【Science】2024年6月-2024年7月刊论文导读
期刊介绍:
《Science》杂志是一份享有盛誉的学术期刊,由美国科学促进会(American Association for the Advancement of Science, AAAS)出版。它成立于1880年,现已成为世界上最具影响力的科学期刊之一。《Science》杂志涵盖了广泛的科学领域,包括生物学、化学、地球科学、物理学、天文学、医学、环境科学等。影响因子指数49.962。
本期文献导读将呈现2024年6月-2024年7月刊共2个月内医学生物学相关的主要刊物内容。

Volume 385|Issue 6707|26 Jul 2024
在2024年7月26日,Science共发表文章34篇,其中包括1篇EDITORIAL; 6篇NEWS; 10篇INSIGHTS; 16篇RESEARCH,其中2篇RESEARCH HIGHLIGHTS,14篇RESEARCH ARTICLES; 1篇CAREERS。
1.Chromatin plasticity predetermines neuronal eligibility for memory trace formation
染色质可塑性预先决定了神经元的记忆痕迹的形成

瑞士洛桑联邦理工学院生命科学学院等
Abstract:
Memories are encoded by sparse populations of neurons but how such sparsity arises remains largely unknown. We found that a neuron’s eligibility to be recruited into the memory trace depends on its epigenetic state prior to encoding. Principal neurons in the mouse lateral amygdala display intrinsic chromatin plasticity, which when experimentally elevated favors neuronal allocation into the encoding ensemble. Such chromatin plasticity occurred at genomic regions underlying synaptic plasticity and was accompanied by increased neuronal excitability in single neurons in real time. Lastly, optogenetic silencing of the epigenetically altered neurons prevented memory expression, revealing a cell-autonomous relationship between chromatin plasticity and memory trace formation. These results identify the epigenetic state of a neuron as a key factor enabling information encoding.
记忆由稀疏的神经元群体编码,但如何产生稀疏性的机制仍然大部分未知。研究人员发现,神经元被招募进入记忆痕迹的能力由编码前的表观遗传状态决定。小鼠外侧杏仁核的主要神经元显示出内在的染色质可塑性,活性增高有利于神经元整合至集合网络的过程。这种染色质可塑性发生在突触可塑性对应的基因组区域,并且实时增加单神经元的兴奋性。最后,研究人员对表观遗传上发生改变的神经元进行光遗传学沉默以阻止记忆的形成,揭示了染色质可塑性与记忆痕迹形成之间的自主关系。这些结果表明神经元的表观遗传状态是实现信息编码的关键因素。

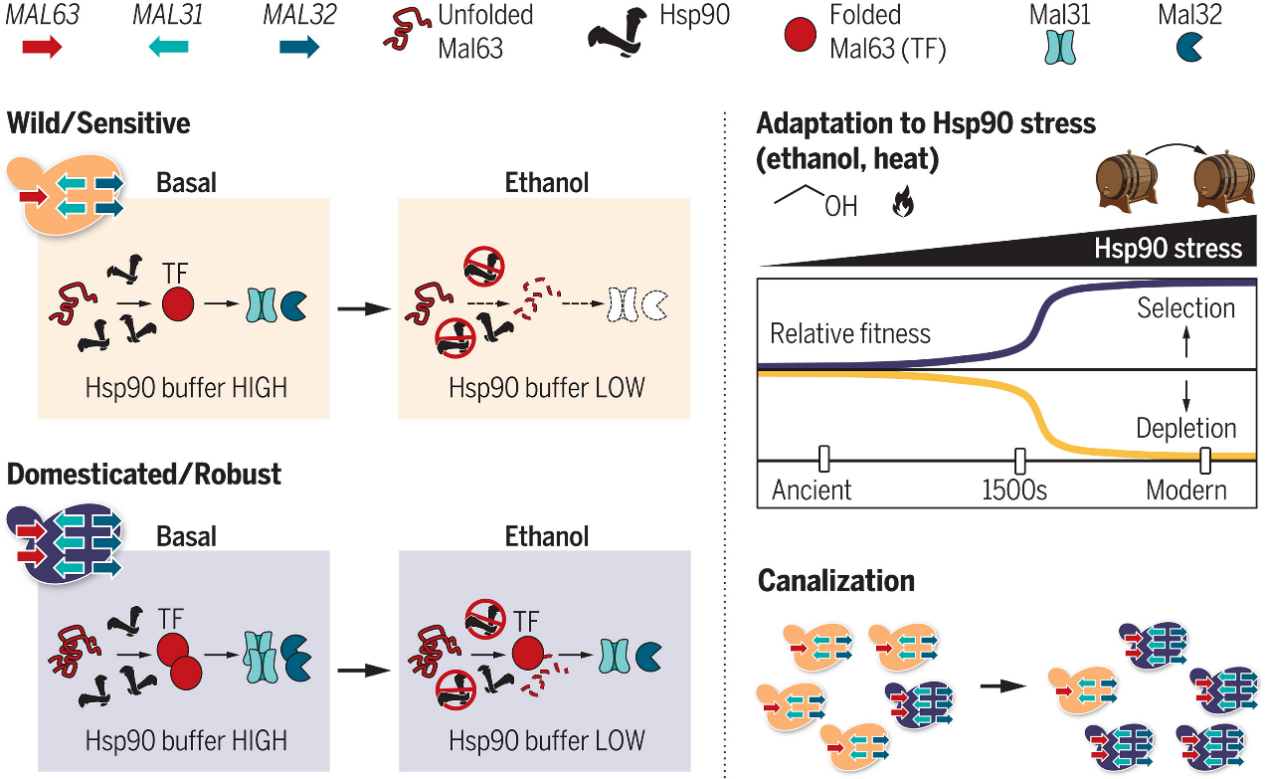
2.Selection for robust metabolism in domesticated yeasts is driven by adaptation to Hsp90 stress
驯化酵母对Hsp90应激的适应性推动了对稳健代谢的选择

美国德克萨斯大学 MD 安德森癌症中心等
Abstract:
Protein folding both promotes and constrains adaptive evolution. We uncover this surprising duality in the role of the protein-folding chaperone heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) in maintaining the integrity of yeast metabolism amid proteotoxic stressors within industrial domestication niches. Ethanol disrupts critical Hsp90-dependent metabolic pathways and exerts strong selective pressure for redundant duplications of key genes within these pathways, yielding the classical genomic signatures of beer and bread domestication. This work demonstrates a mechanism of adaptive canalization in an ecology of major economic importance and highlights Hsp90-dependent variation as an important source of phantom heritability in complex traits.
蛋白质折叠既促进又限制了适应性进化。研究人员揭示了在工业化驯化环境的酵母代谢过程中,蛋白质折叠伴侣热休克蛋白90(Hsp90)在蛋白质毒性应激条件下维持酵母代谢完整性方面的令人惊讶的双重作用。乙醇破坏了关键的Hsp90依赖的代谢途径,给代谢途径中的关键基因冗余复制施加了强烈的选择压力,从而产生了啤酒和面包驯化的经典基因组特征。这项工作展示了在具有重大经济重要性的生态中适应渠化的机制,并强调了Hsp90依赖性变异作为复杂性状的的隐性遗传的重要来源。
3.Tuning cohesin trajectories enables differential readout of the Pcdhα cluster across neurons
调整原钙黏蛋白轨迹可实现神经元间Pcdhα簇的差异性读取

美国加州大学旧金山分校威尔神经科学研究所等
Abstract:
Expression of Protocadherin (Pcdh) genes is critical to the generation of neuron identity and wiring of the nervous system. Pcdhα genes are arranged in clusters and exhibit a range of expression profiles, from stochastic to deterministic. Because Pcdhα promoters have high sequence identity and share distal enhancers, how distinct neurons choose which gene to express remains unclear. We show that the interplay between multiple enhancers, epigenetics, and genome folding orchestrates differential readouts of the locus across neurons. The probability of Pcdhα promoter choice depends on enhancer/promoter encounters catalyzed by cohesin, whose extrusion trajectories determine the likelihood that an individual promoter can “escape” heterochromatin-mediated silencing. We propose that tunable locus-specific regulatory elements and cell type–specific cohesin activity underlie the generation of cellular diversity by Pcdh genes.
原钙粘蛋白(Pcdh)基因的表达对于神经元特性的生成和神经系统的连接至关重要。Pcdhα基因以簇状排列,表现出从随机性到确定性的一系列表达特征。由于Pcdhα启动子具有高度的序列相似性和共享远端增强子的特性,不同神经元如何选择特定基因进行表达仍然未知。研究人员发现,多种增强子、表观遗传机制以及基因组折叠之间的相互作用,共同协调了该位点在不同神经元中的差异性读取。Pcdhα启动子的选择概率取决于由钙黏蛋白催化的增强子/启动子的接触,而钙黏蛋白的外泌轨迹决定了个别启动子“逃脱”异染色质介导的沉默的可能性。研究人员提出,可调控的位点特异性调控元件以及细胞类型特异性的钙黏蛋白活性,是Pcdh基因生成细胞多样性的关键机制。
4.Neurons for infant social behaviors in the mouse zona incerta
小鼠未定带中控制幼鼠社交行为的神经元

