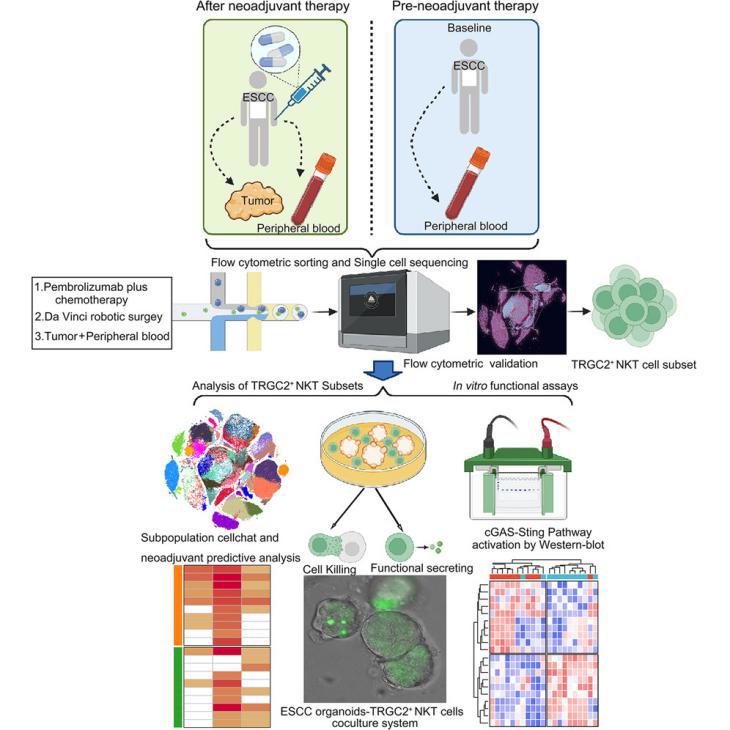
In this phase II study, 47 patients with locally advanced, resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) received three cycles of pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy, followed by Da Vinci robot-assisted surgery. The primary endpoints were safety and major pathological response (MPR). Key secondary endpoints included complete pathological response (pCR) and survival. No grade ≥3 adverse events or surgical delays occurred during neoadjuvant therapy. Among 46 patients studied for efficacy, the MPR and pCR rates were 72% and 41%, respectively. After a median follow-up of 27.2 months, the 2-year overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) rates were 91% and 89%, respectively. Expansion of TRGC2+ NKT cells in peripheral blood correlated with neoadjuvant treatment effectiveness, which was validated by in vitro organoid experiments and external cancer datasets, and its functional classification and mechanism of action were further explored. These findings show preoperative pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy is a promising therapeutic strategy for resectable ESCC.
在这项II期临床研究中,47例局部晚期、可切除的食管鳞状细胞癌(ESCC)患者接受了三周期的帕姆单抗联合化疗,随后进行达芬奇机器人手术。主要终点为安全性和主要病理学反应(MPR),次要终点包括完全病理反应(pCR)和生存率。结果显示,新辅助治疗期间未发生3级及以上不良事件或手术延迟。在46名患者中,MPR和pCR率分别为72%和41%。在中位随访27.2个月后,2年总生存率(OS)和无病生存率(DFS)分别为91%和89%。另外,研究发现外周血TRGC2+NKT细胞的扩增与新辅助治疗效果相关,并在体外类器官实验和外部癌症数据集中得到验证,其功能分类和作用机制需要进一步探究。这些结果显示,术前帕姆单抗联合化疗是一种有前景的治疗策略。
13.Cross-tissue human fibroblast atlas reveals myofibroblast subtypes with distinct roles in immune modulation
跨组织人类成纤维细胞图谱揭示了具有不同免疫调节功能的肌成纤维细胞亚型

北京大学深圳研究生院化学生物学与生物技术学院
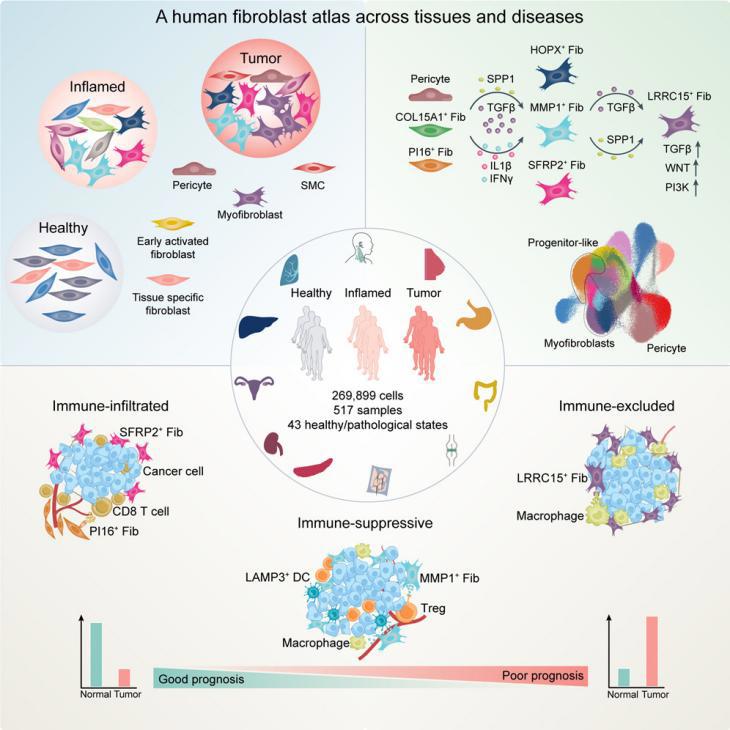
