
【Nature Genetics】2025年4-5月刊论文导读
期刊介绍:
Nature Genetics创刊于1992年,由NATURE RESEARCH出版商出版,发表最高质量的遗传学研究。它包括对人类和植物性状以及其他模式生物的遗传和功能基因组研究。目前的重点是通过扰动实验研究常见和复杂疾病的遗传基础以及基因网络的功能机制、结构和进化。在行业领域中学术影响力很大,属于国际一流期刊,影响因子指数41.307。

Volume 57 Issue 4, April 2025
在2025年4月,Nature Genetics共发表33篇文章,其中包括Comment 1篇,Research Highlights 4篇,News & Views 2篇,Research Briefings 3篇,Letters 1篇,Articles:20篇,Technical Reports 2篇。主要内容包括罕见编码变异、全基因组关联荟萃分析、单细胞多组学研究等内容。
1.Genome-wide association study meta-analysis provides insights into the etiology of heart failure and its subtypes
全基因组关联研究荟萃分析揭示心力衰竭及其亚型的病因学机制


伦敦大学学院心血管科学研究所
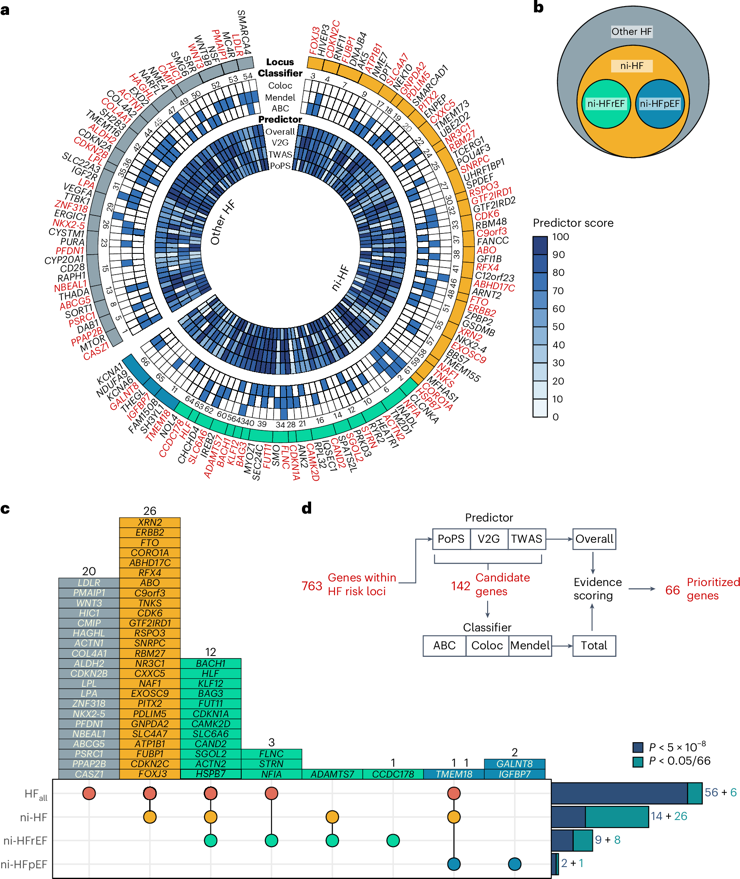
Heart failure (HF) is a major contributor to global morbidity and mortality. While distinct clinical subtypes, defined by etiology and left ventricular ejection fraction, are well recognized, their genetic determinants remain inadequately understood. In this study, we report a genome-wide association study of HF and its subtypes in a sample of 1.9 million individuals. A total of 153,174 individuals had HF, of whom 44,012 had a nonischemic etiology (ni-HF). A subset of patients with ni-HF were stratified based on left ventricular systolic function, where data were available, identifying 5,406 individuals with reduced ejection fraction and 3,841 with preserved ejection fraction. We identify 66 genetic loci associated with HF and its subtypes, 37 of which have not previously been reported. Using functionally informed gene prioritization methods, we predict effector genes for each identified locus, and map these to etiologic disease clusters through phenome-wide association analysis, network analysis and colocalization. Through heritability enrichment analysis, we highlight the role of extracardiac tissues in disease etiology. We then examine the differential associations of upstream risk factors with HF subtypes using Mendelian randomization. These findings extend our understanding of the mechanisms underlying HF etiology and may inform future approaches to prevention and treatment.
心力衰竭(HF)是导致全球发病率和死亡率上升的主要因素。尽管根据病因和左心室射血分数划分的不同临床亚型已得到广泛认可,但其遗传决定因素仍未被充分阐明。本研究通过对190万样本进行全基因组关联分析,系统探索了心力衰竭及其亚型的遗传基础。研究队列包括153,174例心衰患者,其中44,012例为非缺血性病因(ni-HF)。在可获得左心室收缩功能数据的患者亚群中,进一步识别出5,406例射血分数降低型患者和3,841例射血分数保留型患者。研究共鉴定出66个与心力衰竭及其亚型相关的遗传位点,其中37个为首次报道。通过功能注释的基因优先排序方法,该研究预测了每个位点的效应基因,并借助全表型组关联分析、网络分析和共定位技术将这些基因映射至病因学疾病簇。遗传力富集分析揭示了心外组织在疾病发生中的重要作用。进一步采用孟德尔随机化方法,研究解析了上游风险因素对不同心衰亚型的差异化影响。这些发现深化了对心力衰竭发病机制的理解,或将为未来预防和治疗策略的制定提供新思路。
2.Common-variant and rare-variant genetic architecture of heart failure across the allele-frequency spectrum
全等位基因频率谱中心力衰竭的常见变异与罕见变异遗传架构
宾夕法尼亚大学佩雷尔曼医学院基因组学与计算生物学系
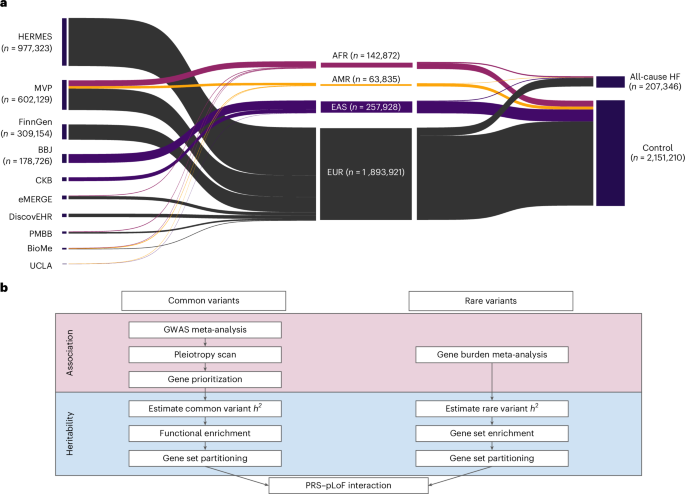
Heart failure is a complex trait, influenced by environmental and genetic factors, affecting over 30 million individuals worldwide. Here we report common-variant and rare-variant association studies of all-cause heart failure and examine how different classes of genetic variation impact its heritability. We identify 176 common-variant risk loci at genome-wide significance in 2,358,556 individuals and cluster these signals into five broad modules based on pleiotropic associations with anthropomorphic traits/obesity, blood pressure/renal function, atherosclerosis/lipids, immune activity and arrhythmias. In parallel, we uncover exome-wide significant associations for heart failure and rare predicted loss-of-function variants in TTN, MYBPC3, FLNC and BAG3 using exome sequencing of 376,334 individuals. We find that total burden heritability of rare coding variants is highly concentrated in a small set of Mendelian cardiomyopathy genes, while common-variant heritability is diffusely spread throughout the genome. Finally, we show that common-variant background modifies heart failure risk among carriers of rare pathogenic truncating variants in TTN. Together, these findings discern genetic links between dysregulated metabolism and heart failure and highlight a polygenic component to heart failure not captured by current clinical genetic testing.