美国耶鲁大学医学院比较医学系行为生理学实验室等
Abstract:
Understanding the neural basis of infant social behaviors is crucial for elucidating the mechanisms of early social and emotional development. In this work, we report a specific population of somatostatin-expressing neurons in the zona incerta (ZISST) of preweaning mice that responds dynamically to social interactions, particularly those with their mother. Bidirectional neural activity manipulations in pups revealed that widespread connectivity of preweaning ZISST neurons to sensory, emotional, and cognitive brain centers mediates two key adaptive functions associated with maternal presence: the reduction of behavior distress and the facilitation of learning. These findings reveal a population of neurons in the infant mouse brain that coordinate the positive effects of the relationship with the mother on an infant’s behavior and physiology.
理解婴儿社交行为的神经基础对于阐明早期社交和情感发展的机制至关重要。在这项工作中,研究人员报告了一种特定的未断奶期小鼠的未定带(ZISST)中表达生长抑素的神经元群体,这类神经元对社交互动(特别是与母亲的互动)有动态反应。对幼鼠的双向神经活动操控揭示了:未断奶期小鼠的未定带的神经元到感觉、情感和认知脑的广泛连接,这些连接介导了与母亲在场时两个关键适应功能:减少行为困扰和促进学习。这些发现揭示了小鼠大脑中一群协调母亲关系和对婴儿行为和生理产生积极影响的神经元。
5.GLP-1 increases preingestive satiation via hypothalamic circuits in mice and humans
GLP-1通过下丘脑回路增加小鼠和人类的摄食前饱腹感
韩国首尔国立大学医学院生物医学系等
Abstract:
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) are effective antiobesity drugs. However, the precise central mechanisms of GLP-1RAs remain elusive. We administered GLP-1RAs to patients with obesity and observed a heightened sense of preingestive satiation. Analysis of human and mouse brain samples pinpointed GLP-1 receptor (GLP-1R) neurons in the dorsomedial hypothalamus (DMH) as candidates for encoding preingestive satiation. Optogenetic manipulation of DMHGLP-1R neurons caused satiation. Calcium imaging demonstrated that these neurons are actively involved in encoding preingestive satiation. GLP-1RA administration increased the activity of DMHGLP-1R neurons selectively during eating behavior. We further identified that an intricate interplay between DMHGLP-1R neurons and neuropeptide Y/agouti-related peptide neurons of the arcuate nucleus (ARCNPY/AgRP neurons) occurs to regulate food intake. Our findings reveal a hypothalamic mechanism through which GLP-1RAs control preingestive satiation, offering previously unexplored neural targets for obesity and metabolic diseases.
胰高血糖素样肽-1(GLP-1)受体激动剂(GLP-1RAs)是有效的抗肥胖药物。然而,GLP-1RAs的具体中枢机制仍然不清晰。研究者们对肥胖患者使用GLP-1RAs干预,观察到肥胖者摄食前饱腹感的增强。对人类和小鼠脑样本的分析精准显示,背内侧下丘脑(DMH)中的GLP-1受体(GLP-1R)神经元是编码摄食前饱腹感的候选机制。DMHGLP-1R神经元的光遗传学调控导致了摄食前饱腹感。钙成像技术显示了这些神经元积极参与编码摄食前饱腹感的过程。使用GLP-1RA在进食期间选择性地增加了DMHGLP-1R神经元的活动。研究者们进一步确定了DMHGLP-1R神经元与弓状核的神经肽Y/Agouti相关肽神经元(ARCNPY/AgRP神经元)之间复杂的相互作用,以调节食物摄入。研究者们的研究揭示了GLP-1RAs控制摄食前饱腹感的下丘脑机制,为肥胖和代谢疾病提供了未经探索的神经靶点。

Volume 385|Issue 6706|19 Jul 2024
在2024年7月19日,Science共发表文章41篇,其中包括1篇EDITORIAL; 10篇NEWS; 11篇INSIGHTS; 18篇RESEARCH,其中2篇RESEARCH HIGHLIGHTS,1篇REVIEW,15篇RESEARCH ARTICLES; 1篇CAREERS。
1. Diversity and scale: Genetic architecture of 2068 traits in the VA Million Veteran Program
多样性与大规模:百万退伍军人计划中2068种性状的遗传结构

美国宾夕法尼亚大学佩雷尔曼医学院医学系、转化医学和人类遗传学分部等
Abstract:
One of the justifiable criticisms of human genetic studies is the underrepresentation of participants from diverse populations. Lack of inclusion must be addressed at-scale to identify causal disease factors and understand the genetic causes of health disparities. We present genome-wide associations for 2068 traits from 635,969 participants in the Department of Veterans Affairs Million Veteran Program, a longitudinal study of diverse United States Veterans. Systematic analysis revealed 13,672 genomic risk loci; 1608 were only significant after including non-European populations. Fine-mapping identified causal variants at 6318 signals across 613 traits. One-third (n = 2069) were identified in participants from non-European populations. This reveals a broadly similar genetic architecture across populations, highlights genetic insights gained from underrepresented groups, and presents an extensive atlas of genetic associations.
既往对人类遗传研究的合理批评是多样性人群的代表性不足。为了识别疾病的致病因素并了解健康差异的遗传学因素,必须大规模地解决包容性不足的问题。研究人员展示了在一项针对不同背景的美国退伍军人的长期研究——美国退伍军人事务部“百万退伍军人项目”中的635,969名参与者的2068种性状的全基因组关联数据。系统分析揭示了13,672个基因组风险位点,其中1608个在包括非欧洲人群后才显著。精细定位提示在613种性状的6318个信号通路中确定了致病变异。在非欧洲人群参与者中发现其中1/3(2069个)信号通路。这表明各人群之间具有广泛相似的遗传结构,突显了从代表性不足的群体中获得的遗传见解,并提供了广泛的遗传关联图谱。
2.The human mitochondrial mRNA structurome reveals mechanisms of gene expression
人类线粒体mRNA结构组揭示了基因表达的机制

美国迈阿密大学米勒医学院生物化学与分子生物学系等
Abstract:
The human mitochondrial genome encodes crucial oxidative phosphorylation system proteins, pivotal for aerobic energy transduction. They are translated from nine monocistronic and two bicistronic transcripts whose native structures remain unexplored, posing a gap in understanding mitochondrial gene expression. In this work, we devised the mitochondrial dimethyl sulfate mutational profiling with sequencing (mitoDMS-MaPseq) method and applied detection of RNA folding ensembles using expectation-maximization (DREEM) clustering to unravel the native mitochondrial messenger RNA (mt-mRNA) structurome in wild-type (WT) and leucine-rich pentatricopeptide repeat–containing protein (LRPPRC)–deficient cells. Our findings elucidate LRPPRC’s role as a holdase contributing to maintaining mt-mRNA folding and efficient translation. mt-mRNA structural insights in WT mitochondria, coupled with metabolic labeling, unveil potential mRNA-programmed translational pausing and a distinct programmed ribosomal frameshifting mechanism. Our data define a critical layer of mitochondrial gene expression regulation. These mt-mRNA folding maps provide a reference for studying mt-mRNA structures in diverse physiological and pathological contexts.
人类线粒体基因组编码了对有氧能量转导至关重要的氧化磷酸化系统蛋白。这些蛋白从九个单顺反子和两个双顺反子转录本中翻译而来,但这些转录本的天然结构尚未被探索,造成了对线粒体基因表达方面的空白。在这项研究中,研究者们发明了线粒体二甲基硫酸盐突变谱分析测序(mitoDMS-MaPseq)方法,并使用了利用期望最大化(DREEM)聚类技术检测RNA折叠集合,以揭示野生型(WT)和富含亮氨酸的五肽重复序列蛋白(LRPPRC)缺陷型细胞中的天然线粒体信使RNA(mt-mRNA)结构组。这项研究阐明了LRPPRC作为维持mt-mRNA折叠和高效翻译的组装体的作用。WT线粒体中的mt-mRNA结构信息,结合代谢标记,揭示了潜在的mRNA程序性翻译暂停和独特的编程性核糖体框架移位机制机制。研究数据定义了线粒体基因表达调控的关键层面。这些mt-mRNA折叠图谱为在不同生理和病理背景下研究mt-mRNA结构提供了参考依据。
3.Live chromosome identifying and tracking reveals size-based spatial pathway of meiotic errors in oocytes
活体染色体识别和追踪揭示了卵母细胞中基于大小的减数分裂错误的空间路径