Fibroblasts, known for their functional diversity, play crucial roles in inflammation and cancer. In this study, we conduct comprehensive single-cell RNA sequencing analyses on fibroblast cells from 517 human samples, spanning 11 tissue types and diverse pathological states. We identify distinct fibroblast subpopulations with universal and tissue-specific characteristics. Pathological conditions lead to significant shifts in fibroblast compositions, including the expansion of immune-modulating fibroblasts during inflammation and tissue-remodeling myofibroblasts in cancer. Within the myofibroblast category, we identify four transcriptionally distinct subpopulations originating from different developmental origins, with LRRC15+ myofibroblasts displaying terminally differentiated features. Both LRRC15+ and MMP1+ myofibroblasts demonstrate pro-tumor potential that contribute to the immune-excluded and immune-suppressive tumor microenvironments (TMEs), whereas PI16+ fibroblasts show potential anti-tumor functions in adjacent non-cancerous regions. Fibroblast-subtype compositions define patient subtypes with distinct clinical outcomes. This study advances our understanding of fibroblast biology and suggests potential therapeutic strategies for targeting specific fibroblast subsets in cancer treatment.
成纤维细胞的功能复杂,在炎症和癌症中发挥重要作用。在本研究中,研究者对来自11种组织类型和不同病理状态的517个样本的成纤维细胞进行了scRNA测序分析,识别出具有普遍和组织特异性特征的不同成纤维细胞亚群。结果发现,特定的病理状态会导致成纤维细胞组成的显著变化,包括炎症期间免疫调节成纤维细胞的扩增,以及癌症中的组织重塑肌成纤维细胞的扩增。在肌成纤维细胞类别中,研究发现四种转录上不同的亚群,源自不同的发育来源,其中LRRC15+肌成纤维细胞表现出终末分化特征。LRRC15+MMP1+肌成纤维细胞在肿瘤微环境(TME)中表现出促肿瘤潜能,能导致免疫排除和免疫抑制,而PI16+成纤维细胞则在邻近非癌组织中具有潜在的抗肿瘤作用。成纤维细胞亚型的组成能定义不同临床结果的患者亚型。总的来说,本研究加深了人们对成纤维细胞的理解,并提出了在癌症治疗中靶向特定成纤维细胞亚群的潜在策略。

汇报人:夏晓旭
导师:赵宇、任建君
审核:邱轲、杨柠菲、任建君