心力衰竭是一种由环境因素和遗传因素共同作用的复杂疾病,全球患者人数已超过3000万。本研究通过对2,358,556人进行全基因组常见变异关联分析,以及对376,334人进行外显子组测序来研究罕见变异,系统性地探讨了不同类型遗传变异对心力衰竭遗传力的影响。作者在全基因组范围内鉴定出176个与心力衰竭显著相关的常见变异风险位点,根据这些位点与不同表型的多效性关联,可将其分为五大类:与体型/肥胖相关、与血压/肾功能相关、与动脉粥样硬化/脂代谢相关、与免疫活性相关,以及与心律失常相关。同时,通过外显子组测序,在TTN、MYBPC3、FLNC和BAG3基因中发现了与心力衰竭显著相关的罕见功能缺失变异。研究发现,罕见编码变异的遗传力主要集中在少数几个孟德尔遗传的心肌病相关基因上,而常见变异的遗传力则广泛分布于整个基因组。此外还发现常见变异背景能够显著影响TTN基因罕见致病性截短变异携带者发生心力衰竭的风险。这些研究成果不仅揭示了代谢失调与心力衰竭之间的遗传关联,更重要的是发现了当前临床基因检测未能覆盖的多基因组分在心力衰竭发生中的重要作用。这一发现为深入理解心力衰竭的发病机制和开发新的诊疗策略提供了重要依据。
3.Cross-ancestry and sex-stratified genome-wide association analyses of amygdala and subnucleus volumes
跨祖先与性别分层的杏仁核及其亚核体积全基因组关联分析
天津医科大学总医院放射科,天津市功能影像重点实验室,实验血液学国家重点实验室
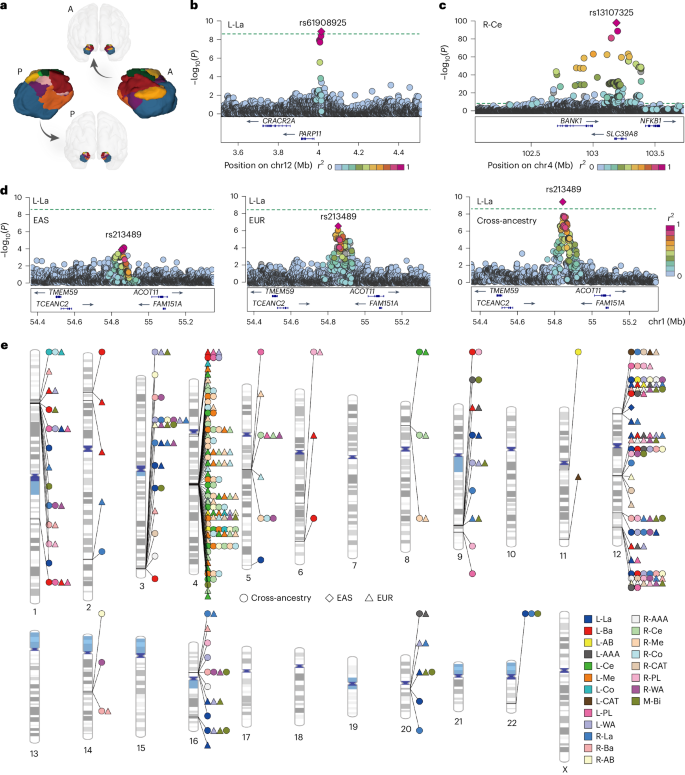
The amygdala is a small but critical multi-nucleus structure for emotion, cognition and neuropsychiatric disorders. Although genetic associations with amygdala volumetric traits have been investigated in sex-combined European populations, cross-ancestry and sex-stratified analyses are lacking. Here we conducted cross-ancestry and sex-stratified genome-wide association analyses for 21 amygdala volumetric traits in 6,923 Chinese and 48,634 European individuals. We identified 191 variant–trait associations (P < 2.38 × 10−9), including 47 new associations (12 new loci) in sex-combined univariate analyses and seven additional new loci in sex-combined and sex-stratified multivariate analyses. We identified 12 ancestry-specific and two sex-specific associations. The identified genetic variants include 16 fine-mapped causal variants and regulate amygdala and fetal brain gene expression. The variants were enriched for brain development and colocalized with mood, cognition and neuropsychiatric disorders. These results indicate that cross-ancestry and sex-stratified genetic association analyses may provide insight into the genetic architectures of amygdala and subnucleus volumes.
杏仁核是调控情绪、认知和神经精神疾病的关键多核团结构。尽管此前已在欧洲混合性别人群中开展过杏仁核体积特征的遗传关联研究,但跨人群和性别分层分析仍然缺失。本研究对6,923名中国人和48,634名欧洲人的21项杏仁核体积特征进行了跨人群和性别分层的全基因组关联分析。共鉴定出191个变异-性状关联,其中在混合性别单变量分析中发现47个新关联(涉及12个新位点),在混合性别和性别分层多变量分析中又发现7个新位点。研究识别出12个人群特异性关联和2个性别特异性关联。这些遗传变异包含16个精细定位的致病变异,可调控杏仁核和胎儿大脑的基因表达。这些变异富集于大脑发育相关通路,并与情绪、认知和神经精神疾病存在共定位关系。这些结果表明,跨人群和性别分层的遗传关联分析可为解析杏仁核及其亚核体积的遗传结构提供新的见解。
4.Selection for somatic escape variants in SERPINA1 in the liver of patients with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
α-1抗胰蛋白酶缺乏症患者肝脏中SERPINA1基因体细胞逃逸变异的选择
英国剑桥大学剑桥生物医学园区基思·彼得斯大楼剑桥医学研究所
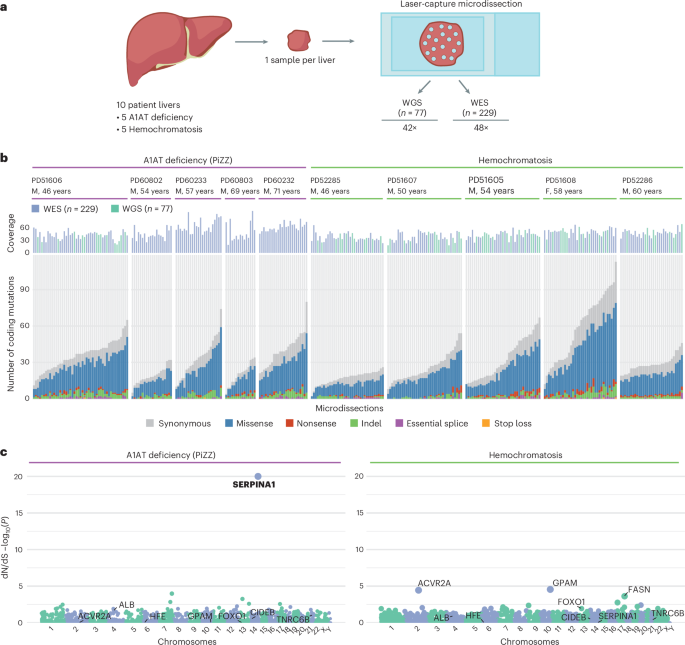
Somatic variants accumulate in non-malignant tissues with age. Functional variants, leading to clonal advantage of hepatocytes, accumulate in the liver of patients with acquired chronic liver disease (CLD). Whether somatic variants are common to CLD from differing etiologies is unknown. We analyzed liver somatic variants in patients with genetic CLD from alpha-1 antitrypsin (A1AT) deficiency or hemochromatosis. We show that somatic variants in SERPINA1, the gene encoding A1AT, are strongly selected for in A1AT deficiency, with evidence of convergent evolution. Acquired SERPINA1 variants are clustered at the carboxyl terminus of A1AT, leading to truncation. In vitro and in vivo, C-terminal truncation variants reduce disease-associated Z-A1AT polymer accumulation and disruption of the endoplasmic reticulum, supporting the C-terminal domain swap mechanism. Therefore, somatic escape variants from a deleterious germline variant are selected for in A1AT deficiency, suggesting that functional somatic variants are disease-specific in CLD and point to disease-associated mechanisms.