日本神户理化学研究所生物系统动力学研究中心等
Abstract:
Meiotic errors of relatively small chromosomes in oocytes result in egg aneuploidies that cause miscarriages and congenital diseases. Unlike somatic cells, which preferentially mis-segregate larger chromosomes, aged oocytes preferentially mis-segregate smaller chromosomes through unclear processes. Here, we provide a comprehensive three-dimensional chromosome identifying-and-tracking dataset throughout meiosis I in live mouse oocytes. This analysis reveals a prometaphase pathway that actively moves smaller chromosomes to the inner region of the metaphase plate. In the inner region, chromosomes are pulled by stronger bipolar microtubule forces, which facilitates premature chromosome separation, a major cause of segregation errors in aged oocytes. This study reveals a spatial pathway that facilitates aneuploidy of small chromosomes preferentially in aged eggs and implicates the role of the M phase in creating a chromosome size–based spatial arrangement.
卵母细胞中相对较小的染色体的减数分裂错误会导致卵子出现非整倍体,进而引发流产和先天性疾病。与错误分离较大染色体的体细胞不同,衰老的卵母细胞通过不明机制优先错误分离较小的染色体。在此,研究者们提供了一个全面涵盖了小鼠活体模型卵母细胞减数分裂I期过程的实时三维染色体识别和追踪数据集。这项分析揭示了一个能将较小的染色体主动移动到中期板的内侧区域的前中期通路。在中期板内侧区域,染色体受到更强的双极微管力的牵拉,这促进了染色体过早分离,这是老化卵母细胞中出现分离错误的主要原因。本研究揭示了一条在老化卵子中优先促进小型染色体的非整倍性的空间通路,揭示了M期在创建基于染色体大小的空间排列方面所起的作用。

Volume 385|Issue 6705|12 Jul 2024
在2024年7月12日,Science共发表文章37篇,其中包括1篇EDITORIAL; 8篇NEWS; 10篇INSIGHTS; 17篇RESEARCH,其中2篇RESEARCH HIGHLIGHTS,15篇RESEARCH ARTICLES,1篇CAREERS。
1. Recurrent gene flow between Neanderthals and modern humans over the past 200,000 years
过去20万年间尼安德特人与现代人之间的反复基因交流

中国东南大学医学院医学遗传学与发育生物学系
联合美国林斯顿大学刘易斯-西格勒综合基因组学研究所等
Abstract:
Although it is well known that the ancestors of modern humans and Neanderthals admixed, the effects of gene flow on the Neanderthal genome are not well understood. We develop methods to estimate the amount of human-introgressed sequences in Neanderthals and apply it to whole-genome sequence data from 2000 modern humans and three Neanderthals. We estimate that Neanderthals have 2.5 to 3.7% human ancestry, and we leverage human-introgressed sequences in Neanderthals to revise estimates of Neanderthal ancestry in modern humans, show that Neanderthal population sizes were significantly smaller than previously estimated, and identify two distinct waves of modern human gene flow into Neanderthals. Our data provide insights into the genetic legacy of recurrent gene flow between modern humans and Neanderthals.
尽管现代人类的祖先与尼安德特人之间存在基因混合已得到公认,但基因流动对尼安德特人基因组的影响尚未明确。研究者们开发了估算尼安德特人基因组中人类导入序列的方法,并将其应用于2000名现代人和三名尼安德特人的全基因组序列数据。研究者们估计尼安德特人拥有2.5%至3.7%的人类祖先基因成分,并充分利用尼安德特人中的人类遗传序列来重新估算现代人中的尼安德特人祖先的比例,发现尼安德特人群体的规模显著小于既往估计情况,并识别出两次不同的现代人基因流入尼安德特人基因的事件。研究者们的数据揭示了现代人与尼安德特人之间反复基因流动的基因遗留。
2. Mutant IDH1 inhibition induces dsDNA sensing to activate tumor immunity
突变体IDH1抑制诱导dsDNA感应激活肿瘤免疫的机制
美国马萨诸塞总医院克兰茨家族癌症研究中心等
Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) is the most commonly mutated metabolic gene across human cancers. Mutant IDH1 (mIDH1) generates the oncometabolite (R)-2-hydroxyglutarate, disrupting enzymes involved in epigenetics and other processes. A hallmark of IDH1-mutant solid tumors is T cell exclusion, whereas mIDH1 inhibition in preclinical models restores antitumor immunity. Here, we define a cell-autonomous mechanism of mIDH1-driven immune evasion. IDH1-mutant solid tumors show selective hypermethylation and silencing of the cytoplasmic double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) sensor CGAS, compromising innate immune signaling. mIDH1 inhibition restores DNA demethylation, derepressing CGAS and transposable element (TE) subclasses. dsDNA produced by TE-reverse transcriptase (TE-RT) activates cGAS, triggering viral mimicry and stimulating antitumor immunity. In summary, we demonstrate that mIDH1 epigenetically suppresses innate immunity and link endogenous RT activity to the mechanism of action of a US Food and Drug Administration-approved oncology drug.
异柠檬酸脱氢酶1(IDH1)是在人类癌症中最常见的突变代谢基因。突变的IDH1(mIDH1)产生致癌代谢物(R)-2-羟基戊二酸(R-2HG),破坏与表观遗传学和其他过程相关酶的功能。IDH1突变实体瘤的一个特征是T细胞排斥,而在临床前模型中,抑制mIDH1可恢复抗肿瘤免疫。在本研究中,研究者们定义了一种由mIDH1驱动的细胞自主性免疫逃逸机制。IDH1突变实体瘤表现出选择性高甲基化并沉默细胞质双链DNA (dsDNA) 传感器CGAS,削弱了先天免疫信号传导。mIDH1抑制能够恢复DNA去甲基化,从而解除对CGAS和可转座元件(TE)亚类的抑制。由TE逆转录酶(TE-RT)生成的dsDNA激活了cGAS,引发病毒模拟效应并刺激抗肿瘤免疫。总之,研究者证实mIDH1通过表观遗传途径抑制先天免疫,并将内源性RT活性与美国食品药品监督管理局(FDA)批准的肿瘤药物的作用机制相关联。
3. Antagonistic conflict between transposon-encoded introns and guide RNAs
转座子编码内含子与引导RNA之间的拮抗性冲突

美国哥伦比亚大学生物化学与分子生物物理系等
TnpB nucleases represent the evolutionary precursors to CRISPR-Cas12 and are widespread in all domains of life. IS605-family TnpB homologs function as programmable RNA-guided homing endonucleases in bacteria, driving transposon maintenance through DNA double-strand break-stimulated homologous recombination. In this work, we uncovered molecular mechanisms of the transposition life cycle of IS607-family elements that, notably, also encode group I introns. We identified specific features for a candidate "IStron" from Clostridium botulinum that allow the element to carefully control the relative levels of spliced products versus functional guide RNAs. Our results suggest that IStron transcripts evolved an ability to balance competing and mutually exclusive activities that promote selfish transposon spread while limiting adverse fitness costs on the host. Collectively, this work highlights molecular innovation in the multifunctional utility of transposon-encoded noncoding RNAs.
TnpB核酸酶代表了CRISPR-Cas12的进化前体,广泛存在于所有生命领域中。IS605家族的TnpB同源物在细菌中作为可编程的RNA引导的定向内切酶发挥作用,通过DNA双链断裂刺激同源重组来驱动转座子的维持。在这项工作中,研究者们揭示了IS607家族元素转座生命周期的分子机制,值得注意的是,这些元素还编码I组内含子。研究者识别了来自肉毒梭菌的候选“IStron”的特定特征,使该元素能够精细控制剪接产物与功能引导RNA的相对水平。研究者们的结果表明,IStron转录本演化出了一种互相平衡竞争和互斥活动的能力,促进自私转座子传播的同时限制了对宿主的不利适应性代价。总之,这项工作突出了转座子编码的非编码RNA的多功能应用方面的分子创新。
4. High-resolution electron cryomicroscopy of V-ATPase in native synaptic vesicles
在天然突触囊泡中使用高分辨率电子冷冻显微镜观察V-ATP酶的三维结构
加拿大安大略省多伦多大学儿童医院等
Intercellular communication in the nervous system occurs through the release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft between neurons. In the presynaptic neuron, the proton pumping vesicular- or vacuolar-type ATPase (V-ATPase) powers neurotransmitter loading into synaptic vesicles (SVs), with the V1complex dissociating from the membrane region of the enzyme before exocytosis. We isolated SVs from rat brain using SidK, a V-ATPase-binding bacterial effector protein. Single-particle electron cryomicroscopy allowed high-resolution structure determination of V-ATPase within the native SV membrane. In the structure, regularly spaced cholesterol molecules decorate the enzyme's rotor and the abundant SV protein synaptophysin binds the complex stoichiometrically. ATP hydrolysis during vesicle loading results in a loss of the V1region of V-ATPase from the SV membrane, suggesting that loading is sufficient to induce dissociation of the enzyme.
神经系统中的细胞间通信通过神经递质释放入神经元之间的突触间隙来实现。在前突触神经元中,质子泵作用的囊泡型或液泡型ATP酶(V-ATP酶)为神经递质装载到突触囊泡(SVs)提供动力,在胞吐前V1复合体从酶的膜区域解离。研究者使用SidK(一种于V-ATP酶结合的细菌效应蛋白)从大鼠大脑中分离出SVs。单粒子电子冷冻显微镜技术能够在天然SV膜内高分辨率地确定V-ATP酶的结构。在V-ATP酶结构中,规律间隔分布的胆固醇分子装饰着酶的转子,丰富的SV蛋白突触素以化学计量比与该复合体结合。在囊泡装载期间的ATP水解导致V-ATP酶的V1区域从SV膜上丢失,这表明装载过程足以诱导该酶的解离。
5. Integrated translation and metabolism in a partially self-synthesizing biochemical network
在部分自合成的生化网络中整合翻译与代谢过程
德国马克斯·普朗克物质与生命研究所等
One of the hallmarks of living organisms is their capacity for self-organization and regeneration, which requires a tight integration of metabolic and genetic networks. We sought to construct a linked metabolic and genetic network in vitro that shows such lifelike behavior outside of a cellular context and generates its own building blocks from nonliving matter. We integrated the metabolism of the crotonyl-CoA/ethyl-malonyl-CoA/hydroxybutyryl-CoA cycle with cell-free protein synthesis using recombinant elements. Our network produces the amino acid glycine from CO2and incorporates it into target proteins following DNA-encoded instructions. By orchestrating ~50 enzymes we established a basic cell-free operating system in which genetically encoded inputs into a metabolic network are programmed to activate feedback loops allowing for self-integration and (partial) self-regeneration of the complete system.
生物体的一个显著特征是其自我组织和再生的能力,这需要代谢网络和遗传网络的紧密整合。研究者旨在在体外构建一个相互关联的的代谢与遗传网络,使其在细胞环境之外展现出类似生命的行为,并从非生命物质中生成自身的构建模块。研究者利用重组元件将巴豆酰辅酶 A/乙基丙二酸辅酶 A/羟基丁酰辅酶 A 循环的代谢过程与无细胞蛋白合成相整合。研究者的网络能够将二氧化碳转化为氨基酸甘氨酸,并根据DNA编码的指令将其整合到目标蛋白中。通过协调约50种酶,研究者建立了一个基本的无细胞操作系统,在该系统中,代谢网络中的基因编码输入被编程以激活反馈回路,从而实现系统的自我整合和(部分)自我再生。

Volume 385|Issue 6704|5 Jul 2024
在2024年7月5日,Science共发表文章36篇,其中包括1篇EDITORIAL;7篇NEWS;8篇INSIGHTS;3篇ESSAYS;18篇RESEARCH,其中2篇RESEARCH HIGHLIGHTS,15篇RESEARCH ARTICLES,1篇CAREERS。
1. An atlas of transcribed enhancers across helper T cell diversity for decoding human diseases
用于解码人类疾病的辅助T细胞多样性转录增强子图谱,

日本化学研究所整合医学科学中心RIKEN-IFOM癌症基因组联合实验室等
Transcribed enhancer maps can reveal nuclear interactions underpinning each cell type and connect specific cell types to diseases. Using a 5' single-cell RNA sequencing approach, we defined transcription start sites of enhancer RNAs and other classes of coding and noncoding RNAs in human CD4+T cells, revealing cellular heterogeneity and differentiation trajectories. Integration of these datasets with single-cell chromatin profiles showed that active enhancers with bidirectional RNA transcription are highly cell type-specific and that disease heritability is strongly enriched in these enhancers. The resulting cell type-resolved multimodal atlas of bidirectionally transcribed enhancers, which we linked with promoters using fine-scale chromatin contact maps, enabled us to systematically interpret genetic variants associated with a range of immune-mediated diseases.
转录增强子图谱能够揭示支撑每种细胞类型的核相互作用,并将特定细胞类型与疾病关联起来。研究者通过运用5'单细胞RNA测序方法,确定了人类CD4+ T细胞中增强子RNA及其他编码和非编码RNA的转录起始位点,揭示了细胞异质性和分化轨迹。将这些数据集与单细胞染色质谱相整合显示,结果表明具有双向RNA转录的活性增强子具有高度的细胞类型特异性,并且这些增强子在疾病遗传易感性方面显著富集。研究者构建的细胞类型解析的双向转录增强子的多模态图谱,通过精细的染色质接触图与启动子关联,使研究者们能够系统性地解读与一系列免疫介导疾病相关的遗传变异。
2. Evolution and host-specific adaptation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
铜绿假单胞菌的演化及其对宿主特异性适应
英国剑桥大学维克多·菲利普·达赫德心肺研究所等
The major human bacterial pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa causes multidrug-resistant infections in people with underlying immunodeficiencies or structural lung diseases such as cystic fibrosis (CF). We show that a few environmental isolates, driven by horizontal gene acquisition, have become dominant epidemic clones that have sequentially emerged and spread through global transmission networks over the past 200 years. These clones demonstrate varying intrinsic propensities for infecting CF or non-CF individuals (linked to specific transcriptional changes enabling survival within macrophages); have undergone multiple rounds of convergent, host-specific adaptation; and have eventually lost their ability to transmit between different patient groups. Our findings thus explain the pathogenic evolution of P. aeruginosa and highlight the importance of global surveillance and cross-infection prevention in averting the emergence of future epidemic clones.
人类主要的细菌病原体假单胞菌(Pseudomonas aeruginosa)致使免疫缺陷或具有结构性肺病(如囊性纤维化,CF)的人群发生多重耐药性感染。研究者发现,在水平基因获取的驱动下,部分环境分离株已成为占主导地位的流行克隆株,在过去200年中通过全球传播网络相继出现并扩散。这些克隆株在感染CF或非CF个体方面表现出不同的内在倾向(与能够在巨噬细胞内存活的特定转录变化相关);经历了多轮趋同的、针对宿主的特异性适应;最终失去了在不同患者群体之间传播的能力。因此,研究者们的研究结果解释了假单胞菌的致病演化过程,并强调全球监测和交叉感染预防在避免未来流行克隆株出现方面的重要性。
3. A metabolic dependency of EBV can be targeted to hinder B cell transformation
EBV的代谢依赖性可被靶向用于阻碍B细胞转化

瑞士巴塞尔大学生物医学系等
After infection of B cells, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) engages host pathways that mediate cell proliferation and transformation, contributing to the propensity of the virus to drive immune dysregulation and lymphomagenesis. We found that the EBV protein EBNA2 initiates nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) de novo biosynthesis by driving expression of the metabolic enzyme indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) in infected B cells. Virus-enforced NAD production sustained mitochondrial complex I activity, to match adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production with bioenergetic requirements of proliferation and transformation. In transplant patients, IDO1 expression in EBV-infected B cells, and a serum signature of increased IDO1 activity, preceded development of lymphoma. In humanized mice infected with EBV, IDO1 inhibition reduced both viremia and lymphomagenesis. Virus-orchestrated NAD biosynthesis is therefore a druggable metabolic vulnerability of EBV-driven B cell transformation, opening therapeutic possibilities for EBV-related diseases.
在感染B细胞后,人类疱疹病毒第四型(EBV)参与宿主介导细胞增殖和转化的途径,使得该病毒易于引发免疫失调和淋巴瘤形成的倾向。研究者发现EBV蛋白EBNA2通过驱动感染B细胞中代谢酶吲哚胺2,3-双加氧酶1(IDO1)的表达,启动烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸(NAD)的新生物合成。病毒强制产生的NAD维持了线粒体复合体I的活性,以使三磷酸腺苷(ATP)的生成与增殖和转化的生物能量需求相匹配。在移植患者中,EBV感染的B细胞中IDO1的表达以及血清中IDO1活性增加的特征,先于淋巴瘤的发展。在感染EBV的人源化小鼠中, IDO1抑制可减少病毒血症和淋巴瘤的形成。因此,病毒协调的NAD生物合成成为EBV驱动的B细胞转化的可靶向代谢弱点,为EBV相关疾病的治疗提供了可能的治疗选择。
4. Genomic investigation of 18,421 lines reveals the genetic architecture of rice
对18,421个品系的基因组学研究揭示了水稻的遗传结构
中国上海师范大学生命科学学院植物种质资源开发中心等
Understanding how numerous quantitative trait loci (QTL) shape phenotypic variation is an important question in genetics. To address this, we established a permanent population of 18,421 (18K) rice lines with reduced population structure. We generated reference-level genome assemblies of the founders and genotyped all 18K-rice lines through whole-genome sequencing. Through high-resolution mapping, 96 high-quality candidate genes contributing to variation in 16 traits were identified, including OsMADS22 and OsFTL1 verified as causal genes for panicle number and heading date, respectively. We identified epistatic QTL pairs and constructed a genetic interaction network with 19 genes serving as hubs. Overall, 170 masking epistasis pairs were characterized, serving as an important factor contributing to genetic background effects across diverse varieties. The work provides a basis to guide grain yield and quality improvements in rice.
了解众多数量性状基因座(QTL)如何影响表型变异是遗传学中的重要问题。为此,研究者建立了一个包含18,421个(18K)水稻品系组成的永久性种群,以减少种群结构多样性的影响。研究者对创始品系进行了参考水平的基因组组装,并通过全基因组测序对所有18K水稻品系进行了基因分型。通过高分辨率作图,鉴定出96个影响16个性状变异的高质量候选基因,包括分别被验证为穗数和抽穗期的致因基因OsMADS22和OsFTL1。研究者识别出表型间存在上位性效应的QTL对,并构建了一个包含19个基因枢纽的遗传互动网络。总体而言,该研究证实了170对掩蔽上位性效应的QTL对,这些是不同品种遗传背景效应的重要因素,为指导水稻的产量和质量改良提供了依据。
5. Unsupervised evolution of protein and antibody complexes with a structure-informed language model
基于结构信息语言模型进行蛋白质和抗体复合物的无监督进化