体细胞变异会随着年龄增长在非恶性组织中积累。在获得性慢性肝病(CLD)患者肝脏中,可导致肝细胞克隆优势的功能性变异会不断累积。目前尚不清楚不同病因导致的CLD是否具有共同的体细胞变异特征。作者分析了α-1抗胰蛋白酶(A1AT)缺乏症和血色素沉着症等遗传性CLD患者的肝脏体细胞变异。研究发现,在A1AT缺乏症患者中,编码A1AT的SERPINA1基因的体细胞变异存在强烈选择压力,并显示出趋同进化证据。获得的SERPINA1变异集中在A1AT的羧基末端,导致蛋白截短。体外和体内实验证实,C端截短变异能减少疾病相关Z-A1AT聚合物在内质网的积累及其对内质网的破坏,这支持了C端结构域交换机制。
因此,在A1AT缺乏症中,有害种系变异产生的体细胞逃逸变异会被正向选择。这表明功能性体细胞变异具有疾病特异性,并揭示了CLD的疾病相关机制。
5.The complexity of tobacco smoke-induced mutagenesis in head and neck cancer
烟草烟雾诱导头颈癌突变的复杂性
法国里昂国际癌症研究机构(IARC/WHO)基因组流行病学分部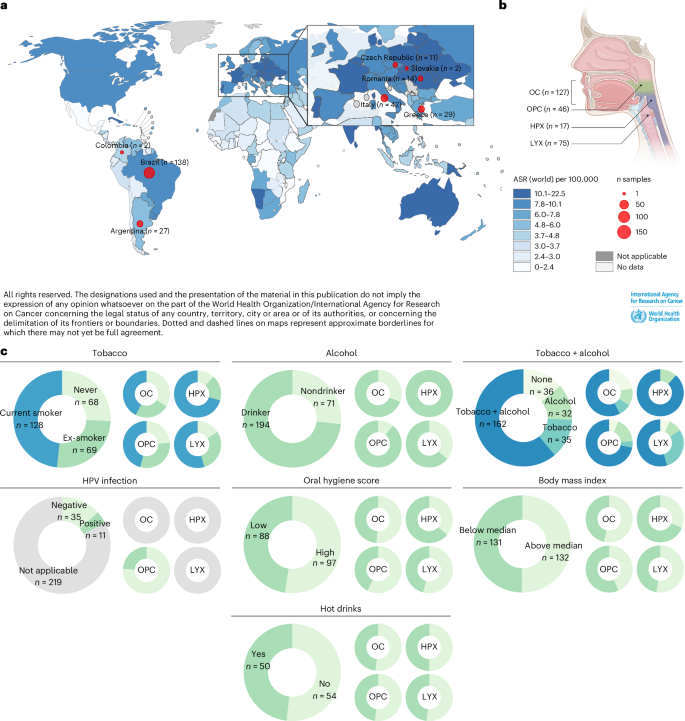
Tobacco smoke, alone or combined with alcohol, is the predominant cause of head and neck cancer (HNC). We explore how tobacco exposure contributes to cancer development by mutational signature analysis of 265 whole-genome sequenced HNC samples from eight countries. Six tobacco-associated mutational signatures were detected, including some not previously reported. Differences in HNC incidence between countries corresponded with differences in mutation burdens of tobacco-associated signatures, consistent with the dominant role of tobacco in HNC causation. Differences were found in the burden of tobacco-associated signatures between anatomical subsites, suggesting that tissue-specific factors modulate mutagenesis. We identified an association between tobacco smoking and alcohol-related signatures, indicating a combined effect of these exposures. Tobacco smoking was associated with differences in the mutational spectra, repertoire of driver mutations in cancer genes and patterns of copy number change. Our results demonstrate the multiple pathways by which tobacco smoke can influence the evolution of cancer cell clones.
烟草烟雾(无论是单独作用还是与酒精共同作用)是头颈部肿瘤(HNC)的主要致病因素。作者通过对来自8个国家的265例全基因组测序HNC样本进行突变特征分析,揭示了烟草暴露促进肿瘤发生的机制。研究发现六种烟草相关突变特征,其中包括一些既往未报道的新特征。不同国家HNC发病率的差异与烟草相关特征突变负荷的差异相对应,这印证了烟草在HNC致病中的主导作用。研究还发现不同解剖部位间烟草相关突变负荷存在差异,表明组织特异性因素会影响突变发生过程。该研究首次证实了吸烟与酒精相关突变特征之间存在关联,提示这些暴露因素具有协同效应。此外,吸烟状况与突变谱差异、驱动基因突变谱以及拷贝数变异模式均密切相关。这些发现系统阐明了烟草烟雾通过多种分子途径促进癌细胞克隆演化的机制。
6.Quantitative characterization of cell niches in spatially resolved omics data
空间分辨组学数据中细胞生态位的定量表征
德国慕尼黑亥姆霍兹中心(德国环境健康研究中心)健康人工智能研究所
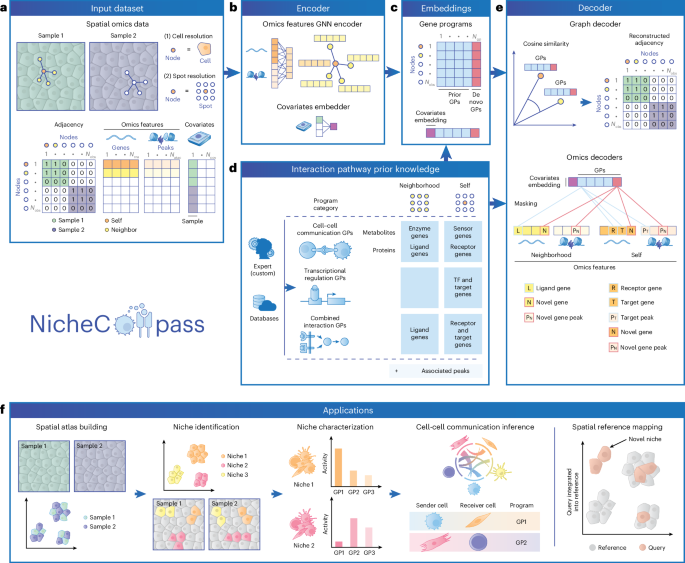
Spatial omics enable the characterization of colocalized cell communities that coordinate specific functions within tissues. These communities, or niches, are shaped by interactions between neighboring cells, yet existing computational methods rarely leverage such interactions for their identification and characterization. To address this gap, here we introduce NicheCompass, a graph deep-learning method that models cellular communication to learn interpretable cell embeddings that encode signaling events, enabling the identification of niches and their underlying processes. Unlike existing methods, NicheCompass quantitatively characterizes niches based on communication pathways and consistently outperforms alternatives. We show its versatility by mapping tissue architecture during mouse embryonic development and delineating tumor niches in human cancers, including a spatial reference mapping application. Finally, we extend its capabilities to spatial multi-omics, demonstrate cross-technology integration with datasets from different sequencing platforms and construct a whole mouse brain spatial atlas comprising 8.4 million cells, highlighting NicheCompass’ scalability. Overall, NicheCompass provides a scalable framework for identifying and analyzing niches through signaling events.
空间组学技术能够表征组织中协调特定功能的共定位细胞群落。这些群落或生态位由邻近细胞间的相互作用塑造,然而现有的计算方法很少利用这种相互作用来进行生态位的识别与表征。为填补这一空白,本研究提出NicheCompass——一种图深度学习方法,该方法通过模拟细胞通讯来学习可解释的细胞嵌入特征,这些特征编码了信号传导事件,从而实现对生态位及其潜在过程的识别。与现有方法不同,NicheCompass基于通讯通路对生态位进行定量表征,并始终表现出更优的性能。通过绘制小鼠胚胎发育过程中的组织结构,以及描绘人类癌症中的肿瘤生态位(包括空间参考图谱应用),验证了该方法的通用性。最后,将其功能扩展至空间多组学领域,展示了与不同测序平台数据集的跨技术整合能力,并构建了一个包含840万个细胞的小鼠全脑空间图谱,彰显了NicheCompass的可扩展性。总体而言,NicheCompass为通过信号传导事件识别和分析生态位提供了一个可扩展的框架。
7.Quantitative characterization of tissue states using multiomics and ecological spatial analysis
基于多组学与生态空间分析的组织状态定量表征

美国加利福尼亚州斯坦福大学生物医学数据科学系
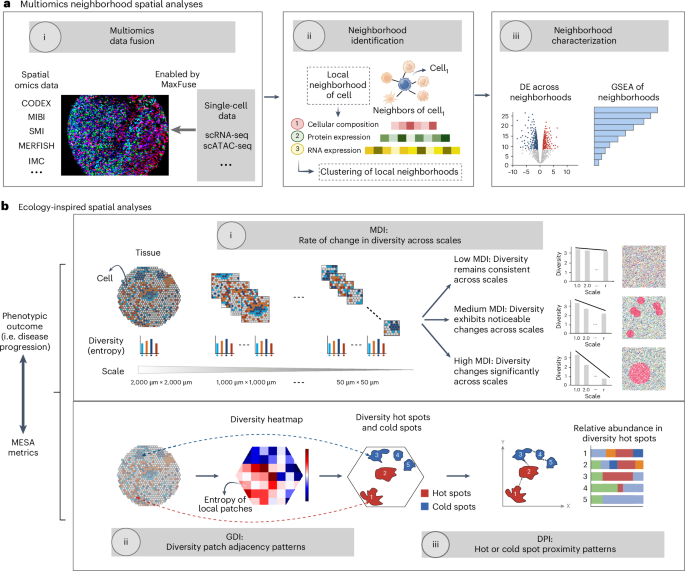
The spatial organization of cells in tissues underlies biological function, and recent advances in spatial profiling technologies have enhanced our ability to analyze such arrangements to study biological processes and disease progression. We propose MESA (multiomics and ecological spatial analysis), a framework drawing inspiration from ecological concepts to delineate functional and spatial shifts across tissue states. MESA introduces metrics to systematically quantify spatial diversity and identify hot spots, linking spatial patterns to phenotypic outcomes, including disease progression. Furthermore, MESA integrates spatial and single-cell multiomics data to facilitate an in-depth, molecular understanding of cellular neighborhoods and their spatial interactions within tissue microenvironments. Applying MESA to diverse datasets demonstrates additional insights it brings over prior methods, including newly identified spatial structures and key cell populations linked to disease states. Available as a Python package, MESA offers a versatile framework for quantitative decoding of tissue architectures in spatial omics across health and disease.
组织中细胞的空间组织结构是生物学功能的基础,而空间分析技术的最新进展提升了作者通过分析这种排列来研究生物过程和疾病发展的能力。作者提出MESA(多组学与生态空间分析)框架,该框架借鉴生态学概念来描绘组织状态间的功能与空间变化。MESA引入了一系列指标来系统量化空间多样性并识别热点区域,将空间模式与表型结果(包括疾病进展)相关联。此外,MESA整合了空间和单细胞多组学数据,以促进对细胞邻域及其在组织微环境中的空间相互作用的深入分子理解。将MESA应用于多种数据集的结果表明,相较于现有方法,它能带来更多新发现,包括新识别的空间结构以及与疾病状态相关的关键细胞群体。作为Python软件包提供的MESA,为定量解码健康和疾病状态下空间组学的组织结构提供了一个多功能框架。
8.Spatially resolved transcriptomic analysis of the adult human prostate
成人前列腺空间分辨转录组分析
中国上海海军军医大学附属上海长征医院泌尿外科
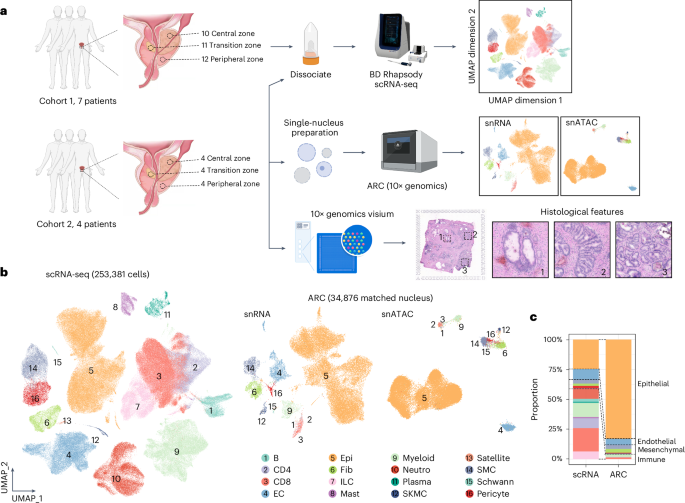
The prostate is an organ characterized by significant spatial heterogeneity. To better understand its intricate structure and cellular composition, we constructed a comprehensive single-cell atlas of the adult human prostate. Our high-resolution mapping effort identified 253,381 single cells and 34,876 nuclei sampled from 11 patients who underwent radical resection of bladder cancer, which were categorized into 126 unique subpopulations. This work revealed various new cell types in the human prostate and their specific spatial localization. Notably, we discovered four distinct acini, two of which were tightly associated with E-twenty-six transcription factor family (ETS)-fusion-negative prostate cancer. Through the integration of spatial, single-cell and bulk-seq analyses, we propose that two specific luminal cell types could serve as the common origins of prostate cancer. Additionally, our findings suggest that zone-specific fibroblasts may contribute to the observed heterogeneity among luminal cells. This atlas will serve as a valuable reference for studying prostate biology and diseases such as prostate cancer.
前列腺是一个具有显著空间异质性的器官。为了更好地理解其复杂结构和细胞组成,作者构建了成人前列腺全面的单细胞图谱。这项高分辨率绘图研究从11例接受膀胱癌根治切除术的患者样本中鉴定出253,381个单细胞和34,876个细胞核,并将其划分为126个独特的亚群。该研究揭示了人类前列腺中多种新细胞类型及其特定的空间定位。通过整合空间组学、单细胞组学和批量测序分析,作者提出两种特定的管腔细胞类型可能作为前列腺癌的共同起源。此外,研究结果表明,区域特异性成纤维细胞可能是导致管腔细胞异质性的原因之一。该图谱将为研究前列腺生物学及前列腺癌等疾病提供重要参考。
9.The landscape of N6-methyladenosine in localized primary prostate cancer
局限性原发性前列腺癌的N6-甲基腺苷修饰图谱
四川大学华西公共卫生学院/华西第四医院 生物治疗国家重点实验室
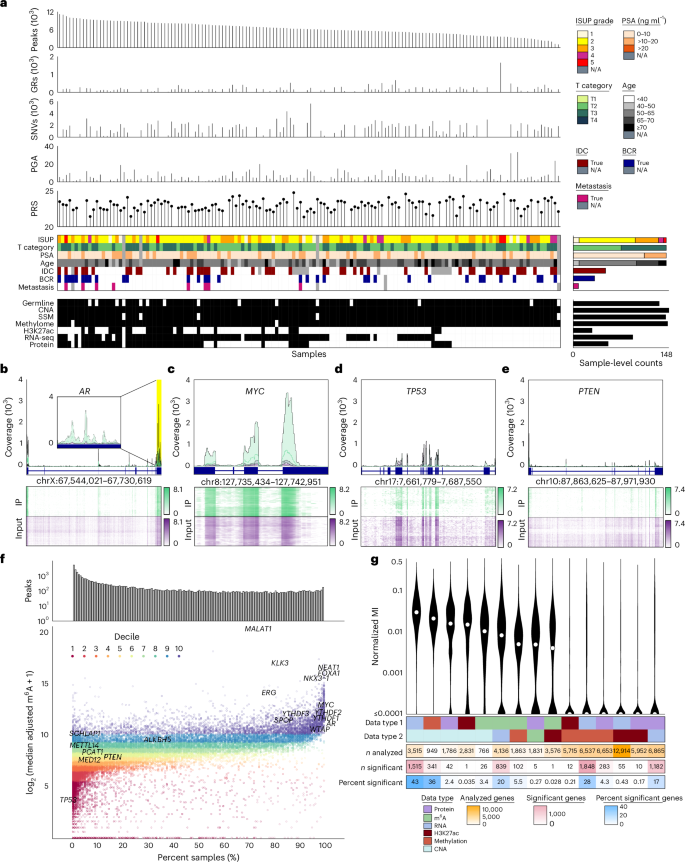
N6-methyladenosine (m6A), the most abundant internal RNA modification in humans, regulates most aspects of RNA processing. Prostate cancer is characterized by widespread transcriptomic dysregulation; therefore, we characterized the m6A landscape of 162 localized prostate tumors with matched DNA, RNA and protein profiling. m6A abundance varied dramatically across tumors, with global patterns emerging via complex germline–somatic cooperative regulation. Individual germline polymorphisms regulated m6A abundance, cooperating with somatic mutation of cancer driver genes and m6A regulators. The resulting complex patterns were associated with prognostic clinical features and established the biomarker potential of global and locus-specific m6A patterns. Tumor hypoxia dysregulates m6A profiles, bridging prior genomic and proteomic observations. Specific m6A sites, such as those in VCAN, drive disease aggression, associating with poor outcomes, tumor growth and metastasis. m6A dysregulation is thus associated with key events in the natural history of prostate cancer: germline risk, microenvironmental dysregulation, somatic mutation and metastasis.