美国斯坦福大学医学院及Chan Zuckerberg生物中心等
Large language models trained on sequence information alone can learn high-level principles of protein design. However, beyond sequence, the three-dimensional structures of proteins determine their specific function, activity, and evolvability. Here, we show that a general protein language model augmented with protein structure backbone coordinates can guide evolution for diverse proteins without the need to model individual functional tasks. We also demonstrate that ESM-IF1, which was only trained on single-chain structures, can be extended to engineer protein complexes. Using this approach, we screened about 30 variants of two therapeutic clinical antibodies used to treat severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. We achieved up to 25-fold improvement in neutralization and 37-fold improvement in affinity against antibody-escaped viral variants of concern BQ.1.1 and XBB.1.5, respectively. These findings highlight the advantage of integrating structural information to identify efficient protein evolution trajectories without requiring any task-specific training data.
仅基于序列信息训练的大型语言模型可以学习蛋白质设计的高级原则。然而,除了序列之外,蛋白质的三维结构决定了其特定功能、活性和可进化性。在此,研究者展示了一种通用的蛋白质语言模型,通过添加蛋白质结构的主链坐标,可以指导多种蛋白质的进化,而无需针对每个功能任务单独建模。研究者还证明了仅通过单链结构训练的ESM-IF1可以扩展到工程蛋白质复合物。采用这种方法,研究者筛选了用于治疗严重急性呼吸综合症冠状病毒2(SARS-CoV-2)感染的两种治疗性临床抗体的约30种变体,分别实现了高达25倍的中和能力和37倍的亲和力改善,以对抗抗体逃逸的病毒变异体BQ.1.1和XBB.1.5。这些发现突显了整合结构信息以识别高效蛋白质进化轨迹的优势,而无需任何任务特定的训练数据。
6. Trigeminal ganglion neurons are directly activated by influx of CSF solutes in a migraine model
在偏头痛模型中脑脊液溶质的流入激活三叉神经节神经元

丹麦哥本哈根大学转化神经医学中心等
Classical migraine patients experience aura, which is transient neurological deficits associated with cortical spreading depression (CSD), preceding headache attacks. It is not currently understood how a pathological event in cortex can affect peripheral sensory neurons. In this study, we show that cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flows into the trigeminal ganglion, establishing nonsynaptic signaling between brain and trigeminal cells. After CSD, ~11% of the CSF proteome is altered, with up-regulation of proteins that directly activate receptors in the trigeminal ganglion. CSF collected from animals exposed to CSD activates trigeminal neurons in naïve mice in part by CSF-borne calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP). We identify a communication pathway between the central and peripheral nervous system that might explain the relationship between migrainous aura and headache.
经典型偏头痛患者会出现先兆症状,这是一种与皮层扩散性抑制(CSD)相关的短暂性神经功能缺损,先于头痛发作。目前尚未明确皮层中的病理事件如何影响外周感觉神经元的机制。在本研究中,研究者展示了脑脊液(CSF)流入三叉神经节,在大脑与三叉神经元间建立了非突触信号传递。CSD发生后,约11%的脑脊液蛋白质组发生变化,其中上调的蛋白质可直接激活三叉神经节中的受体。从接触CSD的动物中收集的脑脊液,部分通过脑脊液转运的降钙素基因相关肽(CGRP)激活了处于未受CSD影响的小鼠的三叉神经元。研究者确定了中枢神经系统与外周神经系统之间的通信通路,这可能解释了偏头痛先兆症状与头痛之间的关系。

Volume 384|Issue 6703|28 Jun 2024
在2024年6月28日,Science共发表文章37篇,其中包括1篇EDITORIAL;7篇NEWS;12篇INSIGHTS;17篇RESEARCH,其中2篇RESEARCH HIGHLIGHTS,15篇RESEARCH ARTICLES,1篇CAREERS。
1.Type I conventional dendritic cells facilitate immunotherapy in pancreatic cancer
I型常规树突状细胞有助于胰腺癌的免疫疗法
美国德克萨斯大学MD安德森癌症中心等
Inflammation and tissue damage associated with pancreatitis can precede or occur concurrently with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). We demonstrate that in PDAC coupled with pancreatitis (ptPDAC), antigen-presenting type I conventional dendritic cells (cDC1s) are specifically activated. Immune checkpoint blockade therapy (iCBT) leads to cytotoxic CD8+T cell activation and elimination of ptPDAC with restoration of life span even upon PDAC rechallenge. Using PDAC antigen-loaded cDC1s as a vaccine, immunotherapy-resistant PDAC was rendered sensitive to iCBT with elimination of tumors. cDC1 vaccination coupled with iCBT identified specific CDR3 sequences in the tumor-infiltrating CD8+T cells with potential therapeutic importance. This study identifies a fundamental difference in the immune microenvironment in PDAC concurrent with, or without, pancreatitis and provides a rationale for combining cDC1 vaccination with iCBT as a potential treatment option.
与胰腺炎相关的炎症和组织损伤可能在胰腺导管腺癌(PDAC)之前或与之同时发生。研究者展示了在伴有胰腺炎的PDAC(ptPDAC)中,抗原呈递的I型常规树突状细胞(cDC1s)被特异性激活。免疫检查点抑制治疗(iCBT)导致细胞毒性CD8+T细胞的激活和ptPDAC的消除,即使在PDAC复发时也能如此。将负载PDAC抗原的cDC1s作为疫苗,使得对免疫疗法耐药的PDAC对iCBT变得敏感,并消除肿瘤。cDC1疫苗接种联合iCBT确定了肿瘤浸润CD8+T细胞中具有潜在治疗效应的特定CDR3序列。这项研究识别了伴或不伴胰腺炎时的PDAC免疫微环境的根本差异,并提供了将cDC1疫苗接种与iCBT相结合作为潜在治疗方案的理论基础。
2.Mef2d potentiates type-2 immune responses and allergic lung inflammation
Mef2d能增强2型免疫反应和过敏性肺部炎症
英国剑桥大学MRC分子生物学实验室等
Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) and adaptive T lymphocytes promote tissue homeostasis and protective immune responses. Their production depends on the transcription factor GATA3, which is further elevated specifically in ILC2s and T helper 2 cells to drive type-2 immunity during tissue repair, allergic disorders, and anti-helminth immunity. The control of this crucial up-regulation is poorly understood. Using CRISPR screens in ILCs we identified previously unappreciated myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2d (Mef2d)-mediated regulation of GATA3-dependent type-2 lymphocyte differentiation. Mef2d-deletion from ILC2s and/or T cells specifically protected against an allergen lung challenge. Mef2d repressed Regnase-1 endonuclease expression to enhance IL-33 receptor production and IL-33 signaling and acted downstream of calcium-mediated signaling to translocate NFAT1tothenucleustopromotetype-2cytokine-mediatedimmunity.
固有淋巴样细胞(ILCs)和适应性T淋巴细胞能够促进组织内稳态和保护性免疫应答。其生成取决于转录因子GATA3,该因子在ILC2s和2型辅助性T细胞中会特异性升高,从而在组织修复、过敏性疾病以及抗蠕虫免疫过程中驱动2型免疫反应。然而,这种重要的上调过程的控制机制尚不清楚。研究者通过在ILCs中进行CRISPR筛选,发现了此前未被重视的肌细胞特异性增强因子2d(Mef2d)介导的GATA3依赖性2型淋巴细胞分化的调控机制。从ILC2s和/或T细胞中敲除Mef2d可特异性地防止过敏原对肺部的刺激。Mef2d抑制Regnase-1内切核酸酶的表达,以增强IL-33受体的生成和IL-33信号,并在钙介导的信号下游发挥作用,将NFAT1转运至细胞核,以促进2型细胞因子介导的免疫反应。
3.A neutralizing antibody prevents postfusion transition of measles virus fusion protein
中和抗体可防止麻疹病毒融合蛋白的后融合转变
美国拉荷亚免疫研究所疫苗创新中心等
Measles virus (MeV) presents a public health threat that is escalating as vaccine coverage in the general population declines and as populations of immunocompromised individuals, who cannot be vaccinated, increase. There are no approved therapeutics for MeV. Neutralizing antibodies targeting viral fusion are one potential therapeutic approach but have not yet been structurally characterized or advanced to clinical use. We present cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of prefusion F alone [2.1-angstrom (Å) resolution], F complexed with a fusion-inhibitory peptide (2.3-Å resolution), F complexed with the neutralizing and protective monoclonal antibody (mAb) 77 (2.6-Å resolution), and an additional structure of postfusion F (2.7-Å resolution). In vitro assays and examination of additional EM classes show that mAb 77 binds prefusion F, arrests F in an intermediate state, and prevents transition to the postfusion conformation. These structures shed light on antibody-mediated neutralization that involves arrest of fusion proteins in an intermediate state.
随着一方面普通人群中的疫苗覆盖率下降,另一方面无法接种疫苗的免疫功能低下个体数量增多,麻疹病毒(MeV)对公共卫生构成的威胁正不断加剧。目前尚无获批的MeV治疗药物。以病毒融合为靶点的中和抗体是一种潜在的治疗方法,但尚未进行结构表征或推进至临床应用。研究者展示了预融合F蛋白的冷冻电子显微镜(cryo-EM)结构(分辨率为2.1Å)、F蛋白与融合抑制肽复合物(分辨率为2.3Å)、F蛋白与中和及保护性单克隆抗体(mAb)77复合物(分辨率为2.6Å),以及后融合F蛋白的另一种结构(分辨率为2.7Å)。体外试验和对其他EM类别的检测表明,mAb77与预融合F蛋白结合,将F蛋白阻滞于中间状态,并阻止其向融合后构象转变。这些结构揭示了涉及将融合蛋白阻滞于中间状态的抗体介导的中和作用。
4.Brainwide silencing of prion protein by AAV-mediated delivery of an engineered compact epigenetic editor
通过AAV介导递送工程化紧凑型表观遗传编辑器实现全脑范围内的朊蛋白沉默
美国麻省理工学院生物工程系等
Prion disease is caused by misfolding of the prion protein (PrP) into pathogenic self-propagating conformations, leading to rapid-onset dementia and death. However, elimination of endogenous PrP halts prion disease progression. In this study, we describe Coupled Histone tail for Autoinhibition Release of Methyltransferase (CHARM), a compact, enzyme-free epigenetic editor capable of silencing transcription through programmable DNA methylation. Using a histone H3 tail-Dnmt3l fusion, CHARM recruits and activates endogenous DNA methyltransferases, thereby reducing transgene size and cytotoxicity. When delivered to the mouse brain by systemic injection of adeno-associated virus (AAV), Prnp-targeted CHARM ablates PrP expression across the brain. Furthermore, we have temporally limited editor expression by implementing a kinetically tuned self-silencing approach. CHARM potentially represents a broadly applicable strategy to suppress pathogenic proteins, including those implicated in other neurodegenerative diseases.
朊毒体病是由于朊蛋白(PrP)错误折叠成致病性的自我传播构象所引起的,导致快速发作的痴呆和死亡。然而,消除内源性PrP可以阻止朊毒体病的进展。在这项研究中,研究者描述了一种“耦合组蛋白尾用于甲基转移酶自抑制释放(CHARM)”紧凑、无酶的表观遗传编辑器,能够通过可编程的DNA甲基化来沉默转录。CHARM通过组蛋白H3尾-Dnmt3l融合体,招募并激活内源性DNA甲基转移酶,从而减少转基因的大小和细胞毒性。当通过全身系统性注射腺相关病毒(AAV)递送到小鼠大脑时,针对Prnp的CHARM能够消除全脑的PrP表达。此外,研究者通过实施动力学调节的自沉默方法限制了编辑器的表达时间。CHARM可能代表了一种广泛适用的用于抑制致病蛋白的策略,包括那些与其他神经退行性疾病相关的蛋白。