N6-甲基腺苷(m6A)是人类细胞内最丰富的RNA修饰,调控RNA加工的各个方面。前列腺癌的特征是广泛的转录组失调,因此作者对162例局限性前列腺肿瘤进行了m6A修饰图谱分析,并匹配了DNA、RNA和蛋白质组数据。m6A丰度在不同肿瘤间差异显著,其整体模式通过复杂的种系-体细胞协同调控形成。个体种系多态性可调控m6A丰度,并与癌症驱动基因的体细胞突变及m6A调控因子协同作用。这些复杂模式与预后临床特征相关,证实了整体和位点特异性m6A模式的生物标志物潜力。肿瘤缺氧会导致m6A谱失调,这连接了既往基因组学和蛋白质组学的观察结果。特定的m6A位点(如VCAN基因中的位点)可驱动疾病侵袭性,与不良预后、肿瘤生长和转移相关。因此,m6A失调与前列腺癌自然病程中的关键事件相关:种系风险、微环境失调、体细胞突变和转移。

Volume 57 Issue 5, May 2025
在2025年5月,Nature Genetics共发表24篇文章,其中包括Research Highlights 4篇,News & Views 3篇,Research Briefings 3篇,Review Articles 2篇,Matters arising 2篇,Articles 16篇,Analysis 1篇,Technical Reports 1篇。主要内容包括全基因组关联分析、肿瘤微环境、三维基因组等内容。
1.Genome-wide analyses identify 25 infertility loci and relationships with reproductive traits across the allele frequency spectrum
全基因组分析揭示25个不孕不育相关位点及其与全等位基因频率谱中生殖性状的关联 
英国牛津大学李嘉诚健康信息与发现中心大数据研究所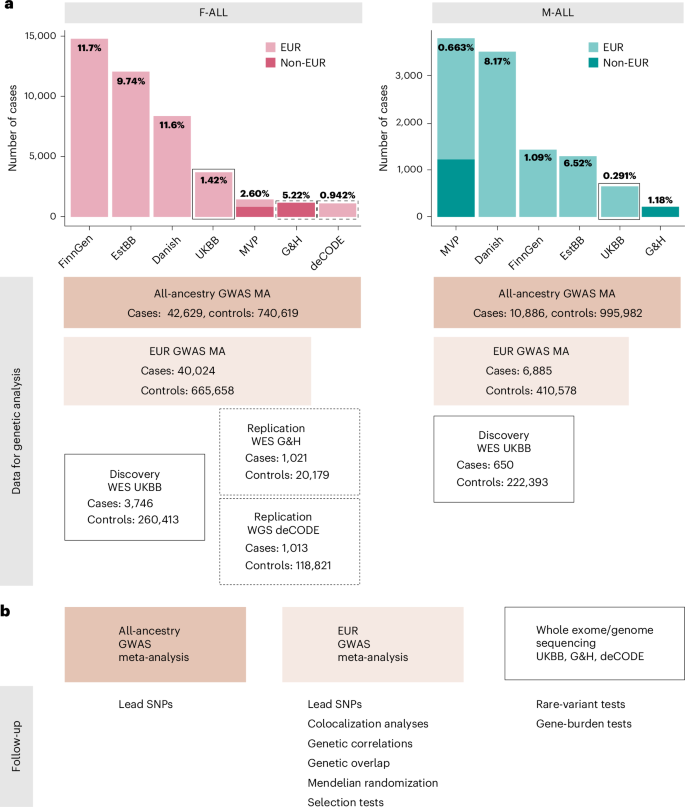
Genome-wide association studies (GWASs) may help inform the etiology of infertility. Here, we perform GWAS meta-analyses across seven cohorts in up to 42,629 cases and 740,619 controls and identify 25 genetic risk loci for male and female infertility. We additionally identify up to 269 genetic loci associated with follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, estradiol and testosterone through sex-specific GWAS meta-analyses (n = 6,095–246,862). Exome sequencing analyses reveal that women carrying testosterone-lowering rare variants in some genes are at risk of infertility. However, we find no local or genome-wide genetic correlation between female infertility and reproductive hormones. While infertility is genetically correlated with endometriosis and polycystic ovary syndrome, we find limited genetic overlap between infertility and obesity. Finally, we show that the evolutionary persistence of infertility-risk alleles may be explained by directional selection. Taken together, we provide a comprehensive view of the genetic determinants of infertility across multiple diagnostic criteria.
全基因组关联研究(GWAS)可能有助于阐明不孕不育的病因学。本研究通过对多达42,629例病例和740,619例对照的七个队列进行GWAS荟萃分析,鉴定出25个与男性和女性不孕不育相关的遗传风险位点。通过性别特异性GWAS荟萃分析(样本量n=6,095-246,862),作者还发现了多达269个与促卵泡激素、黄体生成素、雌二醇和睾酮相关的遗传位点。外显子组测序分析显示,携带某些基因中睾酮降低罕见变异的女性存在不孕风险。然而,作者发现女性不孕与生殖激素之间不存在局部或全基因组水平的遗传相关性。虽然不孕不育与子宫内膜异位症和多囊卵巢综合征存在遗传相关性,但发现不孕不育与肥胖之间的遗传重叠有限。最后,证明不孕风险等位基因的进化持续性可能通过定向选择来解释。总之,该研究提供了跨多种诊断标准的不孕不育遗传决定因素的综合解析。
2.A redefined InDel taxonomy provides insights into mutational signatures
重新定义的插入缺失突变分类系统为解析突变特征提供新视角

英国剑桥大学临床医学院基因组医学系
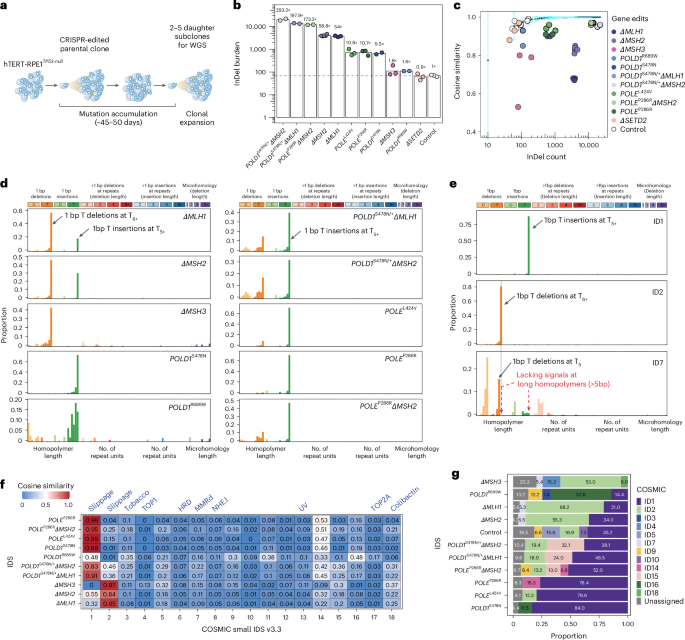
Despite their deleterious effects, small insertions and deletions (InDels) have received far less attention than substitutions. Here we generated isogenic CRISPR-edited human cellular models of postreplicative repair dysfunction (PRRd), including individual and combined gene edits of DNA mismatch repair (MMR) and replicative polymerases (Pol ε and Pol δ). Unique, diverse InDel mutational footprints were revealed. However, the prevailing InDel classification framework was unable to discriminate these InDel signatures from background mutagenesis and from each other. To address this, we developed an alternative InDel classification system that considers flanking sequences and informative motifs (for example, longer homopolymers), enabling unambiguous InDel classification into 89 subtypes. Through focused characterization of seven tumor types from the 100,000 Genomes Project, we uncovered 37 InDel signatures; 27 were new. In addition to unveiling previously hidden biological insights, we also developed PRRDetect—a highly specific classifier of PRRd status in tumors, with potential implications for immunotherapies.
尽管小片段插入缺失突变(InDels)具有有害效应,但其研究关注度远不及碱基替换。本研究通过CRISPR基因编辑技术构建了复制后修复功能障碍(PRRd)的同基因型人类细胞模型,包括DNA错配修复(MMR)和复制聚合酶(Pol ε与Pol δ)的单独及组合基因编辑。研究揭示了独特且多样化的InDel突变特征谱,但现有InDel分类框架无法将这些特征与背景突变及彼此区分。为此,研究者开发了新的InDel分类系统,通过考虑侧翼序列和信息性基序(如较长同聚物),将InDel明确划分为89个亚型。基于对10万基因组计划中七种肿瘤类型的分析,研究者鉴定出37个InDel特征,其中27个为新发现。除揭示先前未知的生物学机制外,还开发了PRRDetect——一种对肿瘤PRRd状态具有高度特异性的分类器,可能为免疫治疗提供新思路。
3.Longitudinal single-cell multiomic atlas of high-risk neuroblastoma reveals chemotherapy-induced tumor microenvironment rewiring
高危神经母细胞瘤纵向单细胞多组学图谱揭示化疗诱导的肿瘤微环境重构
美国宾夕法尼亚州费城儿童医院儿童癌症研究中心
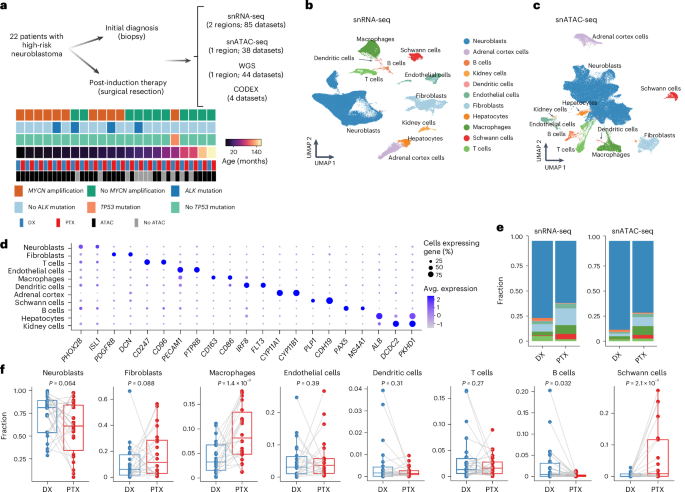
High-risk neuroblastoma, a leading cause of pediatric cancer mortality, exhibits substantial intratumoral heterogeneity, contributing to therapeutic resistance. To understand tumor microenvironment evolution during therapy, we longitudinally profiled 22 patients with high-risk neuroblastoma before and after induction chemotherapy using single-nucleus RNA and ATAC sequencing and whole-genome sequencing. This revealed profound shifts in tumor and immune cell subpopulations after therapy and identified enhancer-driven transcriptional regulators of neuroblastoma neoplastic states. Poor outcome correlated with proliferative and metabolically active neoplastic states, whereas more differentiated neuronal-like states predicted better prognosis. Proportions of mesenchymal neoplastic cells increased after therapy and a high proportion correlated with a poorer chemotherapy response. Macrophages significantly expanded towards pro-angiogenic, immunosuppressive and metabolic phenotypes. We identified paracrine signaling networks and validated the HB-EGF–ERBB4 axis between macrophage and neoplastic subsets, which promoted tumor growth through the induction of ERK signaling. These findings collectively reveal intrinsic and extrinsic regulators of therapy response in high-risk neuroblastoma.
高危神经母细胞瘤作为儿童癌症死亡的主要原因,表现出显著的瘤内异质性,这导致其产生治疗抵抗。为了解治疗过程中肿瘤微环境的演变,采用单细胞核RNA测序、ATAC测序和全基因组测序技术,对22例高危神经母细胞瘤患者在诱导化疗前后进行了纵向分析。研究发现治疗后肿瘤和免疫细胞亚群发生变化,并鉴定出神经母细胞瘤恶性状态的增强子驱动转录调控因子。不良预后与增殖和代谢活跃的恶性状态相关,而更分化的神经元样状态则预示较好预后。间充质型肿瘤细胞比例在治疗后增加,且高比例与较差的化疗反应相关。巨噬细胞显著向促血管生成、免疫抑制和代谢表型扩增。发现了旁分泌信号网络,并验证了巨噬细胞与肿瘤亚群之间的HB-EGF-ERBB4轴可通过诱导ERK信号通路促进肿瘤生长。这些发现共同揭示了高危神经母细胞瘤治疗反应的内在与外在调控机制。
4.The multilayered transcriptional architecture of glioblastoma ecosystems
多层级转录架构解析胶质母细胞瘤生态系统
美国哈佛大学医学院附属麻省总医院病理科及Krantz家族癌症研究中心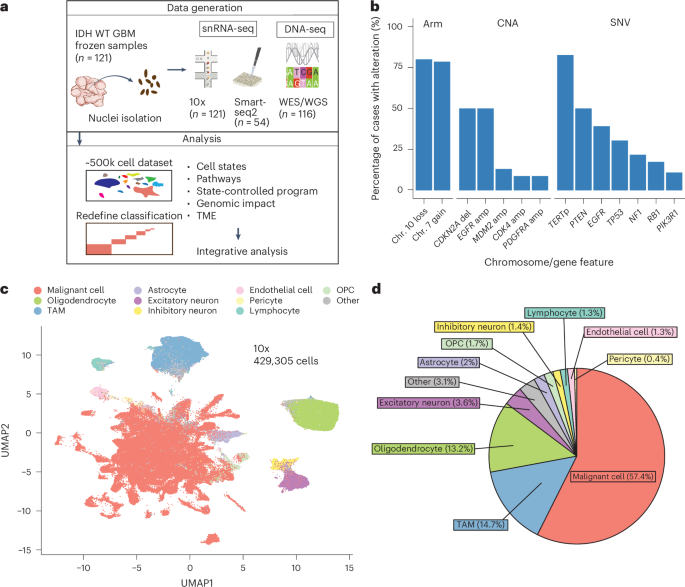
In isocitrate dehydrogenase wildtype glioblastoma (GBM), cellular heterogeneity across and within tumors may drive therapeutic resistance. Here we analyzed 121 primary and recurrent GBM samples from 59 patients using single-nucleus RNA sequencing and bulk tumor DNA sequencing to characterize GBM transcriptional heterogeneity. First, GBMs can be classified by their broad cellular composition, encompassing malignant and nonmalignant cell types. Second, in each cell type we describe the diversity of cellular states and their pathway activation, particularly an expanded set of malignant cell states, including glial progenitor cell-like, neuronal-like and cilia-like. Third, the remaining variation between GBMs highlights three baseline gene expression programs. These three layers of heterogeneity are interrelated and partially associated with specific genetic aberrations, thereby defining three stereotypic GBM ecosystems. This work provides an unparalleled view of the multilayered transcriptional architecture of GBM. How this architecture evolves during disease progression is addressed in the companion manuscript by Spitzer et al.