Volume 384|Issue 6702|21 Jun 2024
在2024年6月21日,Science发表了共计38篇文章,其中包括1篇EDITORIAL、8篇NEWS、11篇INSIGHTS;17篇RESEARCHARTICLES,其中2篇RESEARCHHIGHLIGHTS,15篇RESEARCHARTICLES,1篇CAREERS。
1.JAK inhibition enhances checkpoint blockade immunotherapy in patients with Hodgkin lymphoma
JAK抑制剂增强霍奇金淋巴瘤患者的免疫检查点阻断免疫治疗
美国斯克里普斯研究所等
Unleashing antitumor T cell activity by checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy is effective in cancer patients, but clinical responses are limited. Cytokine signaling through the Janus kinase (JAK)-signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathway correlates with checkpoint immunotherapy resistance. We report a phase I clinical trial of the JAK inhibitor ruxolitinib with anti-PD-1 antibody nivolumab in Hodgkin lymphoma patients relapsed or refractory following checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy. The combination yielded a best overall response rate of 53% (10/19). Ruxolitinib significantly reduced neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratios and percentages of myeloid suppressor cells but increased numbers of cytokine-producing T cells. Ruxolitinib rescued the function of exhausted T cells and enhanced the efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade in preclinical solid tumor and lymphoma models. This synergy was characterized by a switch from suppressive to immunostimulatory myeloid cells, which enhanced T cell division.
通过免疫检查点抑制剂免疫疗法释放抗肿瘤T细胞活性在癌症患者中是有效的,但临床响应有限。通过Janus激酶(JAK)-信号转导和转录激活因子(STAT)通路的细胞因子信号与免疫检查点免疫疗法的耐药性相关。研究者报告了一项针对霍奇金淋巴瘤患者的I期临床试验,这些患者在接受免疫检查点抑制剂治疗后出现复发或耐药难治,试验联合使用了JAK抑制剂鲁索利替尼与抗PD-1抗体纳武利尤单抗治疗。该组合的最佳总体缓解率为53%(10/19)。鲁索利替尼显著降低了中性粒细胞与淋巴细胞的比率和髓系抑制细胞的百分比,但增加了产生细胞因子的T细胞数量。鲁索利替尼在临床前实体瘤和淋巴瘤模型中恢复了耗竭T细胞的功能,并增强了免疫检查点阻断的疗效。这种协同作用的特征是从抑制性髓系细胞向免疫刺激性髓系细胞的转变,从而增强了T细胞的分裂。
2.Combined JAK inhibition and PD-1 immunotherapy for non–small cell lung cancer patients
JAK抑制剂和PD-1免疫疗法联合使用治疗非小细胞肺癌患者
美国宾夕法尼亚大学佩雷尔曼医学院等
Persistent inflammation driven by cytokines such as type-one interferon (IFN-I) can cause immunosuppression. We show that administration of the Janus kinase 1 (JAK1) inhibitor itacitinib after anti-PD-1 (programmed cell death protein 1) immunotherapy improves immune function and antitumor responses in mice and results in high response rates (67%) in a phase 2 clinical trial for metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Patients who failed to respond to initial anti-PD-1 immunotherapy but responded after addition of itacitinib had multiple features of poor immune function to anti-PD-1 alone that improved after JAK inhibition. Itacitinib promoted CD8 T cell plasticity and therapeutic responses of exhausted and effector memory-like T cell clonotypes. Patients with persistent inflammation refractory to itacitinib showed progressive CD8 T cell terminal differentiation and progressive disease. Thus, JAK inhibition may improve the efficacy of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy by pivoting T cell differentiation dynamics.
由一类细胞因子(如I型干扰素,IFN-I)驱动的持续性炎症可导致免疫抑制。研究者发现,在抗PD-1(程序性死亡蛋白1)免疫治疗后给予JAK1抑制剂伊塔替尼可以改善小鼠的免疫功能和抗肿瘤反应,并在一项转移性非小细胞肺癌的II期临床试验中获得了67%的高应答率。对于未能对初始抗PD-1免疫治疗产生反应但联合伊塔替尼后有所应答的患者,在单独接受抗PD-1治疗时表现出多种免疫功能低下的特征,但联合JAK抑制后这些特征得到了改善。伊塔替尼促进了CD8 T细胞的可塑性以及耗竭型和效应记忆样T细胞克隆型的治疗反应。对于对伊塔替尼持续无反应的患者,CD8 T细胞呈现出终末分化的进展性改变和疾病进展。因此,JAK抑制可能通过调整T细胞分化动态来提高抗PD-1免疫治疗的疗效。
3.Breast cancer exploits neural signaling pathways for bone-to-meninges metastasis
乳腺癌利用神经信号通路实现骨至脑膜的转移
美国杜克大学等
The molecular mechanisms that regulate breast cancer cell (BCC) metastasis and proliferation within the leptomeninges (LM) are poorly understood, which limits the development of effective therapies. In this work, we show that BCCs in mice can invade the LM by abluminal migration along blood vessels that connect vertebral or calvarial bone marrow and meninges, bypassing the blood-brain barrier. This process is dependent on BCC engagement with vascular basement membrane laminin through expression of the neuronal pathfinding molecule integrin α6. Once in the LM, BCCs colocalize with perivascular meningeal macrophages and induce their expression of the prosurvival neurotrophin glial-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF). Intrathecal GDNF blockade, macrophage-specific GDNF ablation, or deletion of the GDNF receptor neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) from BCCs inhibits breast cancer growth within the LM. These data suggest integrin α6 and the GDNF signaling axis as new therapeutic targets against breast cancer LM metastasis.
人们对于调控乳腺癌细胞(BCC)在软脑膜(LM)内转移和增殖的分子机制知之甚少,这限制了有效疗法的开发。在本研究中,研究者发现小鼠中的BCC可以沿着连接脊椎或颅骨骨髓和脑膜的血管,通过血管外膜迁移,从而绕过血脑屏障,侵入LM。该过程依赖于BCC通过表达神经引导分子整合素α6与血管基底膜层粘连蛋白的结合。一旦进入LM,BCC与血管周围的脑膜巨噬细胞共定位,并诱导其表达促存活的神经营养因子——胶质细胞源性神经营养因子(GDNF)。鞘内GDNF阻断、巨噬细胞特异性GDNF缺失或从BCC中敲除GDNF受体神经细胞黏附分子(NCAM)均抑制了乳腺癌在LM内的生长。以上数据表明,整合素α6和GDNF信号通路可作为针对乳腺癌LM转移的新治疗靶点。
4.AlphaFold2 structures guide prospective ligand discovery
AlphaFold2结构模型指导潜在的候选药物发现

美国北卡罗来纳大学医学院、加州大学旧金山分校、斯坦福大学和哈佛大学等
AlphaFold2 (AF2) models have had wide impact but mixed success in retrospective ligand recognition. We prospectively docked large libraries against unrefined AF2 models of the σ2and serotonin 2A (5-HT2A) receptors, testing hundreds of new molecules and comparing results with those obtained from docking against the experimental structures. Hit rates were high and similar for the experimental and AF2 structures, as were affinities. Success in docking against the AF2 models was achieved despite differences between orthosteric residue conformations in the AF2 models and the experimental structures. Determination of the cryo-electron microscopy structure for one of the more potent 5-HT2A ligands from the AF2 docking revealed residue accommodations that resembled the AF2 prediction. AF2 models may sample conformations that differ from experimental structures but remain low energy and relevant for ligand discovery, extending the domain of structure-based drug design.
AlphaFold2(AF2)模型已经产生了广泛的影响,但在回顾性配体识别方面的效果参差不齐。研究者前瞻性地将大型文库与未经精炼的 AF2 模型——σ2 和血清素 2A(5-HT2A)受体进行对接,测试了数百种新分子,并将结果与对实验结构的对接结果进行比较。实验结构和AF2结构的命中率均较高且亲和力相似。尽管AF2模型和实验结构中的正统残基构象存在差异,但AF2模型的对接仍取得了成功。从AF2对接中获得的更有效的5-HT2A配体之一的冷冻电镜结构测定显示,残基适应性与AF2模型预测相似。AF2模型可能会采样与实验结构不同的构象,但仍然能保持低能态,并对配体发现具有相关性,从而扩展了基于结构的药物设计的领域。
5.Top-down brain circuits for operant bradycardia
自上而下的脑电路调控操作性心动过缓

日本东京大学及国立信息和通信技术研究所等
Heart rate (HR) can be voluntarily regulated when individuals receive real-time feedback. In a rat model of HR biofeedback, the neocortex and medial forebrain bundle were stimulated as feedback and reward, respectively. The rats reduced their HR within 30 minutes, achieving a reduction of approximately 50% after 5 days of 3-hour feedback. The reduced HR persisted for at least 10 days after training while the rats exhibited anxiolytic behavior and an elevation in blood erythrocyte count. This bradycardia was prevented by inactivating anterior cingulate cortical (ACC) neurons projecting to the ventromedial thalamic nucleus (VMT). Theta-rhythm stimulation of the ACC-to-VMT pathway replicated the bradycardia. VMT neurons projected to the dorsomedial hypothalamus (DMH) and DMH neurons projected to the nucleus ambiguus, which innervates parasympathetic neurons in the heart.
当个体接收到实时反馈时,心率(HR)能够被自主调节。在一项心率生物反馈的大鼠模型中,神经元皮层和中脑束分别被作为反馈和奖励进行刺激。大鼠在30分钟内降低了心率,经过为期 5 天、每天 3 小时的反馈后,心率约降低 50%。在训练结束后的至少 10 天里,心率持续降低,同时大鼠表现出镇静行为,血红细胞计数也有所升高。这种心动过缓可以通过抑制投射到伏隔核(VMT)的前扣带皮层(ACC)神经元来加以预防。激活 ACC-VMT 通路的 θ 节律刺激能够重现心动过缓的情况。 VMT 神经元投射至下丘脑背内侧核(DMH),而 DMH 神经元则投射到迷走神经核(NAc),NAc 神经元支配着心脏的副交感神经。

Volume 384|Issue 6701|14 Jun 2024
在2024年6月14日,Science共发表文章39篇,其中包括1篇EDITORIAL;9篇NEWS;11篇INSIGHTS;17篇RESEARCH,其中2篇RESEARCH HIGHLIGHTS,15篇RESEARCH ARTICLES,1篇CAREERS。
1.Integrated platform for multiscale molecular imaging and phenotyping of the human brain
人脑的多尺度分子成像和表型分析综合平台
美国麻省理工学院医疗工程与科学研究所等
Understanding cellular architectures and their connectivity is essential for interrogating system function and dysfunction. However, we lack technologies for mapping the multiscale details of individual cells and their connectivity in the human organ-scale system. We developed a platform that simultaneously extracts spatial, molecular, morphological, and connectivity information of individual cells from the same human brain. The platform includes three core elements: a vibrating microtome for ultraprecision slicing of large-scale tissues without losing cellular connectivity (MEGAtome), a polymer hydrogel-based tissue processing technology for multiplexed multiscale imaging of human organ-scale tissues (mELAST), and a computational pipeline for reconstructing three-dimensional connectivity across multiple brain slabs (UNSLICE). We applied this platform for analyzing human Alzheimer's disease pathology at multiple scales and demonstrating scalable neural connectivity mapping in the human brain.
理解细胞结构及其连接性对于研究系统功能和功能失调至关重要。然而,在人类器官尺度系统中,研究者们缺乏用于绘制单个细胞及其连接性的多尺度细节的技术。研究者开发了一个能同时从同一人类大脑提取单个细胞的空间、分子、形态和连接信息的平台。该平台包括三个核心元素:用于大规模组织超精密切割且不损失细胞连接性的振动式超薄切片机(MEGAtome)、用于人类器官级组织多重多尺度成像的基于聚合物水凝胶的组织处理技术(mELAST),以及用于跨多个脑切片重建三维连接性的计算管线(UNSLICE)。研究者们将该平台应用于分析人类阿尔茨海默病的病理组织,并展示了人类大脑中实现可扩展神经连接映射的能力。
2.Metabolic inflexibility promotes mitochondrial health during liver regeneration
新陈代谢的不灵活性促进肝脏再生过程中的线粒体健康。
美国德克萨斯大学西南医学中心等
Mitochondria are critical for proper organ function and mechanisms to promote mitochondrial health during regeneration would benefit tissue homeostasis. We report that during liver regeneration, proliferation is suppressed in electron transport chain (ETC)-dysfunctional hepatocytes due to an inability to generate acetyl-CoA from peripheral fatty acids through mitochondrial β-oxidation. Alternative modes for acetyl-CoA production from pyruvate or acetate are suppressed in the setting of ETC dysfunction. This metabolic inflexibility forces a dependence on ETC-functional mitochondria and restoring acetyl-CoA production from pyruvate is sufficient to allow ETC-dysfunctional hepatocytes to proliferate. We propose that metabolic inflexibility within hepatocytes can be advantageous by limiting the expansion of ETC-dysfunctional cells.
线粒体对于器官的正常功能至关重要,再生过程中线粒体健康的机制将有利于组织内的稳态。研究者报告称,在肝脏再生期间,由于无法通过线粒体β-氧化从外周脂肪酸生成乙酰辅酶A,电子传递链(ETC)功能失调的肝细胞增殖受到抑制。在ETC功能失调的情况下,从丙酮酸或乙酸生成乙酰辅酶A的替代途径受到抑制。这种代谢的僵化性迫使细胞依赖于ETC功能正常的线粒体,而恢复从丙酮酸生成的乙酰辅酶A足够使ETC功能失调的肝细胞增殖。研究者提出,肝细胞内的代谢僵化限制了ETC功能失常细胞的扩张,可能是有利的过程。
3.Artemisinins ameliorate polycystic ovarian syndrome by mediating LONP1-CYP11A1 interaction
青蒿素可介导LONP1-CYP11A1相互作用改善多囊卵巢综合征
中国复旦大学基础医学学院生物化学与分子生物学系和中山医院内分泌与代谢科等
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a prevalent reproductive disorder in women of reproductive age, features androgen excess, ovulatory dysfunction, and polycystic ovaries. Despite its high prevalence, specific pharmacologic intervention for PCOS is challenging. In this study, we identified artemisinins as anti-PCOS agents. Our finding demonstrated the efficacy of artemisinin derivatives in alleviating PCOS symptoms in both rodent models and human patients, curbing hyperandrogenemia through suppression of ovarian androgen synthesis. Artemisinins promoted cytochrome P450 family 11 subfamily A member 1 (CYP11A1) protein degradation to block androgen overproduction. Mechanistically, artemisinins directly targeted lon peptidase 1 (LONP1), enhanced LONP1-CYP11A1 interaction, and facilitated LONP1-catalyzed CYP11A1 degradation. Overexpression of LONP1 replicated the androgen-lowering effect of artemisinins. Our data suggest that artemisinin application is a promising approach for treating PCOS and highlight the crucial role of the LONP1-CYP11A1 interaction in controlling hyperandrogenism and PCOS occurrence.
多囊卵巢综合征(PCOS)是一种常见于育龄女性的生殖障碍疾病,具有雄激素过剩、排卵功能紊乱和多囊卵巢等特征。尽管其发病率较高,但针对PCOS的特定药物干预仍然面临挑战。在这项研究中,研究者将青蒿素类物质鉴定为抗 PCOS 药物。研究结果表明,青蒿素衍生物能够在小鼠模型和人类患者中有效缓解PCOS症状,通过抑制卵巢雄激素合成来控制高雄激素血症。青蒿素促进细胞色素P450家族11亚家族A成员1(CYP11A1)蛋白降解,以阻止雄激素的过量产生。从机制上看,青蒿素直接靶向长肽酶1(LONP1),增强了LONP1-CYP11A1相互作用,并促进LONP1催化的CYP11A1降解。LONP1的过表达复制了青蒿素降低雄激素的作用。以上数据表明,青蒿素的应用是一种颇具前景的PCOS疗法,并强调了LONP1-CYP11A1相互作用在控制高雄激素血症和PCOS发生中的关键作用。
4.A phage tail–like bacteriocin suppresses competitors in metapopulations of pathogenic bacteria
一种类似噬菌体尾部的细菌素能抑制病原细菌集合种群中的竞争者。