在异柠檬酸脱氢酶野生型胶质母细胞瘤(GBM)中,肿瘤间和肿瘤内的细胞异质性可能导致治疗抵抗。本研究通过对59例患者的121个原发性和复发性GBM样本进行单细胞核RNA测序和肿瘤组织DNA测序,系统解析了GBM的转录异质性特征。研究发现:首先,GBM可根据其广泛的细胞组成(包括恶性和非恶性细胞类型)进行分类;其次,描述了每种细胞类型的状态多样性及其通路激活特征,特别是发现了一系列扩展的恶性细胞状态,包括胶质祖细胞样、神经元样和纤毛样状态;第三,GBM间剩余的变异特征凸显出三种基线基因表达模式。这三个层次的异质性相互关联,并部分与特定遗传畸变相关,从而定义了三种典型的GBM生态系统。该研究为理解GBM的多层次转录架构提供了全新视角。关于该架构在疾病进展中的演变规律,Spitzer等人在姊妹篇论文中进行了探讨。
5.Deciphering the longitudinal trajectories of glioblastoma ecosystems by integrative single-cell genomics
基于单细胞多组学整合分析解析胶质母细胞瘤生态系统的动态演变规律
以色列雷霍沃特 魏茨曼科学研究所分子细胞生物学系
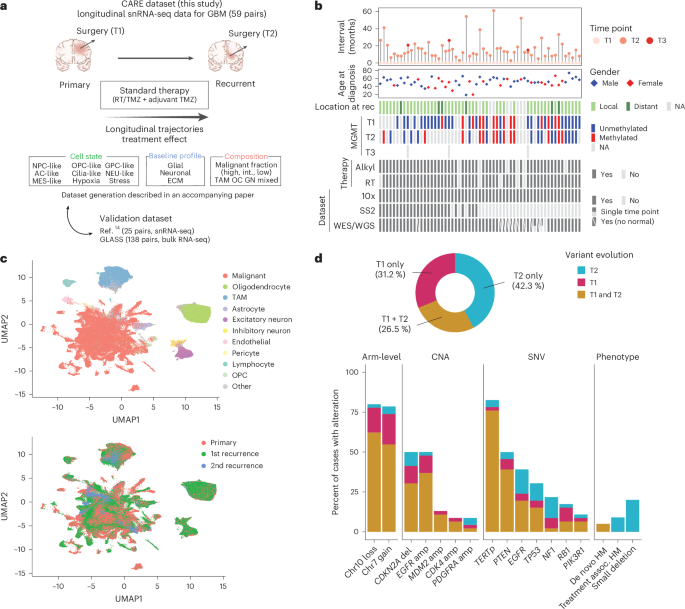
The evolution of isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH)-wildtype glioblastoma (GBM) after standard-of-care therapy remains poorly understood. Here we analyzed matched primary and recurrent GBMs from 59 patients using single-nucleus RNA sequencing and bulk DNA sequencing, assessing the longitudinal evolution of the GBM ecosystem across layers of cellular and molecular heterogeneity. The most consistent change was a lower malignant cell fraction at recurrence and a reciprocal increase in glial and neuronal cell types in the tumor microenvironment (TME). The predominant malignant cell state differed between most matched pairs, but no states were exclusive or highly enriched in either time point, nor was there a consistent longitudinal trajectory across the cohort. Nevertheless, specific trajectories were enriched in subsets of patients. Changes in malignant state abundances mirrored changes in TME composition and baseline profiles, reflecting the co-evolution of the GBM ecosystem. Our study provides a blueprint of GBM’s diverse longitudinal trajectories and highlights the treatment and TME modifiers that shape them.
异柠檬酸脱氢酶(IDH)野生型胶质母细胞瘤(GBM)在标准治疗后的演变机制尚未明确。本研究通过对59例患者的匹配原发和复发GBM样本进行单细胞核RNA测序和批量DNA测序,从细胞和分子异质性层面评估了GBM生态系统的纵向演变。研究发现:复发时恶性细胞比例普遍降低,而肿瘤微环境(TME)中胶质和神经元细胞类型相应增加;大多数配对样本间主要恶性细胞状态存在差异,但未发现任一状态在特定时间点具有排他性或显著富集,整个队列中也未观察到一致的纵向演变轨迹。然而,特定演变轨迹在患者亚群中呈现富集现象。恶性状态丰度的变化与TME组成及基线特征的改变相呼应,反映了GBM生态系统的协同演化。该研究绘制了GBM多样化纵向演变图谱,并揭示了影响这些演变轨迹的治疗因素和TME调节机制。
6.Desmosome mutations impact the tumor microenvironment to promote melanoma proliferation
桥粒基因突变通过重塑肿瘤微环境促进黑色素瘤增殖
美国加利福尼亚州拉荷亚 加州大学圣地亚哥分校医学院内科系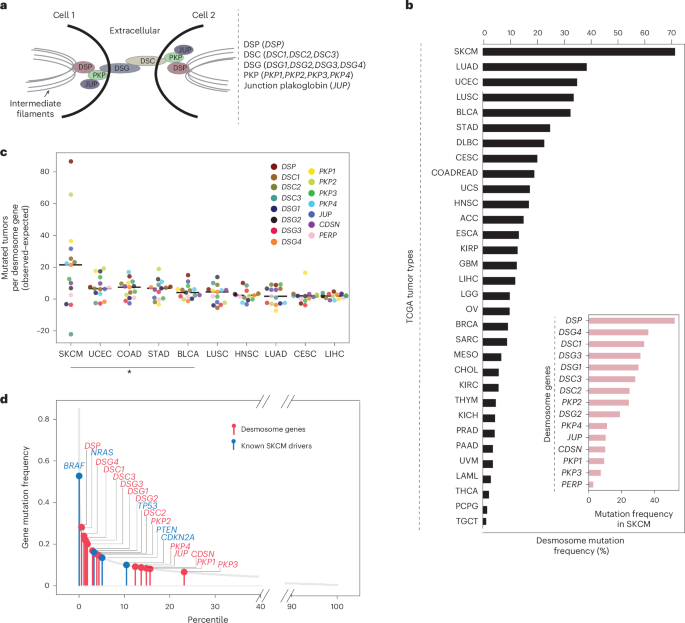
Desmosomes are transmembrane protein complexes that contribute to cell–cell adhesion in epithelia and other tissues. Here, we report the discovery of frequent genetic alterations in the desmosome in human cancers, with the strongest signal seen in cutaneous melanoma, where desmosomes are mutated in more than 70% of cases. In primary but not metastatic melanoma biopsies, the burden of coding mutations in desmosome genes is associated with a strong reduction in desmosome gene expression. Analysis by spatial transcriptomics and protein immunofluorescence suggests that these decreases in expression occur in keratinocytes in the microenvironment rather than in primary melanoma cells. In further support of a microenvironmental origin, we find that desmosome gene knockdown in keratinocytes yields markedly increased proliferation of adjacent melanoma cells in keratinocyte and melanoma cocultures. Similar increases in melanoma proliferation are observed in media preconditioned with desmosome-deficient keratinocytes. Thus, gradual accumulation of desmosome mutations in neighboring cells may prime melanoma cells for neoplastic transformation.
桥粒是介导上皮及其他组织细胞间黏附的跨膜蛋白复合物。作者在人类癌症中发现桥粒频繁发生遗传变异,其中皮肤黑色素瘤变异率最高(>70%病例)。在原发(非转移)性黑色素瘤活检组织中,桥粒基因编码突变负荷与其表达水平显著降低相关。空间转录组与蛋白免疫荧光分析显示,这种表达下调主要发生于微环境中的角质形成细胞,而非原代黑色素瘤细胞。进一步实验证实:在角质形成细胞-黑色素瘤细胞共培养体系中,敲降角质形成细胞的桥粒基因可显著促进邻近黑色素瘤细胞增殖;使用桥粒缺陷型角质形成细胞的条件培养基也观察到类似的促增殖效应。因此,周围细胞中桥粒突变的逐步积累可能为黑色素瘤细胞的恶性转化创造有利条件。
7.Three-dimensional genome landscape of primary human cancers
人类原发性癌症三维基因组图谱

美国斯坦福大学医学院人体动态调控组学中心
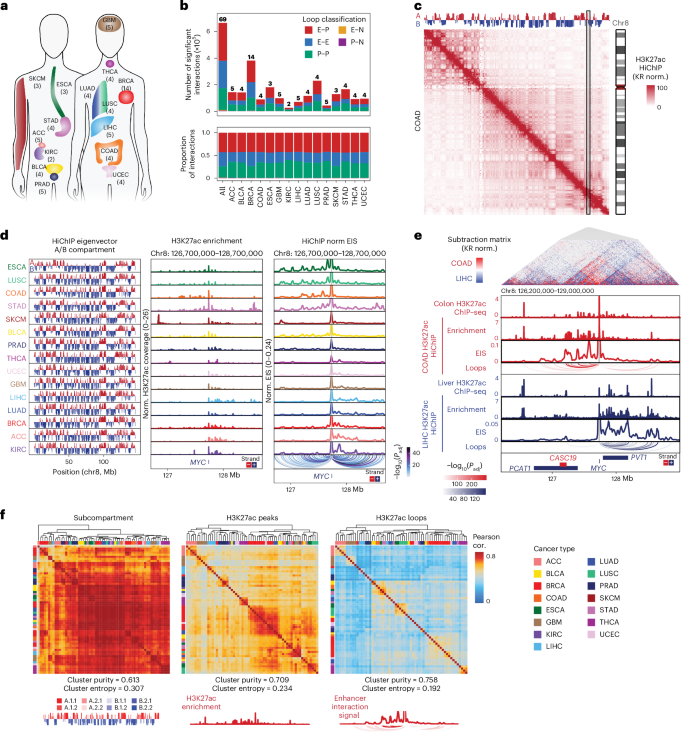
Genome conformation underlies transcriptional regulation by distal enhancers, and genomic rearrangements in cancer can alter critical regulatory interactions. Here we profiled the three-dimensional genome architecture and enhancer connectome of 69 tumor samples spanning 15 primary human cancer types from The Cancer Genome Atlas. We discovered the following three archetypes of enhancer usage for over 100 oncogenes across human cancers: static, selective gain or dynamic rewiring. Integrative analyses revealed the enhancer landscape of noncancer cells in the tumor microenvironment for genes related to immune escape. Deep whole-genome sequencing and enhancer connectome mapping provided accurate detection and validation of diverse structural variants across cancer genomes and revealed distinct enhancer rewiring consequences from noncoding point mutations, genomic inversions, translocations and focal amplifications. Extrachromosomal DNA promoted more extensive enhancer rewiring among several types of focal amplification mechanisms. These results suggest a systematic approach to understanding genome topology in cancer etiology and therapy.