美国犹他大学生物科学学院等
Bacteria can repurpose their own bacteriophage viruses (phage) to kill competing bacteria. Phage-derived elements are frequently strain specific in their killing activity, although there is limited evidence that this specificity drives bacterial population dynamics. Here, we identified intact phage and their derived elements in a metapopulation of wild plant-associated Pseudomonas genomes. We discovered that the most abundant viral cluster encodes a phage remnant resembling a phage tail called a tailocin, which bacteria have co-opted to kill bacterial competitors. Each pathogenic Pseudomonas strain carries one of a few distinct tailocin variants that target the variable polysaccharides in the outer membrane of co-occurring pathogenic Pseudomonas strains. Analysis of herbarium samples from the past 170 years revealed that the same tailocin and bacterial receptor variants have persisted in Pseudomonas populations. These results suggest that tailocin genetic diversity can be mined to develop targeted "tailocin cocktails" for microbial control.
细菌能够重新调整自身的噬菌体(phage)来杀死竞争细菌。尽管关于这种特异性如何驱动细菌种群动态的证据有限,噬菌体衍生成分的杀伤活性上通常具有菌株特异性。在本研究中,研究者在植物相关的野生假单胞菌基因组的复合种群中鉴定出完整的噬菌体及其衍生成分。研究者发现,最丰富的病毒簇编码一种类似于噬菌体尾部的噬菌体残余物,称为尾毒素(tailocin)。细菌利用其来杀灭竞争细菌。每种致病性假单胞菌菌株携带着针对共存致病性假单胞菌菌株外膜中变异多糖的不同尾毒素变体。从过去170年的植物标本馆标本分析表明,相同的尾毒素和细菌受体变体在假单胞菌种群中持续存在。这些结果表明,尾毒素的遗传多样性可以用于开发用于微生物控制的具有针对性的“尾毒素组合”。
5.In vivo editing of lung stem cells for durable gene correction in mice
体内编辑小鼠肺干细胞以实现持久的基因修正
美国德克萨斯大学西南医学中心等
In vivo genome correction holds promise for generating durable disease cures; yet, effective stem cell editing remains challenging. In this work, we demonstrate that optimized lung-targeting lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) enable high levels of genome editing in stem cells, yielding durable responses. Intravenously administered gene-editing LNPs in activatable tdTomato mice achieved >70% lung stem cell editing, sustaining tdTomato expression in >80% of lung epithelial cells for 660 days. Addressing cystic fibrosis (CF), NG-ABE8e messenger RNA (mRNA)-sgR553X LNPs mediated >95% cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) DNA correction, restored CFTR function in primary patient-derived bronchial epithelial cells equivalent to Trikafta for F508del, corrected intestinal organoids and corrected R553X nonsense mutations in 50% of lung stem cells in CF mice. These findings introduce LNP-enabled tissue stem cell editing for disease-modifying genome correction.
体内基因组修正有望为治愈持续性疾病提供解决方案;然而,有效的干细胞编辑仍具挑战。在这项研究中,研究者证明了经过优化的肺靶向脂质纳米颗粒(LNPs)能够在干细胞中实现高水平的基因组编辑,并产生持久效果。在可激活tdTomato小鼠中,静脉注射基因编辑LNPs,实现了超过70%的肺干细胞编辑,并使超过80%的肺上皮细胞中tdTomato持续表达了660天。在囊性纤维化(CF)研究中,NG-ABE8e信使RNA(mRNA)-sgR553X LNPs介导了超过95%的囊性纤维化跨膜传导调节因子(CFTR)DNA修正,恢复了在原代患者来源的支气管上皮细胞的CFTR功能,其效果与针对 F508del 突变的 Trikafta 相当,修正了肠道类器官和CF小鼠的50%肺干细胞中的R553X无义突变。这些发现为疾病相关的基因组修正引入了LNP增强的组织干细胞编辑技术。
6.An AAV capsid reprogrammed to bind human transferrin receptor mediates brain-wide gene delivery
一个结合人类转铁蛋白受体的重编程AAV衣壳可介导全脑范围内基因递送

美国麻省理工学院和哈佛大学布罗德研究等
Developing vehicles that efficiently deliver genes throughout the human central nervous system (CNS) will broaden the range of treatable genetic diseases. We engineered an adeno-associated virus (AAV) capsid, BI-hTFR1, that binds human transferrin receptor (TfR1), a protein expressed on the blood-brain barrier. BI-hTFR1 was actively transported across human brain endothelial cells and, relative to AAV9, provided 40 to 50 times greater reporter expression in the CNS of human TFRC knockin mice. The enhanced tropism was CNS-specific and absent in wild-type mice. When used to deliver GBA1, mutations of which cause Gaucher disease and are linked to Parkinson's disease, BI-hTFR1 substantially increased brain and cerebrospinal fluid glucocerebrosidase activity compared with AAV9. These findings establish BI-hTFR1 as a potential vector for human CNS gene therapy.
开发能够将基因有效递送到人类中枢神经系统(CNS)的基因载体,将拓宽可治疗的遗传疾病的范围。研究者构建了一种腺相关病毒(AAV)衣壳BI-hTFR1,其能够与一种在血脑屏障上表达的人类转铁蛋白受体(TfR1)结合。BI-hTFR1能够被主动运输过人脑内皮细胞,相较于AAV9,在人TFRC基因敲入小鼠的CNS模型中表达了40到50倍更高的报告基因。这种增强的嗜性在野生型小鼠中不存在,是CNS特异性的。当用于递送GBA1(其突变导致戈谢病并与帕金森病相关)时,与AAV9相比,BI-hTFR1显著提高了大脑和脑脊液中的葡萄糖脑苷脂酶活性。这些发现证实了BI-hTFR1作为人类CNS基因治疗的潜在载体。
7.Molecular mechanism of the ischemia-induced regulatory switch in mammalian complex I
缺血诱导的哺乳动物复合物I调控开关的分子机制

英国剑桥大学
Respiratory complex I is an efficient driver for oxidative phosphorylation in mammalian mitochondria, but its uncontrolled catalysis under challenging conditions leads to oxidative stress and cellular damage. Ischemic conditions switch complex I from rapid, reversible catalysis into a dormant state that protects upon reoxygenation, but the molecular basis for the switch is unknown. We combined precise biochemical definition of complex I catalysis with high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structures in the phospholipid bilayer of coupled vesicles to reveal the mechanism of the transition into the dormant state, modulated by membrane interactions. By implementing a versatile membrane system to unite structure and function, attributing catalytic and regulatory properties to specific structural states, we define how a conformational switch in complex I controls its physiological roles.
呼吸复合体I是哺乳动物线粒体中高效驱动氧化磷酸化的关键酶,但在恶劣条件下其不受控的催化作用会引发氧化应激和细胞损伤。缺血条件下,复合体I从快速、可逆的催化状态转变为休眠状态,从而在再氧合时起到保护作用,但其转换的分子基础尚不清楚。研究者将复合体I催化作用的精确生化定义与耦合囊泡磷脂双分子层中的高分辨率冷冻电子显微镜结构相结合,揭示了由膜相互作用所调控的向休眠状态转变的机制。研究者通过实施一种通用的膜系统来整合结构与功能,将催化和调节特性归因于特定的结构状态,明确了复合体I中的构象转换如何控制其生理作用。

汇报人:孙晓茹
导师:刘世喜/邹剑
审核:王欣怡、任建君