基因组三维构象是远端增强子调控转录的基础,而癌症中的基因组重排可能破坏关键调控互作。本研究对癌症基因组图谱(TCGA)中15类人类原发性癌症的69个肿瘤样本进行了三维基因组结构和增强子互作组分析,发现100多个癌基因的增强子使用存在三种原型模式:静态型、选择性获得型和动态重构型。整合分析揭示了肿瘤微环境中非癌细胞与免疫逃逸相关基因的增强子特征谱。通过深度全基因组测序和增强子互作组图谱,实现了癌症基因组中多种结构变异的精准检测与验证,并阐明了非编码点突变、基因组倒位、易位和局灶性扩增等事件导致的差异化增强子重构效应。其中,染色体外DNA在多种局灶性扩增机制中引发了更广泛的增强子重构。这些发现为理解癌症病因和治疗中的基因组拓扑结构提供了系统性研究框架。
8.An integrated transcriptomic cell atlas of human endoderm-derived organoids
人内胚层类器官整合转录组细胞图谱

瑞士罗氏创新中心、罗氏制药研究与早期开发部 人类生物学研究所(IHB)

Human pluripotent stem cells and tissue-resident fetal and adult stem cells can generate epithelial tissues of endodermal origin in vitro that recapitulate aspects of developing and adult human physiology. Here, we integrate single-cell transcriptomes from 218 samples covering organoids and other models of diverse endoderm-derived tissues to establish an initial version of a human endoderm-derived organoid cell atlas. The integration includes nearly one million cells across diverse conditions, data sources and protocols. We compare cell types and states between organoid models and harmonize cell annotations through mapping to primary tissue counterparts. Focusing on the intestine and lung, we provide examples of mapping data from new protocols and show how the atlas can be used as a diverse cohort to assess perturbations and disease models. The human endoderm-derived organoid cell atlas makes diverse datasets centrally available and will be valuable to assess fidelity, characterize perturbed and diseased states, and streamline protocol development.
人多能干细胞及组织驻留的胎儿/成体干细胞可在体外生成内胚层来源的上皮组织,这些组织能部分重现人类发育和成体的生理特征。本研究整合了218个样本(涵盖多种内胚层来源组织的类器官及其他模型)的单细胞转录组数据,构建了首版人内胚层类器官细胞图谱。该整合数据集包含近百万个细胞,覆盖多种培养条件、数据来源和实验方案。作者比较了不同类器官模型的细胞类型和状态,并通过与原代组织对应细胞的比对实现了细胞注释的统一。以肠道和肺类器官为重点,展示了如何利用该图谱评估新实验方案的数据质量,并证明其可作为多样化队列用于扰动分析和疾病模型研究。人类内胚层类器官细胞图谱集中提供了多样化的数据集,对于评估模型保真度、表征扰动和疾病状态,以及优化实验方案开发都具有重要价值。
9.Multi-omic and spatial analysis of mouse kidneys highlights sex-specific differences in gene regulation across the lifespan
小鼠肾脏多组学与空间分析揭示生命周期中基因调控的性别差异

美国华盛顿大学医学院内科
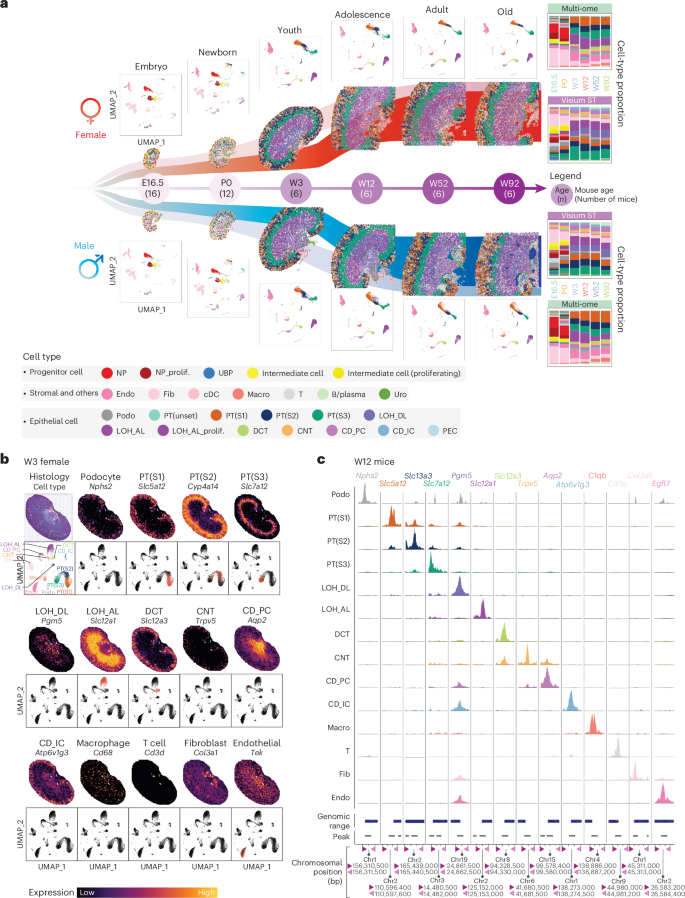
There is a sex bias in the incidence and progression of many kidney diseases. To better understand such sexual dimorphism, we integrated data from six platforms, characterizing 76 kidney samples from 68 mice at six developmental and adult time points, creating a molecular atlas of the mouse kidney across the lifespan for both sexes. We show that proximal tubules have the most sex-biased differentially expressed genes emerging after 3 weeks of age and are associated with hormonal regulations. We reveal potential mechanisms involving both direct and indirect regulation by androgens and estrogens. Spatial profiling identifies distinct sex-biased spatial patterns in the cortex and outer stripe of the outer medulla. Additionally, older mice exhibit more aging-related gene alterations in loops of Henle, proximal tubules and collecting ducts in a sex-dependent manner. Our results enhance the understanding of spatially resolved gene expression and hormone regulation underlying kidney sexual dimorphism across the lifespan.
许多肾脏疾病的发生和发展存在性别差异。为深入理解这种性别二态性,研究者整合了六种技术平台的数据,对68只小鼠在六个发育阶段和成年期的76个肾脏样本进行了分析,构建了涵盖两性全生命周期的小鼠肾脏分子图谱。研究发现:近端小管在3周龄后出现最多性别差异表达基因,这些基因与激素调控相关;揭示了雄激素和雌激素直接与间接调控的潜在机制;空间分析鉴定出皮质和外髓质外带存在不同的性别偏向性空间模式;此外,老年小鼠的亨利氏袢、近端小管和集合管表现出更多与衰老相关的基因改变,且具有性别依赖性。这些发现增进了对全生命周期中肾脏性别二态性相关空间基因表达和激素调控机制的理解。

汇报人:张子妍
导师:赵宇
审核:王肖宇、张宇阳、任建君



